
Which of the following is most reactive towards Markovnikov addition?
Answer
590.1k+ views
Hint: Alkenes undergo electrophilic addition reactions. It is triggered by acid acting as an electrophile toward pi-electrons of the double bond. Markovnikov rule is used to determine how the pi bond will delocalise. The product formed while taking markovnikov rule into consideration is the major product.
Complete step by step answer:
Markovnikov rule states that when an unsymmetrical substituted alkene reacts with a hydrogen halide, the hydrogen atom adds to the carbon that has the greater number of hydrogen atoms i.e. least substituted carbon atom.
We will form the intermediate for the compounds mentioned in the options. The compound having the most stable intermediate will react the fastest. This is in accordance with Markovnikov rule.
It is important to know that resonance is given priority over inductive effect and hyperconjugation.
Compound (A):
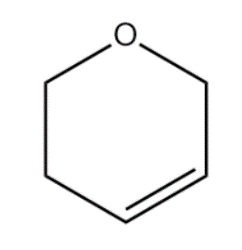
When the double bond is delocalised, the negative charge and positive is on a two-degree carbon atom. There is no possibility of resonance.
Compound (B):
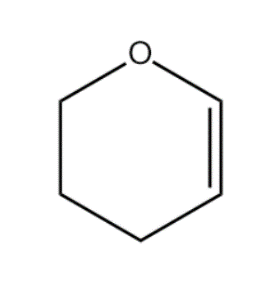
When the double bond is delocalised, the negative charge is on the below carbon atom and positive charge is on the top carbon atom. This is the way double bonds are delocalised because in this configuration there is resonance between the lone pair of oxygen, positive charge and negative charge. This leads to stabilisation of charge and forming stable intermediate.
Compound (C):
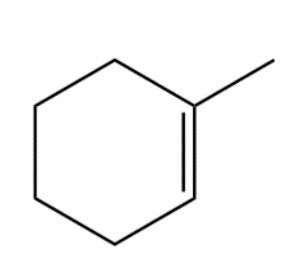
In the above compound, the positive charge is on the three-degree carbon and negative charge on two-degree carbon. In this configuration there is only an inductive effect which leads to formation of relatively less stable intermediate.
Compound (D):
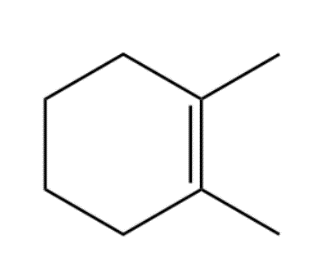
In the above compound, the negative as well as positive charge is on three-degree carbon. Although the positive charge is stabilised through inductive effect, the negative charge is highly unstable due to the same inductive effect offered by methyl groups attached to carbon atoms. The intermediate form is unstable. From the above explanation we can conclude that the most stable intermediate is formed in compound (B) due to resonance.
So, the correct answer is “Option B”.
Note: When an organic peroxide is used along with HBr it leads to the formation of Hoffmann product i.e. the least substituted product. This is because this reaction proceeds through the formation of free radicals. Due to this we consider steric hindrance while deciding the attack of incoming nucleophiles. Since the reaction mechanism is the exact opposite of the process mentioned in markovnikov rule, this rule is also known as anti-markovnikov rule.
Complete step by step answer:
Markovnikov rule states that when an unsymmetrical substituted alkene reacts with a hydrogen halide, the hydrogen atom adds to the carbon that has the greater number of hydrogen atoms i.e. least substituted carbon atom.
We will form the intermediate for the compounds mentioned in the options. The compound having the most stable intermediate will react the fastest. This is in accordance with Markovnikov rule.
It is important to know that resonance is given priority over inductive effect and hyperconjugation.
Compound (A):

When the double bond is delocalised, the negative charge and positive is on a two-degree carbon atom. There is no possibility of resonance.
Compound (B):

When the double bond is delocalised, the negative charge is on the below carbon atom and positive charge is on the top carbon atom. This is the way double bonds are delocalised because in this configuration there is resonance between the lone pair of oxygen, positive charge and negative charge. This leads to stabilisation of charge and forming stable intermediate.
Compound (C):

In the above compound, the positive charge is on the three-degree carbon and negative charge on two-degree carbon. In this configuration there is only an inductive effect which leads to formation of relatively less stable intermediate.
Compound (D):

In the above compound, the negative as well as positive charge is on three-degree carbon. Although the positive charge is stabilised through inductive effect, the negative charge is highly unstable due to the same inductive effect offered by methyl groups attached to carbon atoms. The intermediate form is unstable. From the above explanation we can conclude that the most stable intermediate is formed in compound (B) due to resonance.
So, the correct answer is “Option B”.
Note: When an organic peroxide is used along with HBr it leads to the formation of Hoffmann product i.e. the least substituted product. This is because this reaction proceeds through the formation of free radicals. Due to this we consider steric hindrance while deciding the attack of incoming nucleophiles. Since the reaction mechanism is the exact opposite of the process mentioned in markovnikov rule, this rule is also known as anti-markovnikov rule.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




