
Which of the following amino acids is achiral?
A) Cysteine
B) Alanine
C) Glycine
D) Serine
Answer
573.3k+ views
Hint: We know that the inverse of chiral is achiral. Achiral objects are superimposable with their identical representations. For instance, two bits of paper are achiral. Conversely, chiral atoms, similar to our hands, are non-superimposable identical representations of one another.
Complete answer:
We have to remember that the stereoisomers are isomers that vary in spatial course of action of iotas, as opposed to requests from the nuclear network. One of their most fascinating kinds of isomers is the identical representation stereoisomers, a non-superimposable arrangement of two particles that are a perfect representation of each other. The existences of these atoms are controlled by an idea known as chirality.
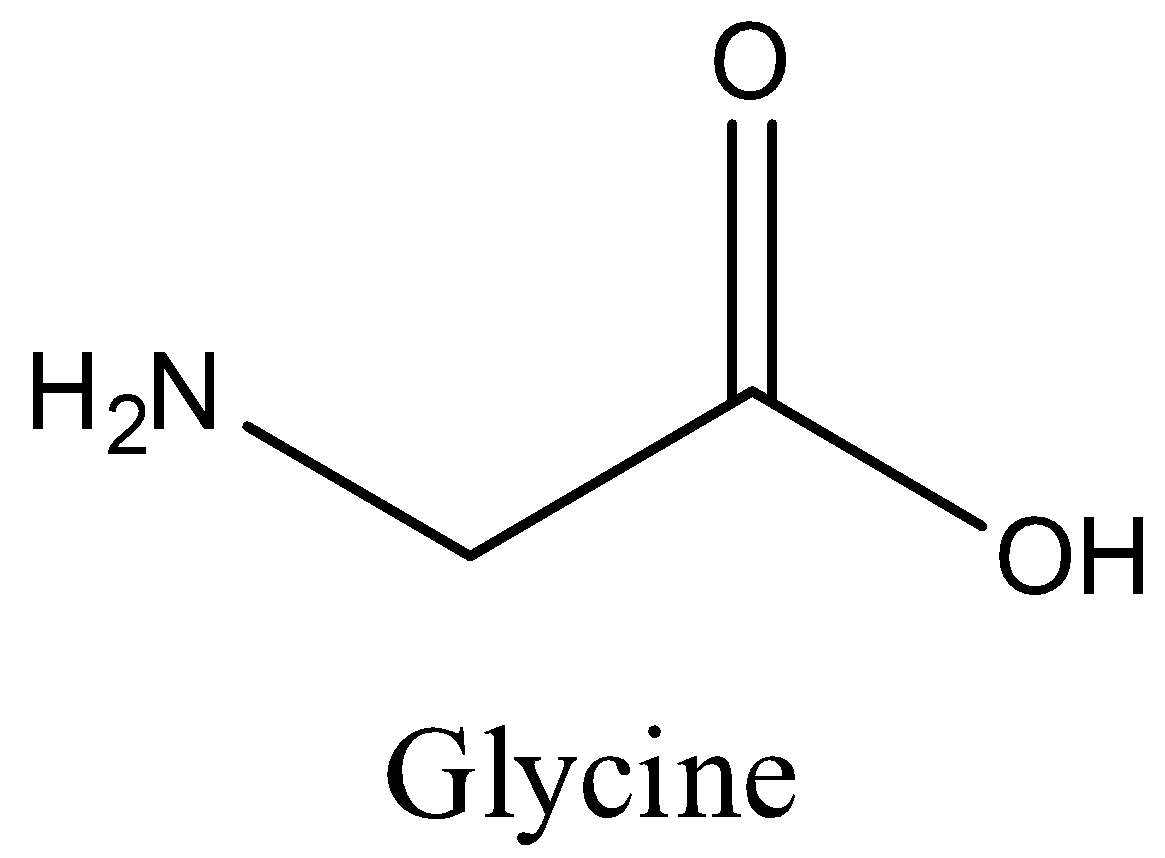
Glycine is achiral. It lacks a chiral Carbon atom. Thus option C is correct.
We can draw the structure of glycine is,
Cysteine, Alanine and serine are chiral. The chiral Carbon atom is marked with an asterisk. We can draw the structures of alanine, cysteine and serine as,
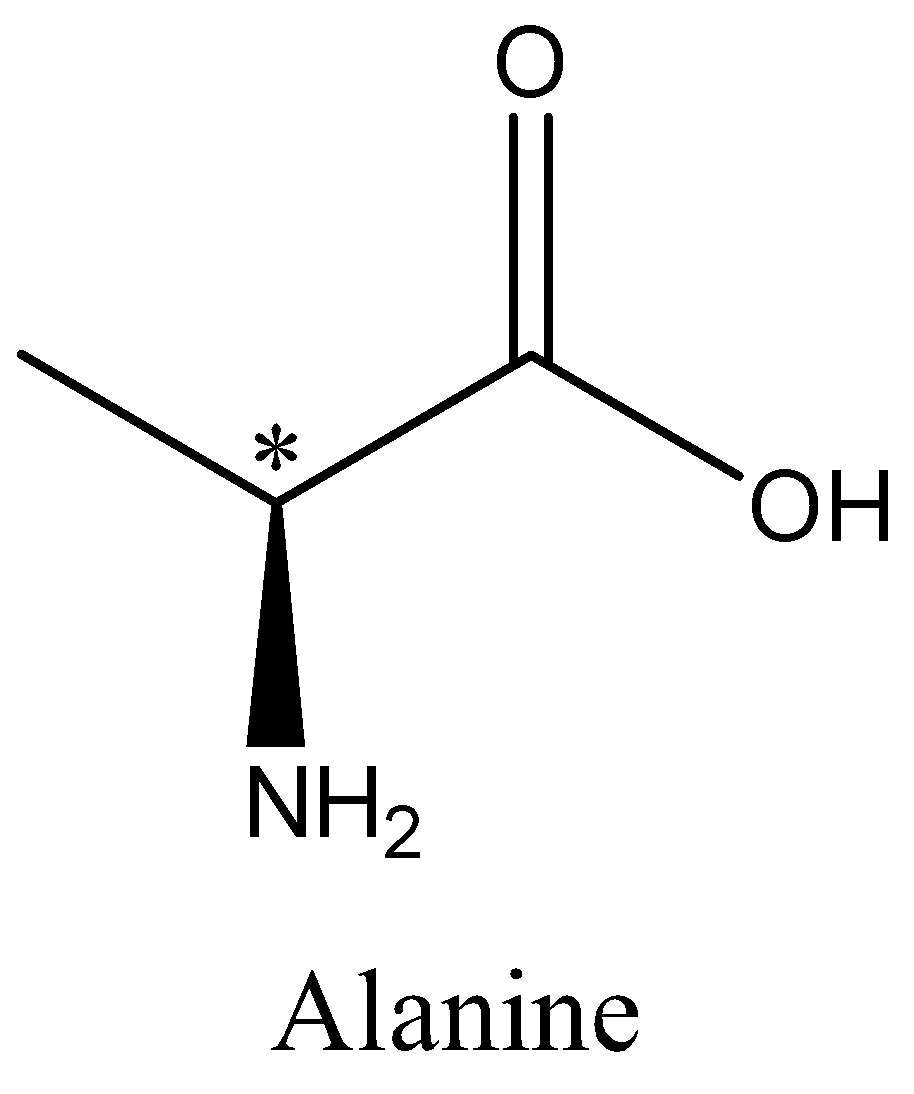
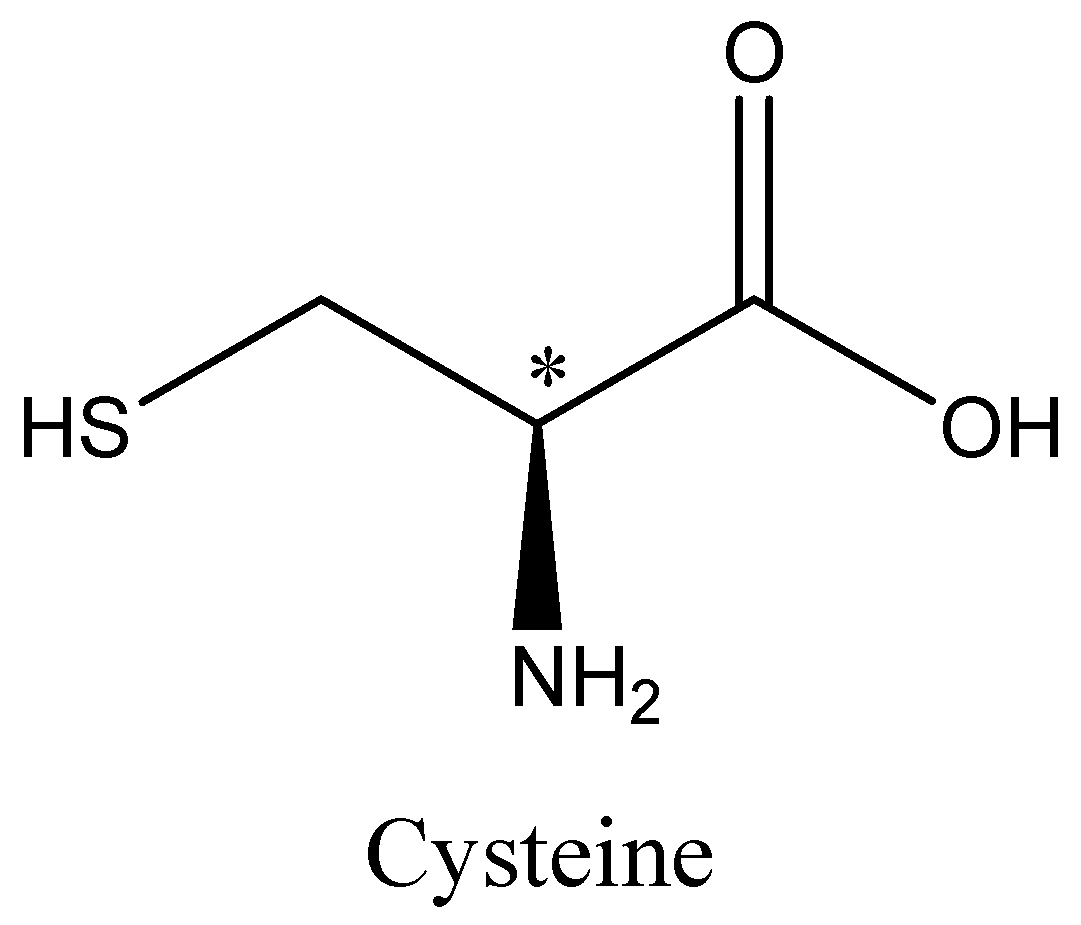
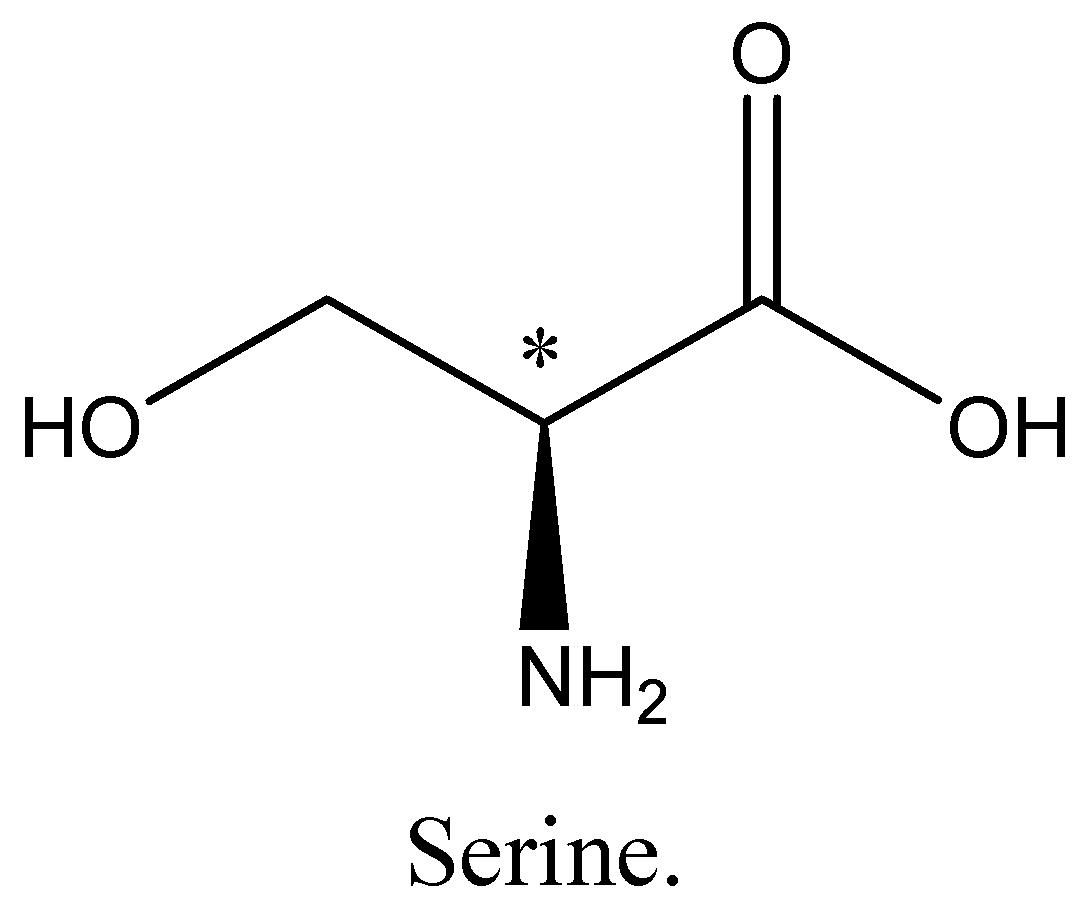
Hence option A, B and D is incorrect.
