
Which of the following alkenes will be most reactive towards electrophilic addition?
(A)
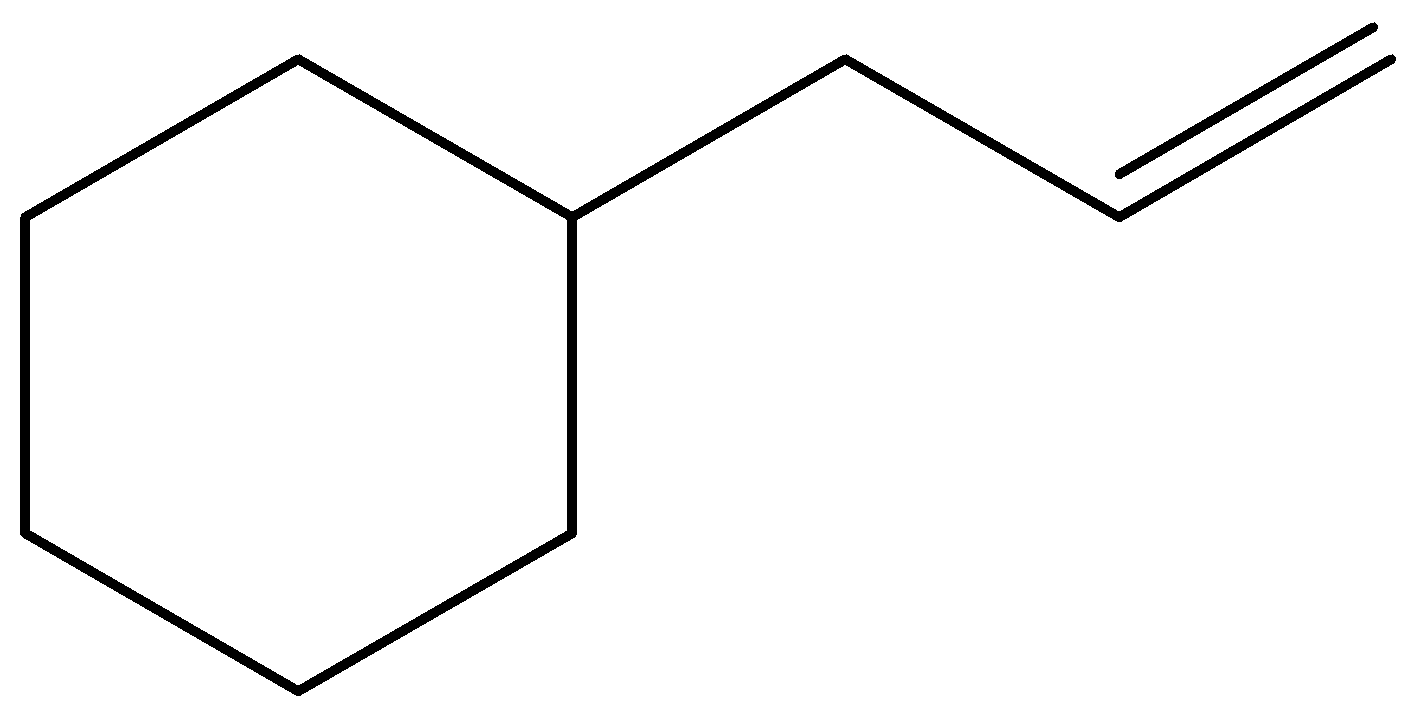
(B)

