
Which of the following reactions produces propane as a major product?
A.

B.
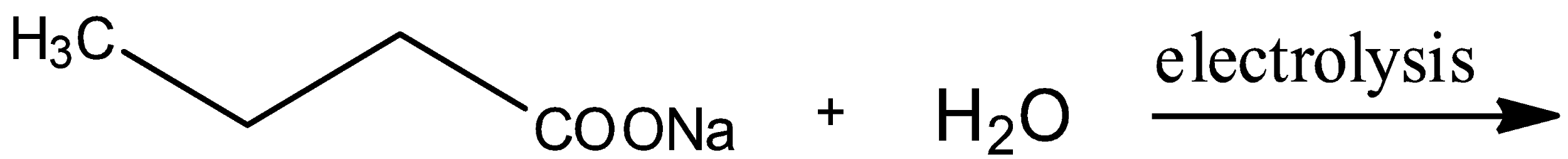
C.
D.
This question has multiple correct options.

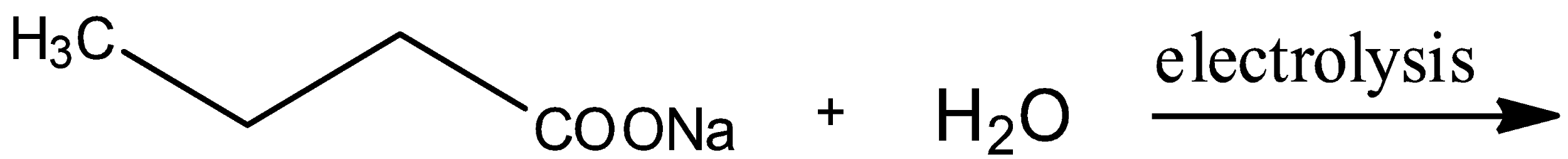


Answer
558.9k+ views
Hint: Think about the general reaction of each of the reactions given in the options and consider the type of molecules that they are making. Substitute the corresponding alkyl group and check whether propane is formed or not.
Complete step by step answer:
To get the solution to this equation, we will check the general reactions of each given reaction one by one and narrow down our options.
- Option A
The general reaction of this option includes the reduction of the molecule given to form an alkane and sodium carbonate. The general reaction for this is:
\[R-COONa+NaOH\xrightarrow{CaO,\Delta }R-H+N{{a}_{2}}C{{O}_{3}}\]
In the reaction given in the option, $R-$ is ${{H}_{3}}C-C{{H}_{2}}-C{{H}_{2}}-$ ; thus, $R-H$ will be ${{H}_{3}}C-C{{H}_{2}}-C{{H}_{3}}$, which is the structure of propane. Hence, option A is correct.
- Option B
The general reaction of this option includes the formation of $RCO{{O}^{-}}$ and $N{{a}^{+}}$ ions. This then leads to the formations of alkyl groups that are free radicals and these two free radicals will combine to form a long alkane. The general reaction is:
\[2R-COONa+{{H}_{2}}O\xrightarrow{electrolysis}R-R+2C{{O}_{2}}\]
In the reaction given in the option, $R-$ is ${{H}_{3}}C-C{{H}_{2}}-C{{H}_{2}}-$; thus, $R-R$ will be ${{H}_{3}}C-C{{H}_{2}}-C{{H}_{2}}-C{{H}_{2}}-C{{H}_{2}}-C{{H}_{3}}$, which is the structure of hexane. Hence, option B is incorrect.
- Option C
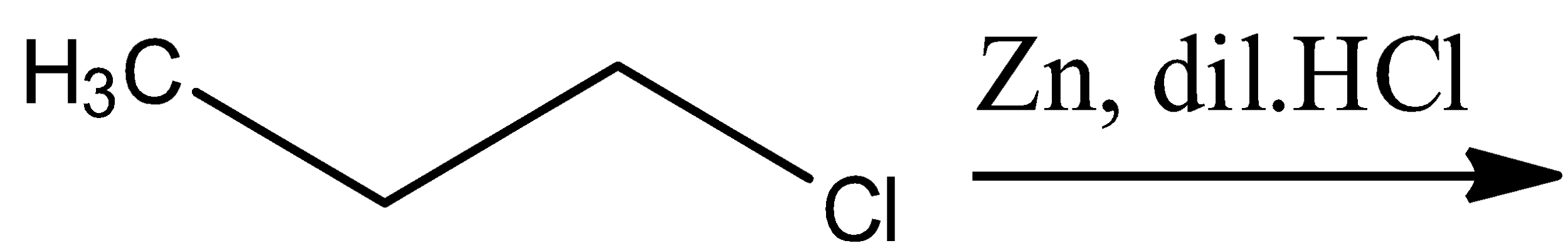
The general reaction of this option includes the reduction of the given alkyl halide. The zinc and hydrochloric acid combine to form zinc chloride and two hydrogen atoms. One of these hydrogen atoms attaches itself to the halogen atom and the other replaces the halogen atom. The general reaction will be:
\[R-Cl\xrightarrow{Zn,dil.HCl}R-H+HCl\]
In the reaction given in the option, $R-$ is ${{H}_{3}}C-C{{H}_{2}}-C{{H}_{2}}-$ ; thus, $R-H$ will be ${{H}_{3}}C-C{{H}_{2}}-C{{H}_{3}}$, which is the structure of propane. Hence, option C is correct.
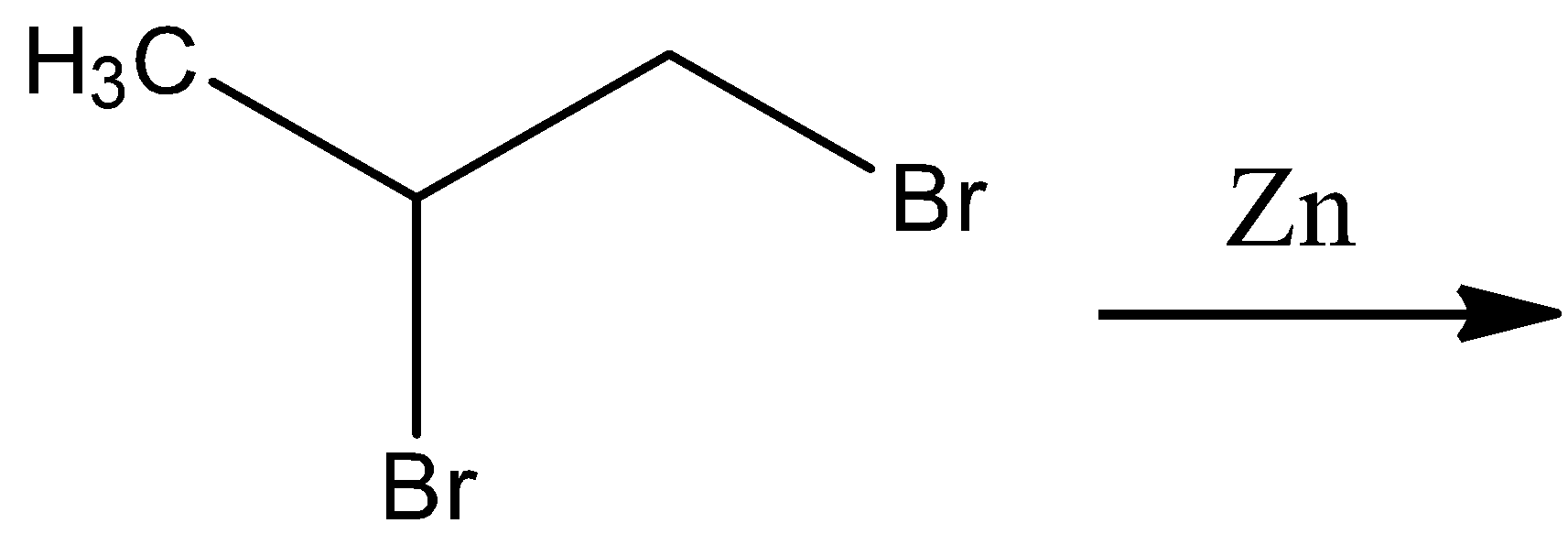
- Option D
The general reaction for this option includes the dehalogenation of the given geminal dihalide and the formation of an alkene. Since the product is going to be an alkene, it is not required to formulate the general reaction for this option since it cannot be propane.
So the correct answer is “A and C”:
Note: In the Kolbe’s electrolysis reaction, it is clear that no unsymmetrical alkane can be formed and only alkanes with an even number of carbon atoms can be formed. But if we use reactants that have two different types of alkyl groups, then an unsymmetrical alkane may be formed.
Complete step by step answer:
To get the solution to this equation, we will check the general reactions of each given reaction one by one and narrow down our options.
- Option A
The general reaction of this option includes the reduction of the molecule given to form an alkane and sodium carbonate. The general reaction for this is:
\[R-COONa+NaOH\xrightarrow{CaO,\Delta }R-H+N{{a}_{2}}C{{O}_{3}}\]
In the reaction given in the option, $R-$ is ${{H}_{3}}C-C{{H}_{2}}-C{{H}_{2}}-$ ; thus, $R-H$ will be ${{H}_{3}}C-C{{H}_{2}}-C{{H}_{3}}$, which is the structure of propane. Hence, option A is correct.
- Option B
The general reaction of this option includes the formation of $RCO{{O}^{-}}$ and $N{{a}^{+}}$ ions. This then leads to the formations of alkyl groups that are free radicals and these two free radicals will combine to form a long alkane. The general reaction is:
\[2R-COONa+{{H}_{2}}O\xrightarrow{electrolysis}R-R+2C{{O}_{2}}\]
In the reaction given in the option, $R-$ is ${{H}_{3}}C-C{{H}_{2}}-C{{H}_{2}}-$; thus, $R-R$ will be ${{H}_{3}}C-C{{H}_{2}}-C{{H}_{2}}-C{{H}_{2}}-C{{H}_{2}}-C{{H}_{3}}$, which is the structure of hexane. Hence, option B is incorrect.
- Option C
The general reaction of this option includes the reduction of the given alkyl halide. The zinc and hydrochloric acid combine to form zinc chloride and two hydrogen atoms. One of these hydrogen atoms attaches itself to the halogen atom and the other replaces the halogen atom. The general reaction will be:
\[R-Cl\xrightarrow{Zn,dil.HCl}R-H+HCl\]
In the reaction given in the option, $R-$ is ${{H}_{3}}C-C{{H}_{2}}-C{{H}_{2}}-$ ; thus, $R-H$ will be ${{H}_{3}}C-C{{H}_{2}}-C{{H}_{3}}$, which is the structure of propane. Hence, option C is correct.
- Option D
The general reaction for this option includes the dehalogenation of the given geminal dihalide and the formation of an alkene. Since the product is going to be an alkene, it is not required to formulate the general reaction for this option since it cannot be propane.
So the correct answer is “A and C”:
Note: In the Kolbe’s electrolysis reaction, it is clear that no unsymmetrical alkane can be formed and only alkanes with an even number of carbon atoms can be formed. But if we use reactants that have two different types of alkyl groups, then an unsymmetrical alkane may be formed.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

What is a transformer Explain the principle construction class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE




