
Which is the wrong statement about oxymercuration-demercuration?
(a)- In the first step, oxymercuration i.e., water and \[Hg{{(OAc)}_{2}}\] add to the double bond.
(b)- In the second step, demercuration i.e., \[NaB{{H}_{4}}\] reduces \[{{(-HgOAc)}_{2}}\] group to hydrogen
(c)- The net reaction is the addition of water according to Markovnikov’s rule.
(d)- Rearrangement takes place.
Answer
592.5k+ views
Hint: In all the steps there is a nucleophilic attack taking place. Oxymercuration-demercuration takes place in the presence of mercuric acetate. There is no formation of carbocation intermediates.
Complete answer:
Oxymercuration-demercuration is a reaction which is used for the synthesis of alcohols.
This reaction takes place according to Markovnikov’s rule which states that reagents would add to the unsymmetrical alkenes in such a way that the negative part of the adding molecule goes to the carbon atom of the double bond which has lesser number of hydrogen atoms.
Oxymercuration-demercuration: Alkenes react with mercuric acetate, \[{{(C{{H}_{3}}COO)}_{2}}Hg\] or \[Hg{{(OAc)}_{2}}\] , to form oxymercuration products which upon reduction with \[NaB{{H}_{4}}\] in basic medium gives alcohols. Thus,
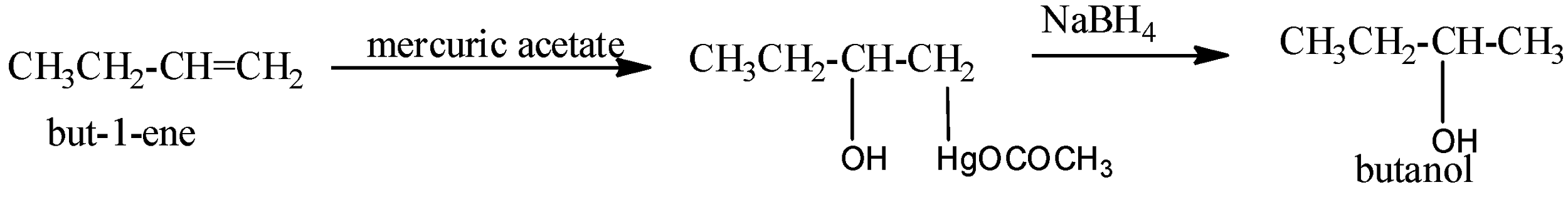
This two-step procedure is called oxymercuration-demercuration or oxymercuration-reduction and gives alcohol corresponding to Markovnikov’s addition of water to alkenes without any rearrangement since carbocation is not the intermediates.
Mechanism: Attack of \[\pi -electrons\] of the double bond of the alkene on mercuric acetate gives an unsymmetrical \[\pi -complex\] (I) with the expulsion of an acetate ion. Nucleophilic attack by \[{{H}_{2}}O\] on the carbon atom of the \[\pi -complex\] carrying the +ve charge gives II which subsequently loses a proton to give the oxymercuration product (III). Another nucleophilic attack on III by hydride ion \[(:{{H}^{-}})\] from \[NaB{{H}_{4}}\] on the carbon atom carrying \[HgOCOC{{H}_{3}}\] group ultimately completes the addition with the expulsion of mercurous acetate.