(C)
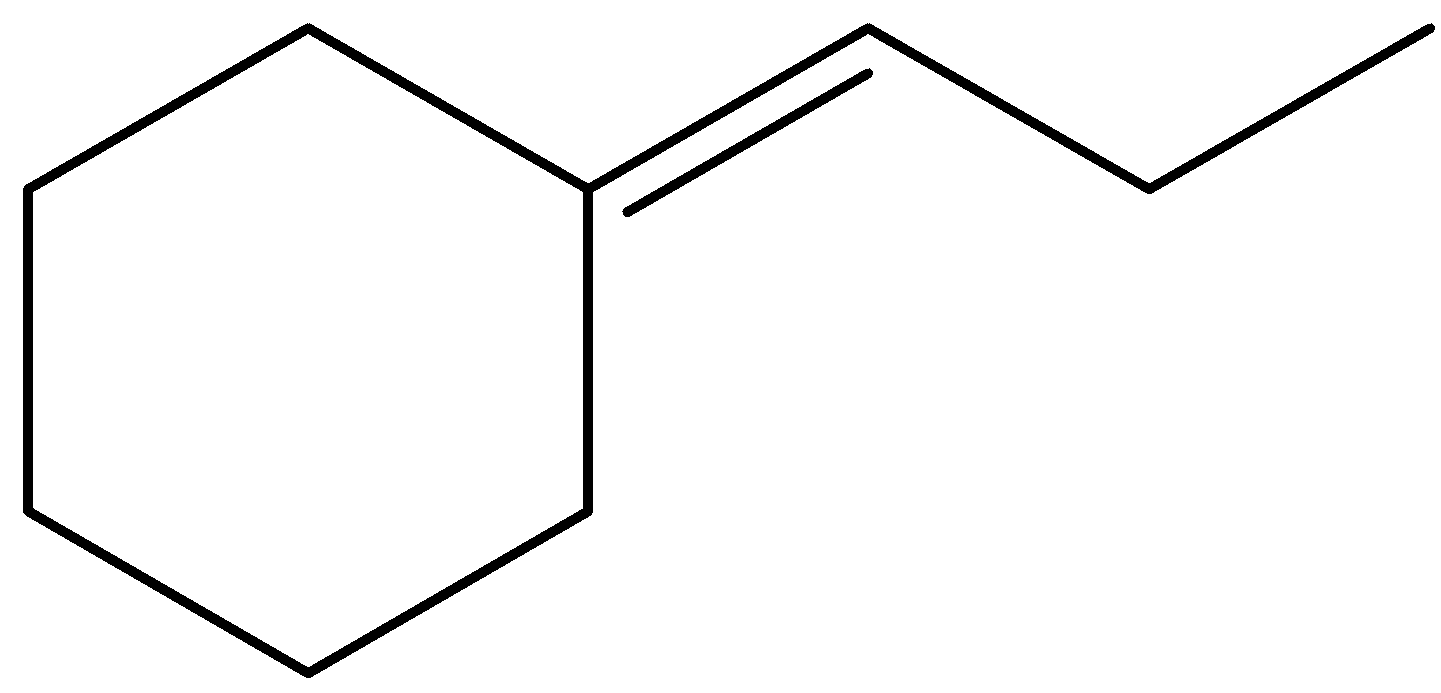
(D)





Answer
567k+ views
Hint: The answer to this question is based on the fact that the stability of tertiary carbocation is more and the one which forms this carbocation gives you the correct answer.
Complete answer:
In our chapters of chemistry, we have studied the stability factor about the carbocations, carbanions etc.
Now, let us see what is an electrophilic addition reaction and how it takes place.
- Electrophilic addition reaction is the reaction in which the electron rich compounds that are the molecules possessing multiple bonds attack an electrophile to form a stable carbocation where the addition of nucleophiles gets easier.
- The stability of carbocation formed in the alkene electrophilic addition plays an important role.
- The stability decreasing of carbocation is as follows: Tertiary > Secondary > Primary.
- In general, electrophilic addition can be defined as the reaction in which addition of an electrophile takes place where a pi – bond is broken to form two new sigma bonds.
For the electrophilic substitution or addition reaction, the necessary requirement is that they must have double or triple bonds.
Now, in the above question, the electrophilic addition takes place where the pi – bond breaks into two sigma bonds and the electrophile is added in such a way the it gives stable neighbouring carbocation and this can be given by,

