
Why is an atom neutral?
Answer
583.5k+ views
Hint: An atom is composed of neutrons, protons and electrons in such a composition such that the atom develops no charge at all. These are all subatomic particles visible at microscopic level as they are very small.
Complete answer:
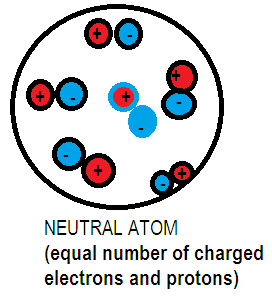
Neutrons are neutral in nature, that is they don’t have a charge of their own and its mass is slightly greater than proton. Protons are positively charged subatomic particles. Each proton has a charge of $1.602 \times {10^{ - 19}}$ C. Electrons are negatively charged sub atomic particles with a charge of $1.602 \times {10^{ - 19}}$C. On observing we come to know that the charge on proton is equivalent to the charge on electron they differ only in their magnitude. Every atom has an equal number of electrons and protons hence the amount of positive charged protons nullifies the amount of negatively charged electrons hence results in no overall charge on the atom.
Additional Information: Many atomic models have been proposed in the past such as Dalton’s invisible atom is composed of subatomic particles carrying positive and negative charges. Different atomic models were proposed to explain the distribution of the charge particles in an atom. Although some of these models were not able to explain the stability of atoms.
Note: Atoms are neutral as long as the numbers of charged protons are equal to the number of charged electrons which will balance all the negative charges to all the positive charges.
Complete answer:
Neutrons are neutral in nature, that is they don’t have a charge of their own and its mass is slightly greater than proton. Protons are positively charged subatomic particles. Each proton has a charge of $1.602 \times {10^{ - 19}}$ C. Electrons are negatively charged sub atomic particles with a charge of $1.602 \times {10^{ - 19}}$C. On observing we come to know that the charge on proton is equivalent to the charge on electron they differ only in their magnitude. Every atom has an equal number of electrons and protons hence the amount of positive charged protons nullifies the amount of negatively charged electrons hence results in no overall charge on the atom.

Additional Information: Many atomic models have been proposed in the past such as Dalton’s invisible atom is composed of subatomic particles carrying positive and negative charges. Different atomic models were proposed to explain the distribution of the charge particles in an atom. Although some of these models were not able to explain the stability of atoms.
Note: Atoms are neutral as long as the numbers of charged protons are equal to the number of charged electrons which will balance all the negative charges to all the positive charges.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




