
Which of the following compounds are chiral and resolvable?
A. $ \left[ {{C}_{6}}{{H}_{5}}{{N}^{+}}\left( C{{H}_{2}}C{{H}_{2}}C{{H}_{3}} \right)\left( {{C}_{2}}{{H}_{5}} \right)\left( C{{H}_{3}} \right)B{{r}^{-}} \right] $
B. $ {{C}_{6}}{{H}_{5}}N\left( C{{H}_{3}} \right)\left( {{C}_{2}}{{H}_{5}} \right) $
C. $ C{{H}_{3}}C{{H}_{2}}CH\left( C{{H}_{3}} \right)N\left( C{{H}_{3}} \right)\left( {{C}_{2}}{{H}_{5}} \right) $
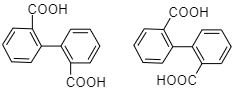
D.

Answer
493.2k+ views
Hint :Chiral molecule is a molecule which consists of one or more carbon atom that has four different or non-identical substituents, and such carbon atoms are called a chiral center or a stereogenic center or a stereocenter while, the molecules which are not superimposable on their mirror image are also called chiral molecule. The property of non-superimposability of a molecule on its mirror image is called chirality.
Complete Step By Step Answer:
A resolvable compound is a compound that is optically active, while a compound which is capable of optical rotation is called optically active. All pure chiral compounds are optically active.
Option (a) is a chiral and resolvable compound because the compound has a non-superimposable mirror image.
In Option (b) due to rapid pyramidal inversion the tertiary amine will always remain in the form of racemic mixture. Therefore, it is optically inactive.
Option (c) is a chiral and resolvable compound because the third carbon atom has four different substituents i.e. ethyl, methyl, hydrogen and a nitrogen moreover, the compound has non-superimposable mirror image.
Option (d) bulker groups are present which would repel on being rotated so rotation would not occur so this compound is optically inactive. Moreover, no carbon atom has four different substituents hence the compound is not chiral.
The correct answer is option A and C.
Note :
Stereoisomers are the isomers which have the same position of atoms or groups but they differ in the spatial arrangement around the central atom.
The stereoisomers which are not mirror images of each other are called diastereomers and a meso compound is one whose molecules are superimposable on their mirror images even though they contain chiral centres.
Complete Step By Step Answer:
A resolvable compound is a compound that is optically active, while a compound which is capable of optical rotation is called optically active. All pure chiral compounds are optically active.
Option (a) is a chiral and resolvable compound because the compound has a non-superimposable mirror image.
In Option (b) due to rapid pyramidal inversion the tertiary amine will always remain in the form of racemic mixture. Therefore, it is optically inactive.
Option (c) is a chiral and resolvable compound because the third carbon atom has four different substituents i.e. ethyl, methyl, hydrogen and a nitrogen moreover, the compound has non-superimposable mirror image.
Option (d) bulker groups are present which would repel on being rotated so rotation would not occur so this compound is optically inactive. Moreover, no carbon atom has four different substituents hence the compound is not chiral.
The correct answer is option A and C.
Note :
Stereoisomers are the isomers which have the same position of atoms or groups but they differ in the spatial arrangement around the central atom.
The stereoisomers which are not mirror images of each other are called diastereomers and a meso compound is one whose molecules are superimposable on their mirror images even though they contain chiral centres.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