The reaction is as shown below,
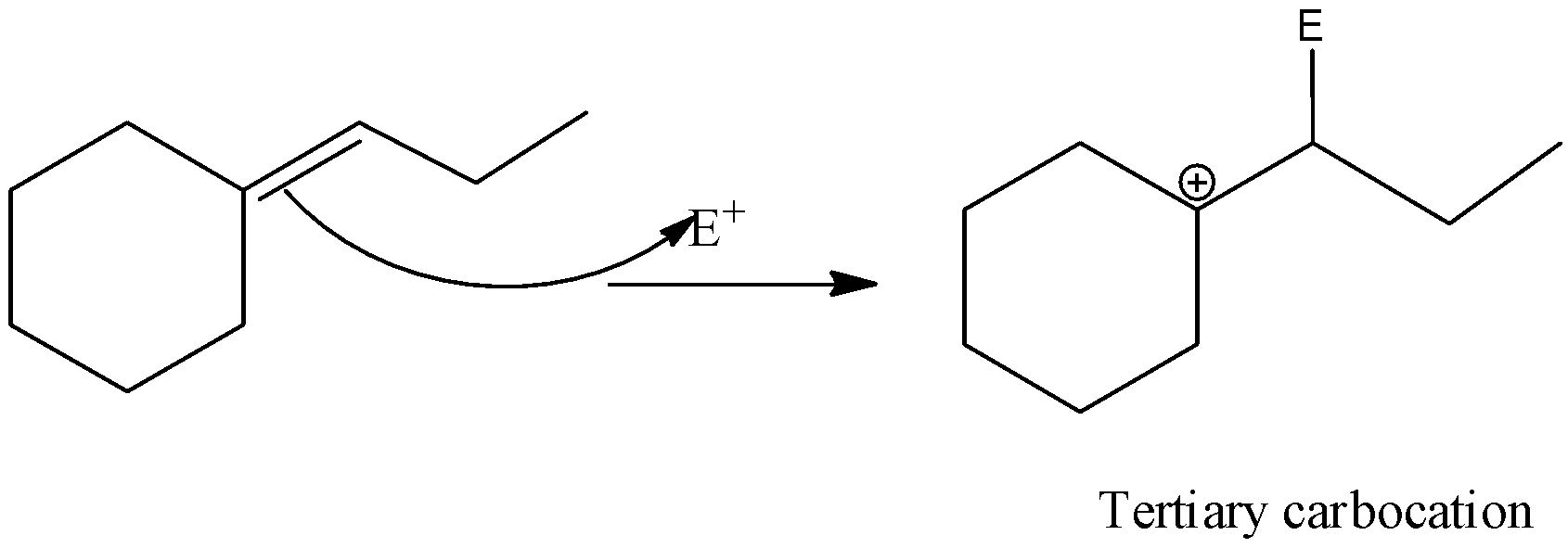
Therefore, the correct answer will be option C).
Note: Note that the electrophilic substitution reaction takes place in the aromatic compound which is accelerated by the Lewis acids and does not undergo electrophilic addition reaction. This is because it preserves the aromaticity of the ring.
Complete answer:
In our chapters of chemistry, we have studied the stability factor about the carbocations, carbanions etc.
Now, let us see what is an electrophilic addition reaction and how it takes place.
- Electrophilic addition reaction is the reaction in which the electron rich compounds that are the molecules possessing multiple bonds attack an electrophile to form a stable carbocation where the addition of nucleophiles gets easier.
- The stability of carbocation formed in the alkene electrophilic addition plays an important role.
- The stability decreasing of carbocation is as follows: Tertiary > Secondary > Primary.
- In general, electrophilic addition can be defined as the reaction in which addition of an electrophile takes place where a pi – bond is broken to form two new sigma bonds.
For the electrophilic substitution or addition reaction, the necessary requirement is that they must have double or triple bonds.
Now, in the above question, the electrophilic addition takes place where the pi – bond breaks into two sigma bonds and the electrophile is added in such a way the it gives stable neighbouring carbocation and this can be given by,

The reaction is as shown below,

Therefore, the correct answer will be option C).
Note: Note that the electrophilic substitution reaction takes place in the aromatic compound which is accelerated by the Lewis acids and does not undergo electrophilic addition reaction. This is because it preserves the aromaticity of the ring.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




