
Which of the following statements is not correct?
A. The bond angle of $C-O-H$ in methanol is ${{108.9}^{0}}$
B. Alcohols are weaker acids than water.
C. Carbon-oxygen bond length in methanol, $C{{H}_{3}}OH$ is shorter than that of $C-O$ bond length in phenol
D. Acid strength of alcohols decreases in the following order: $RC{{H}_{2}}OH>{{R}_{2}}CHOH>{{R}_{3}}COH$
Answer
586.5k+ views
Hint: In option A the bond angle is not standard tetrahedral angle because oxygen has two lone pairs on it, which repels carbon and hydrogen and hence decreases the bond angle. Alcohols are weaker acids than water which can be predicted from their ${{K}_{a}}$ values. Carbon-oxygen bond length in methanol $C{{H}_{3}}OH$ is longer than that of the $C-O$ bond length in phenol because of the resonance occurring in phenol.
As alkyl groups get added, the acidity decreases due to the +I effect of alkyl groups.
Complete step by step answer:
In alcohols , the alkyl group has +I effect as a result it increases the electron density over the oxygen atom. Due to this, the release of ${{H}^{+}}$ ion from alcohol becomes more difficult than from water as a result alcohol is a weaker acid. Moreover alcohols are weaker acids than water which is proved from their respective ka values. In the case of the alkyl alcohols, primary alcohols are more acidic than secondary alcohols which are more acidic than the tertiary alcohols. This is because the strength of the alcohols as an acid is dependent on the corresponding strength of its conjugate base that is the alkoxide ions.
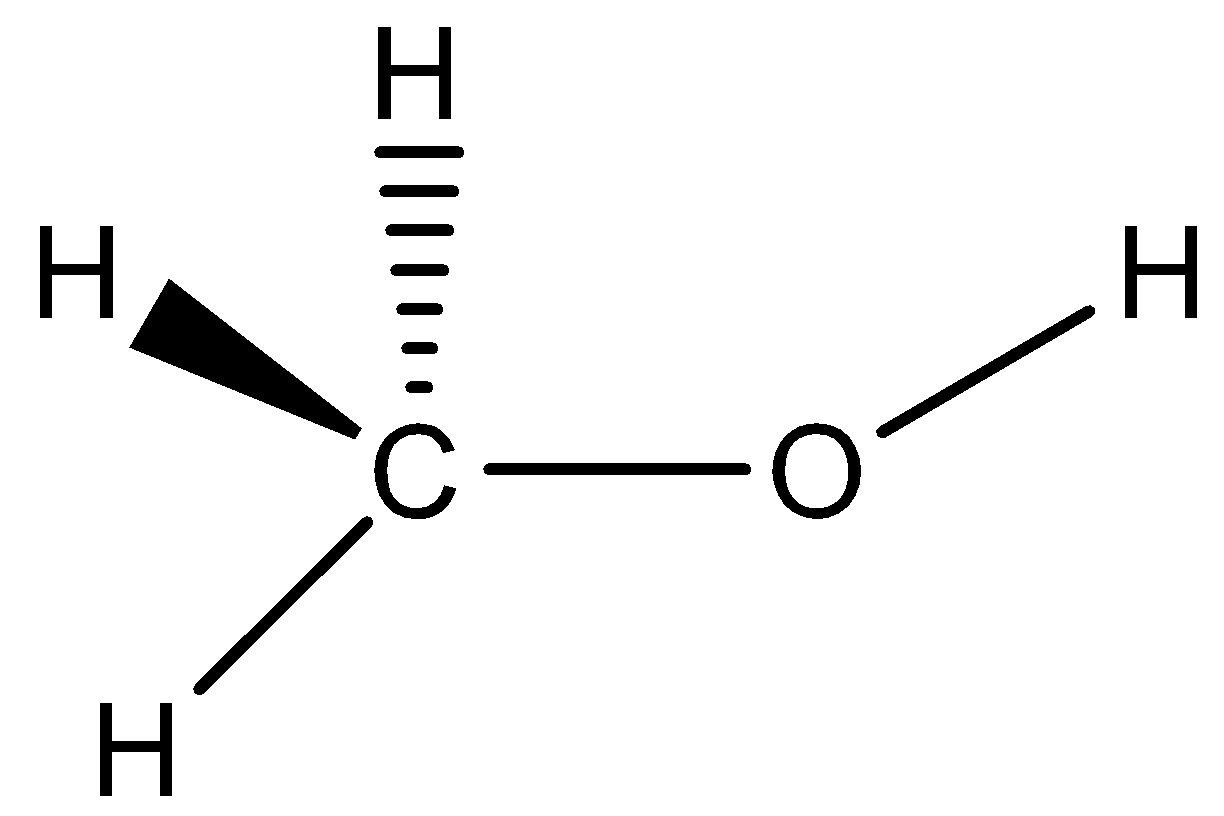
Bond length of $C-O$ bond in phenol is shorter than that in case of the $C{{H}_{3}}OH$ due to the following reasons: In phenol, the conjugation of an unshared electron pair over oxygen with an aromatic ring results in the partial double bond character in the carbon-oxygen bond. In phenol, oxygen is attached to a $s{{p}^{2}}$ hybridized carbon atom while in methanol it is attached to the $s{{p}^{3}}$ hybridized carbon atom. As a result in phenol the lone pair is not available outside the ring. Therefore the option is not correct .
So the answer will be option C.
Note: The bond angle of alcohol between $C-O-H$ above is slightly less than tetrahedral angle (109.5 degree) because of lone pair lone pair repulsions of oxygen atoms. Phenol has a boiling point of ${{181.7}^{0}}C$ whereas the boiling point of methanol is ${{64.7}^{0}}C$.
As alkyl groups get added, the acidity decreases due to the +I effect of alkyl groups.
Complete step by step answer:
In alcohols , the alkyl group has +I effect as a result it increases the electron density over the oxygen atom. Due to this, the release of ${{H}^{+}}$ ion from alcohol becomes more difficult than from water as a result alcohol is a weaker acid. Moreover alcohols are weaker acids than water which is proved from their respective ka values. In the case of the alkyl alcohols, primary alcohols are more acidic than secondary alcohols which are more acidic than the tertiary alcohols. This is because the strength of the alcohols as an acid is dependent on the corresponding strength of its conjugate base that is the alkoxide ions.

Bond length of $C-O$ bond in phenol is shorter than that in case of the $C{{H}_{3}}OH$ due to the following reasons: In phenol, the conjugation of an unshared electron pair over oxygen with an aromatic ring results in the partial double bond character in the carbon-oxygen bond. In phenol, oxygen is attached to a $s{{p}^{2}}$ hybridized carbon atom while in methanol it is attached to the $s{{p}^{3}}$ hybridized carbon atom. As a result in phenol the lone pair is not available outside the ring. Therefore the option is not correct .
So the answer will be option C.
Note: The bond angle of alcohol between $C-O-H$ above is slightly less than tetrahedral angle (109.5 degree) because of lone pair lone pair repulsions of oxygen atoms. Phenol has a boiling point of ${{181.7}^{0}}C$ whereas the boiling point of methanol is ${{64.7}^{0}}C$.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

Draw ray diagrams each showing i myopic eye and ii class 12 physics CBSE

Giving reasons state the signs positive or negative class 12 physics CBSE

Explain esterification reaction with the help of a class 12 chemistry CBSE

What is defined as a solenoid Depict a diagram with class 12 physics CBSE




