
Which of the following is true for nitrate anion.
A.The formal charge on \[N\] is zero
B.The bond order of \[NO\] bond is $\dfrac{4}{3}$
C.The average formal charge on oxygen is \[\dfrac{1}{3}\]
D.There are \[2-\pi \] bonds in the ion
Answer
573.9k+ views
Hint: To answer this question, you should recall the concept of formal charge and bond order. It’s a theoretical charge over an individual atom of an ion as the real charge over a polyatomic molecule or ion is distributed on an ion as a whole and not over a single atom.
The formula used: \[{\text{FC}} = {\text{V}} - {\text{N}} - \dfrac{{\text{B}}}{{\text{2}}}\]
where $V$ is the no. of valence electron \[N\] is the no. of non-bonding electrons and \[B\] is the no. of electrons in the covalent bond
Complete Step by step solution:
The bond order shows the number of chemical bonds present between a pair of atoms. For instance, the bond order of diatomic nitrogen \[N \equiv N\] is 3 and bond order between the carbon atoms in \[H - H \equiv C - H\] is also three. The bond order describes the stability of the bond. The molecular orbital provides an easy understanding of the concept of the bond order of a chemical bond. It quantifies the degree of covalent bonds between the atoms. The formal charge of nitrogen can be calculated using: \[{\text{FC}} = {\text{V}} - {\text{N}} - \dfrac{{\text{B}}}{{\text{2}}}\]
(V = no. of valence electron N = No. of nonbonding electrons B = No. of electrons in covalent bond)
\[{\text{FC of N in N}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{3}}}^ - = 0\]
\[{\text{FC of O in N}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{3}}}^ - = - \dfrac{1}{3}\]
The Lewis structure of nitrate ion can be drawn as:
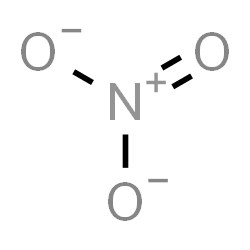
We can see that the total number of bonds = 4.
The number of bond groups between individual atoms = 3 and bond order \[ = \dfrac{{4}}{3} = 1.33\]. There is one pi bond.
Therefore, we can conclude that the correct answer to this question is option D.
Note: In most of the compounds, the oxidation number of oxygen is $ - 2$ . There are two exceptions here.
Peroxides: Each oxygen atom exhibits an oxidation number of $ - 1$ . Example, \[N{a_2}{O_2}\]
Superoxide- Every oxygen atom is allocated an oxidation number of \[ - \dfrac{{{\text{ }}1}}{2}\] . Example, \[K{O_2}\]
Oxygen is bonded to fluorine- Example, dioxygen difluoride where the oxygen atom is allocated an oxidation number of $ + 1$ .
The formula used: \[{\text{FC}} = {\text{V}} - {\text{N}} - \dfrac{{\text{B}}}{{\text{2}}}\]
where $V$ is the no. of valence electron \[N\] is the no. of non-bonding electrons and \[B\] is the no. of electrons in the covalent bond
Complete Step by step solution:
The bond order shows the number of chemical bonds present between a pair of atoms. For instance, the bond order of diatomic nitrogen \[N \equiv N\] is 3 and bond order between the carbon atoms in \[H - H \equiv C - H\] is also three. The bond order describes the stability of the bond. The molecular orbital provides an easy understanding of the concept of the bond order of a chemical bond. It quantifies the degree of covalent bonds between the atoms. The formal charge of nitrogen can be calculated using: \[{\text{FC}} = {\text{V}} - {\text{N}} - \dfrac{{\text{B}}}{{\text{2}}}\]
(V = no. of valence electron N = No. of nonbonding electrons B = No. of electrons in covalent bond)
\[{\text{FC of N in N}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{3}}}^ - = 0\]
\[{\text{FC of O in N}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{3}}}^ - = - \dfrac{1}{3}\]
The Lewis structure of nitrate ion can be drawn as:

We can see that the total number of bonds = 4.
The number of bond groups between individual atoms = 3 and bond order \[ = \dfrac{{4}}{3} = 1.33\]. There is one pi bond.
Therefore, we can conclude that the correct answer to this question is option D.
Note: In most of the compounds, the oxidation number of oxygen is $ - 2$ . There are two exceptions here.
Peroxides: Each oxygen atom exhibits an oxidation number of $ - 1$ . Example, \[N{a_2}{O_2}\]
Superoxide- Every oxygen atom is allocated an oxidation number of \[ - \dfrac{{{\text{ }}1}}{2}\] . Example, \[K{O_2}\]
Oxygen is bonded to fluorine- Example, dioxygen difluoride where the oxygen atom is allocated an oxidation number of $ + 1$ .
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

What organs are located on the left side of your body class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of nephron and explain its structur class 11 biology CBSE

How do I convert ms to kmh Give an example class 11 physics CBSE




