
Which of the following molecules is (are) chiral?
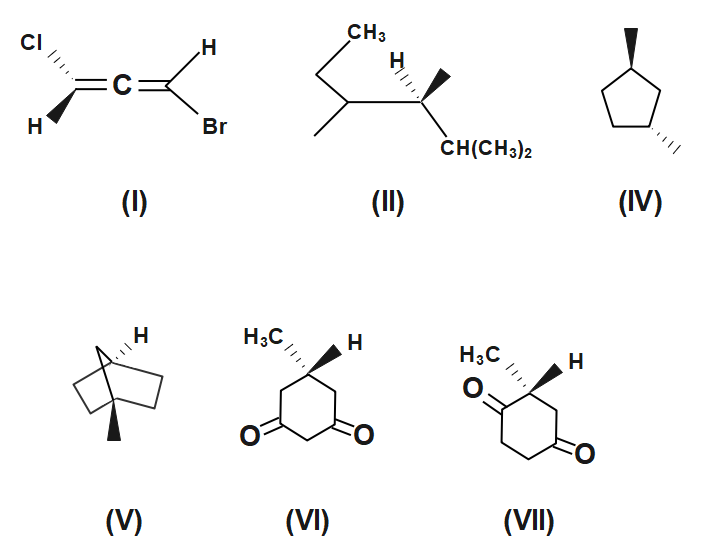
(A) I and II
(B) III and IV
(C) II, IV and VI
(D) I, II, III and VI

Answer
544.2k+ views
Hint: In order to understand chirality and stereoisomers, one must understand the concept of spatial arrangement. Spatial arrangement of atoms means how different t atomic particles and molecules are situated in the space around the organic compound, namely its carbon chain. In this sense, the spatial arrangement of an organic molecule is different; the atomic particles and molecules are situated in the space around the organic compound, namely its carbon chain. In this sense, the spatial arrangement of an organic molecule is dimensional direction by even one degree.
Complete step by step solution:
Chirality means 'mirror-image, non-superimposable molecules', and we can say that a molecule is chiral if its mirror image (it must have one) is not the same as itself. A carbon atom that is bonded to four different, atoms or groups loses all symmetry, and is often referred to as an asymmetric carbon. The configuration of such a molecular unit is called a chiral, and the structure may exist in either a right-handed configuration or a left handed configuration.
In compound I all the C-atoms are symmetric ,so no carbon atom is chiral.
In compound II all the C-atoms are symmetric ,so no carbon atom is chiral.
In compound III all the C-atoms are symmetric ,so no carbon atom is chiral.
In compound IV all the C-atoms are symmetric ,so no carbon atom is chiral.
In compound V groups attached are the same .Hence it is also achiral.
In compound VI groups attached are the same .Hence it is also achiral.
Therefore, compound I, II, III and IV are chiral, i.e. option D is the correct answer.
Note:
A useful step in examining structural formulas to determine whether stereoisomers may exist is to identify all stereo genic elements. A stereo genic element is a center, axis or plane that is a focus of stereoisomerism, such that an interchange of two groups attached to this feature leads to a stereoisomer. Stereogenic elements may be chiral or achiral. An asymmetric carbon is often a chiral stereo genic center, since interchanging any two substituent groups converts one enantiomer to the other.
Complete step by step solution:
Chirality means 'mirror-image, non-superimposable molecules', and we can say that a molecule is chiral if its mirror image (it must have one) is not the same as itself. A carbon atom that is bonded to four different, atoms or groups loses all symmetry, and is often referred to as an asymmetric carbon. The configuration of such a molecular unit is called a chiral, and the structure may exist in either a right-handed configuration or a left handed configuration.
In compound I all the C-atoms are symmetric ,so no carbon atom is chiral.
In compound II all the C-atoms are symmetric ,so no carbon atom is chiral.
In compound III all the C-atoms are symmetric ,so no carbon atom is chiral.
In compound IV all the C-atoms are symmetric ,so no carbon atom is chiral.
In compound V groups attached are the same .Hence it is also achiral.
In compound VI groups attached are the same .Hence it is also achiral.
Therefore, compound I, II, III and IV are chiral, i.e. option D is the correct answer.
Note:
A useful step in examining structural formulas to determine whether stereoisomers may exist is to identify all stereo genic elements. A stereo genic element is a center, axis or plane that is a focus of stereoisomerism, such that an interchange of two groups attached to this feature leads to a stereoisomer. Stereogenic elements may be chiral or achiral. An asymmetric carbon is often a chiral stereo genic center, since interchanging any two substituent groups converts one enantiomer to the other.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

Draw ray diagrams each showing i myopic eye and ii class 12 physics CBSE

Giving reasons state the signs positive or negative class 12 physics CBSE

Explain esterification reaction with the help of a class 12 chemistry CBSE

What is defined as a solenoid Depict a diagram with class 12 physics CBSE