Therefore, the correct option is C.
Note:
Now we discuss how enantiomers and diastereomers differ from each other.
Let’s discuss about the concept of enantiomers as,
Enantiomers: An object or a molecule that cannot be superimposed on its likeness should be asymmetric. Such a combination of molecules concerning each other as an object to its mirror image is thought to be enantiomorphs or enantiomers. The terms chiral and achiral also are wont to designate dissymmetric and non-dissymmetric molecules respectively. A chiral molecule isn't superimposable on its mirror image whereas achiral molecule is superimposable on its mirror image. A chiral atom is any atom empty plane of symmetry and is additionally called chiral centre. Enantiomers exist solely just in case of chiral molecules.
Let’s discuss about the concept of diastereomers as,
Diastereomers: Stereoisomers which are not connected by mirror images are known as Diastereomers. Diastereomers do not have a tendency to form mirror images with one other. Diastereomers contain cis–trans isomers, meso compounds, E-Z isomers, associate degreed non-enantiomeric optical isomers. Diastereomers seldom contain identical physical properties, the meso sort of hydroxy acid types diastereomers combine through each levo and Dextro salt acid, that give a pair of enantiomers.
Complete answer:
We have to remember that the stereoisomers are isomers that vary in spatial course of action of iotas, as opposed to requests from the nuclear network. One of their most fascinating kinds of isomers is the identical representation stereoisomers, a non-superimposable arrangement of two particles that are a perfect representation of each other. The existences of these atoms are controlled by an idea known as chirality.
Glycine is achiral. It lacks a chiral Carbon atom. Thus option C is correct.
We can draw the structure of glycine is,

Cysteine, Alanine and serine are chiral. The chiral Carbon atom is marked with an asterisk. We can draw the structures of alanine, cysteine and serine as,



Hence option A, B and D is incorrect.
Therefore, the correct option is C.
Note:
Now we discuss how enantiomers and diastereomers differ from each other.
Let’s discuss about the concept of enantiomers as,
Enantiomers: An object or a molecule that cannot be superimposed on its likeness should be asymmetric. Such a combination of molecules concerning each other as an object to its mirror image is thought to be enantiomorphs or enantiomers. The terms chiral and achiral also are wont to designate dissymmetric and non-dissymmetric molecules respectively. A chiral molecule isn't superimposable on its mirror image whereas achiral molecule is superimposable on its mirror image. A chiral atom is any atom empty plane of symmetry and is additionally called chiral centre. Enantiomers exist solely just in case of chiral molecules.
Let’s discuss about the concept of diastereomers as,
Diastereomers: Stereoisomers which are not connected by mirror images are known as Diastereomers. Diastereomers do not have a tendency to form mirror images with one other. Diastereomers contain cis–trans isomers, meso compounds, E-Z isomers, associate degreed non-enantiomeric optical isomers. Diastereomers seldom contain identical physical properties, the meso sort of hydroxy acid types diastereomers combine through each levo and Dextro salt acid, that give a pair of enantiomers.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

What is a transformer Explain the principle construction class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE