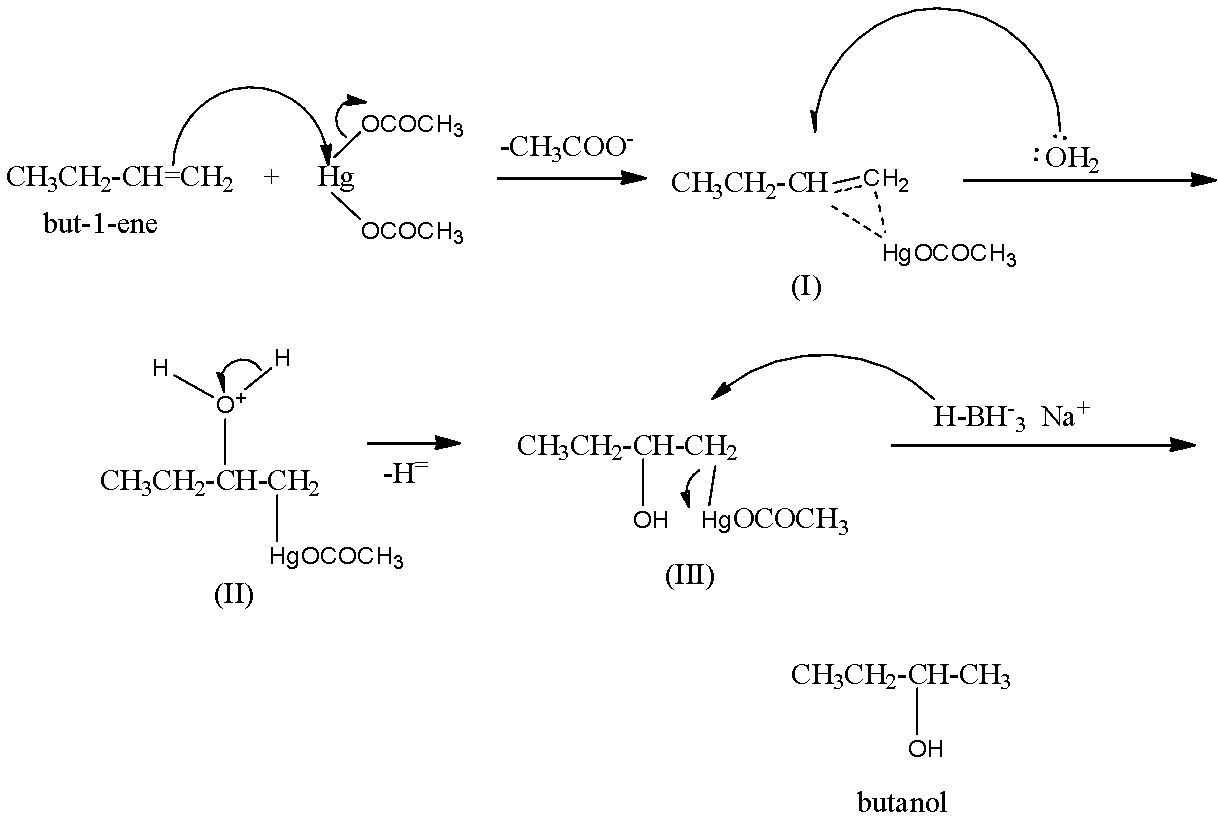
Hence, option (d) is incorrect.
Note: Hydration of alkene occurs through a carbocation intermediate. But hydroboration- oxidation and oxymercuration-reduction do not involve carbocation intermediates and hence always give unexpected or unarranged alcohols.
Complete answer:
Oxymercuration-demercuration is a reaction which is used for the synthesis of alcohols.
This reaction takes place according to Markovnikov’s rule which states that reagents would add to the unsymmetrical alkenes in such a way that the negative part of the adding molecule goes to the carbon atom of the double bond which has lesser number of hydrogen atoms.
Oxymercuration-demercuration: Alkenes react with mercuric acetate, \[{{(C{{H}_{3}}COO)}_{2}}Hg\] or \[Hg{{(OAc)}_{2}}\] , to form oxymercuration products which upon reduction with \[NaB{{H}_{4}}\] in basic medium gives alcohols. Thus,
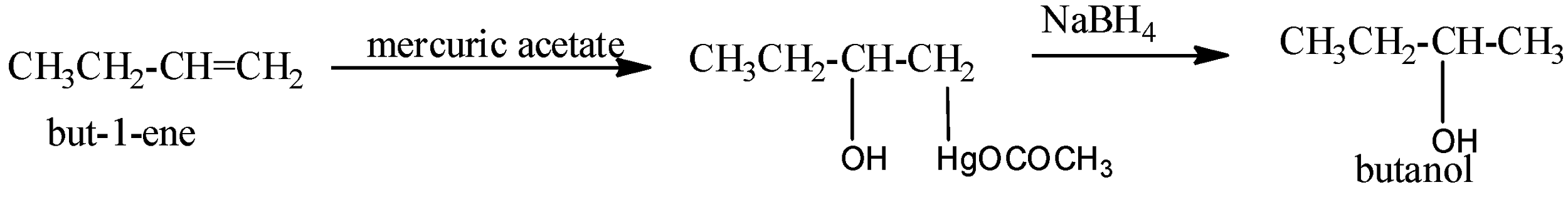
This two-step procedure is called oxymercuration-demercuration or oxymercuration-reduction and gives alcohol corresponding to Markovnikov’s addition of water to alkenes without any rearrangement since carbocation is not the intermediates.
Mechanism: Attack of \[\pi -electrons\] of the double bond of the alkene on mercuric acetate gives an unsymmetrical \[\pi -complex\] (I) with the expulsion of an acetate ion. Nucleophilic attack by \[{{H}_{2}}O\] on the carbon atom of the \[\pi -complex\] carrying the +ve charge gives II which subsequently loses a proton to give the oxymercuration product (III). Another nucleophilic attack on III by hydride ion \[(:{{H}^{-}})\] from \[NaB{{H}_{4}}\] on the carbon atom carrying \[HgOCOC{{H}_{3}}\] group ultimately completes the addition with the expulsion of mercurous acetate.

Hence, option (d) is incorrect.
Note: Hydration of alkene occurs through a carbocation intermediate. But hydroboration- oxidation and oxymercuration-reduction do not involve carbocation intermediates and hence always give unexpected or unarranged alcohols.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




