
Which of the following products is obtained when 2-methyl-2-nitropropane is treated with NaOCl solution?
A.1-chloro-2-methyl-2-nitropropane
B.A mixture of 1-chloro-2-methyl-2-nitropropane and 1,3-dichloro-2-methyl-2-nitropropane
C.1,3-dichloro-2-(chloromethyl)-2-nitropropane
D.None of the above
Answer
565.8k+ views
Hint:For nitro alkanes, one must recall primary nitro alkanes, secondary nitroalkanes and tertiary nitroalkanes. The difference between the primary, secondary and tertiary nitroalkanes is done, based on the carbon to which the nitro group is attached and not on the basis of nitrogen atom. NaOCl is used for halogenation of nitro alkanes.
Complete answer:
Nitro alkanes are organic compounds that contain alkane and nitro functional groups which is \( - N{O_2}\). Nitro group is a group that generally makes a compound explosive. The structure of nitro alkane is given by:
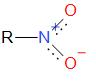
Nitro alkanes are considered to form highly substituted alkanes, alkenes, amines, carboxylic acids, aldehydes, ketones etc.
Primary nitro alkanes are compounds in which the nitro group which is \( - N{O_2}\) is attached to the primary carbon. For example,
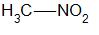 that is 1-nitromethane.
that is 1-nitromethane.
Secondary nitro alkanes are compounds in which the nitro group is attached to the secondary carbon. For example,
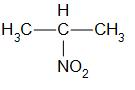 that is 2-nitropropane.
that is 2-nitropropane.
Tertiary nitro alkanes are compounds in which the nitro group is attached to the tertiary carbon. For example,
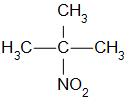 that is 2-methyl-2-nitropropane.
that is 2-methyl-2-nitropropane.
NaOCl solution is used for halogenation of nitro alkanes.
We have understood that 2-methyl-2-nitropropane is a tertiary nitroalkane from the above-mentioned example. Tertiary nitro alkanes do not readily react with NaOCl solutions. Hence no product can be formed when 2-methyl-2-nitropropane is treated with NaOCl solution.
Therefore, the correct option is D.
Note:
Usually, nitro alkanes combine with solid catalysts and they offer the opportunity to perform reactions more efficiently.
Also remember that primary carbons are bonded with only one other carbon, secondary carbons are bonded with two other carbons, tertiary carbons are bonded with three other carbons and quaternary carbons are bonded with four other carbons.
Complete answer:
Nitro alkanes are organic compounds that contain alkane and nitro functional groups which is \( - N{O_2}\). Nitro group is a group that generally makes a compound explosive. The structure of nitro alkane is given by:

Nitro alkanes are considered to form highly substituted alkanes, alkenes, amines, carboxylic acids, aldehydes, ketones etc.
Primary nitro alkanes are compounds in which the nitro group which is \( - N{O_2}\) is attached to the primary carbon. For example,
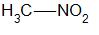
Secondary nitro alkanes are compounds in which the nitro group is attached to the secondary carbon. For example,

Tertiary nitro alkanes are compounds in which the nitro group is attached to the tertiary carbon. For example,

NaOCl solution is used for halogenation of nitro alkanes.
We have understood that 2-methyl-2-nitropropane is a tertiary nitroalkane from the above-mentioned example. Tertiary nitro alkanes do not readily react with NaOCl solutions. Hence no product can be formed when 2-methyl-2-nitropropane is treated with NaOCl solution.
Therefore, the correct option is D.
Note:
Usually, nitro alkanes combine with solid catalysts and they offer the opportunity to perform reactions more efficiently.
Also remember that primary carbons are bonded with only one other carbon, secondary carbons are bonded with two other carbons, tertiary carbons are bonded with three other carbons and quaternary carbons are bonded with four other carbons.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




