
Which of the following molecules has trigonal planar geometry?
A. $I{{F}_{3}}$
B. $PC{{l}_{3}}$
C. $N{{H}_{3}}$
D. $B{{F}_{3}}$
Answer
600.9k+ views
Hint: To find the geometry of a compound we must first find out the hybridisation of the compound and should know about the number of bond pairs and lone pairs present in the compound.
Complete step by step answer:
- We will first find out the hybridisation of each compound and then will see the structure of each. To find out hybridisation we need to find the electron pair count, which is denoted by the symbol Z.
- Electron pair count can be found by the formula:
\[Z=\dfrac{1}{2}\times \left( V+M-C+A \right)\]
Where, Z= Electron pair count
V= Valence electron of central atom
M=Monovalent atom attached to central atom,
C= Cationic charge
A= Anionic charge
- Let’s first see about $I{{F}_{3}}$:
The electronic configuration of Iodine is- $\left[ Kr \right]4{{d}^{10}}5{{s}^{2}}5{{p}^{5}}$, so we can see that there is seven valence electrons present in it. In this compound there are 3 monovalent atoms present. So, the hybridisation in this is:
\[\begin{align}
& Z=\dfrac{1}{2}\times \left( 7+3-0+0 \right) \\
& =5 \\
\end{align}\]
Here, the hybridisation will be: $s{{p}^{3}}d$.
The structure of this is:
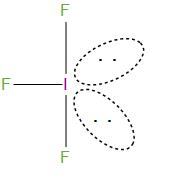
It is T-shape geometry, and was bent due to lone pair- lone pair repulsion.
- Let’s see about $PC{{l}_{3}}$:
The electronic configuration of Phosphorus is- $\left[ Ne \right]3{{s}^{2}}3{{p}^{3}}$ , so we can see that there is five valence electrons present in it. In this compound there are 3 monovalent atoms present. So, the hybridisation in this is:
\[\begin{align}
& Z=\dfrac{1}{2}\times \left( 5+3-0+0 \right) \\
& =4 \\
\end{align}\]
Here, the hybridisation will be: $s{{p}^{3}}$.
The structure of this is:
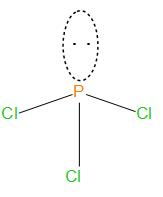
We can see that it is having pyramidal geometry.
- Let’s see about $N{{H}_{3}}$:
The electronic configuration of Nitrogen is- $\left[ He \right]2{{s}^{2}}2{{p}^{3}}$, so we can see that there is five valence electrons present in it. In this compound there are 3 monovalent atoms present. So, the hybridisation in this is:
\[\begin{align}
& Z=\dfrac{1}{2}\times \left( 5+3-0+0 \right) \\
& =4 \\
\end{align}\]
Here, the hybridisation will be: $s{{p}^{3}}$
The structure of this is:
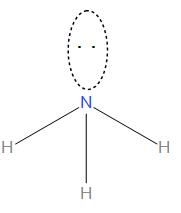
We can see that it is having pyramidal geometry as there is one lone pair and three bond pairs present.
- Let’s see about $B{{F}_{3}}$:
The electronic configuration of Bromine is- $\left[ Ar \right]3{{d}^{10}}4{{s}^{2}}4{{p}^{5}}$, so we can see that there is three valence electrons present in it. In this compound there are 3 monovalent atoms present. So, the hybridisation in this is:
\[\begin{align}
& Z=\dfrac{1}{2}\times \left( 3+3-0+0 \right) \\
& =3 \\
\end{align}\]
Here, the hybridisation will be: $s{{p}^{2}}$
The structure of this is:
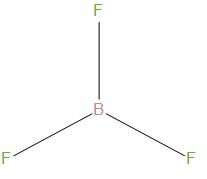
We can see that it is having trigonal planar geometry, and there bond angle is about ${{120}^{\circ }}$
Hence, the correct option is (D).
Note:
- Many of the properties of a substance are determined by the geometry of the compound.
- We should write the electronic configuration correctly in order to find the valence electron in the atom, and should see whether any cationic or anionic charge is present in the compound to find the hybridisation.
Complete step by step answer:
- We will first find out the hybridisation of each compound and then will see the structure of each. To find out hybridisation we need to find the electron pair count, which is denoted by the symbol Z.
- Electron pair count can be found by the formula:
\[Z=\dfrac{1}{2}\times \left( V+M-C+A \right)\]
Where, Z= Electron pair count
V= Valence electron of central atom
M=Monovalent atom attached to central atom,
C= Cationic charge
A= Anionic charge
- Let’s first see about $I{{F}_{3}}$:
The electronic configuration of Iodine is- $\left[ Kr \right]4{{d}^{10}}5{{s}^{2}}5{{p}^{5}}$, so we can see that there is seven valence electrons present in it. In this compound there are 3 monovalent atoms present. So, the hybridisation in this is:
\[\begin{align}
& Z=\dfrac{1}{2}\times \left( 7+3-0+0 \right) \\
& =5 \\
\end{align}\]
Here, the hybridisation will be: $s{{p}^{3}}d$.
The structure of this is:

It is T-shape geometry, and was bent due to lone pair- lone pair repulsion.
- Let’s see about $PC{{l}_{3}}$:
The electronic configuration of Phosphorus is- $\left[ Ne \right]3{{s}^{2}}3{{p}^{3}}$ , so we can see that there is five valence electrons present in it. In this compound there are 3 monovalent atoms present. So, the hybridisation in this is:
\[\begin{align}
& Z=\dfrac{1}{2}\times \left( 5+3-0+0 \right) \\
& =4 \\
\end{align}\]
Here, the hybridisation will be: $s{{p}^{3}}$.
The structure of this is:

We can see that it is having pyramidal geometry.
- Let’s see about $N{{H}_{3}}$:
The electronic configuration of Nitrogen is- $\left[ He \right]2{{s}^{2}}2{{p}^{3}}$, so we can see that there is five valence electrons present in it. In this compound there are 3 monovalent atoms present. So, the hybridisation in this is:
\[\begin{align}
& Z=\dfrac{1}{2}\times \left( 5+3-0+0 \right) \\
& =4 \\
\end{align}\]
Here, the hybridisation will be: $s{{p}^{3}}$
The structure of this is:

We can see that it is having pyramidal geometry as there is one lone pair and three bond pairs present.
- Let’s see about $B{{F}_{3}}$:
The electronic configuration of Bromine is- $\left[ Ar \right]3{{d}^{10}}4{{s}^{2}}4{{p}^{5}}$, so we can see that there is three valence electrons present in it. In this compound there are 3 monovalent atoms present. So, the hybridisation in this is:
\[\begin{align}
& Z=\dfrac{1}{2}\times \left( 3+3-0+0 \right) \\
& =3 \\
\end{align}\]
Here, the hybridisation will be: $s{{p}^{2}}$
The structure of this is:

We can see that it is having trigonal planar geometry, and there bond angle is about ${{120}^{\circ }}$
Hence, the correct option is (D).
Note:
- Many of the properties of a substance are determined by the geometry of the compound.
- We should write the electronic configuration correctly in order to find the valence electron in the atom, and should see whether any cationic or anionic charge is present in the compound to find the hybridisation.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Chemistry: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Draw a diagram of nephron and explain its structur class 11 biology CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

Chemical formula of Bleaching powder is A Ca2OCl2 B class 11 chemistry CBSE

Name the part of the brain responsible for the precision class 11 biology CBSE

The growth of tendril in pea plants is due to AEffect class 11 biology CBSE

One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE




