
Which of the following compounds will undergo HVZ reaction?
A.
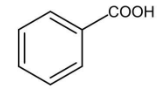
B.
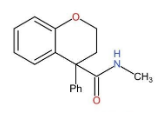
C.
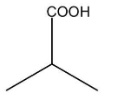
D.
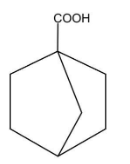




Answer
592.5k+ views
Hint:HVZ reaction stands for Hell-Volhard-Zelinsky halogenation. It is used for the bromination in the alpha position of a compound in the reaction.
Complete step by step answer:
Hell-Volhard-Zelinsky reaction is different from other halogenation reactions because it takes place in the absence of the halogenation carrier. This reaction is used for the halogenation of the carboxylic acids attached at the alpha carbon which has an alpha hydrogen.
- The reaction is initiated by the addition of potassium tribromide and then the addition of one molar equivalent of diatomic bromine.
- This reaction is carried out at very severe conditions involving temperature above 373K and increased reaction time.
- Let us now see which of these compounds have alpha carbon and can undergo HVZ reaction.
Alpha carbon is the first carbon atom that is attached to a functional group (-COOH in this case) and alpha hydrogen is the hydrogen attached to the alpha carbon.
A.
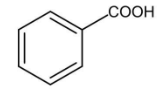
In this compound, there is an alpha carbon present, but there is no alpha hydrogen present in this compound. Therefore, it does not undergo HVZ reaction.
B.
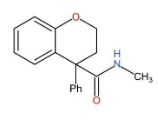
In this compound, there is no carboxylic group present and therefore, it does not undergo HVZ reaction.
C.
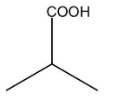
In this compound, there is an alpha carbon present along with the alpha hydrogen. Therefore, this compound will undergo an HVZ reaction. The reaction is shown below:
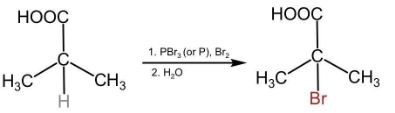
D.
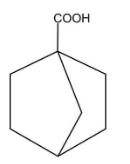
In this compound, there is an alpha carbon present but there is no alpha hydrogen present. Therefore, this compound will not undergo HVZ reaction.
Therefore, only option (c) will undergo HVZ reaction. Hence, the correct option is option (c).
Note:
The HVZ reaction fails the fluorination and iodination of carboxylic acids. And if it is conducted at high temperatures, elimination of hydrogen halides from the product, resulting in the formation of beta unsaturated carboxylic acids.
Complete step by step answer:
Hell-Volhard-Zelinsky reaction is different from other halogenation reactions because it takes place in the absence of the halogenation carrier. This reaction is used for the halogenation of the carboxylic acids attached at the alpha carbon which has an alpha hydrogen.
- The reaction is initiated by the addition of potassium tribromide and then the addition of one molar equivalent of diatomic bromine.
- This reaction is carried out at very severe conditions involving temperature above 373K and increased reaction time.
- Let us now see which of these compounds have alpha carbon and can undergo HVZ reaction.
Alpha carbon is the first carbon atom that is attached to a functional group (-COOH in this case) and alpha hydrogen is the hydrogen attached to the alpha carbon.
A.

In this compound, there is an alpha carbon present, but there is no alpha hydrogen present in this compound. Therefore, it does not undergo HVZ reaction.
B.

In this compound, there is no carboxylic group present and therefore, it does not undergo HVZ reaction.
C.

In this compound, there is an alpha carbon present along with the alpha hydrogen. Therefore, this compound will undergo an HVZ reaction. The reaction is shown below:

D.

In this compound, there is an alpha carbon present but there is no alpha hydrogen present. Therefore, this compound will not undergo HVZ reaction.
Therefore, only option (c) will undergo HVZ reaction. Hence, the correct option is option (c).
Note:
The HVZ reaction fails the fluorination and iodination of carboxylic acids. And if it is conducted at high temperatures, elimination of hydrogen halides from the product, resulting in the formation of beta unsaturated carboxylic acids.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




