
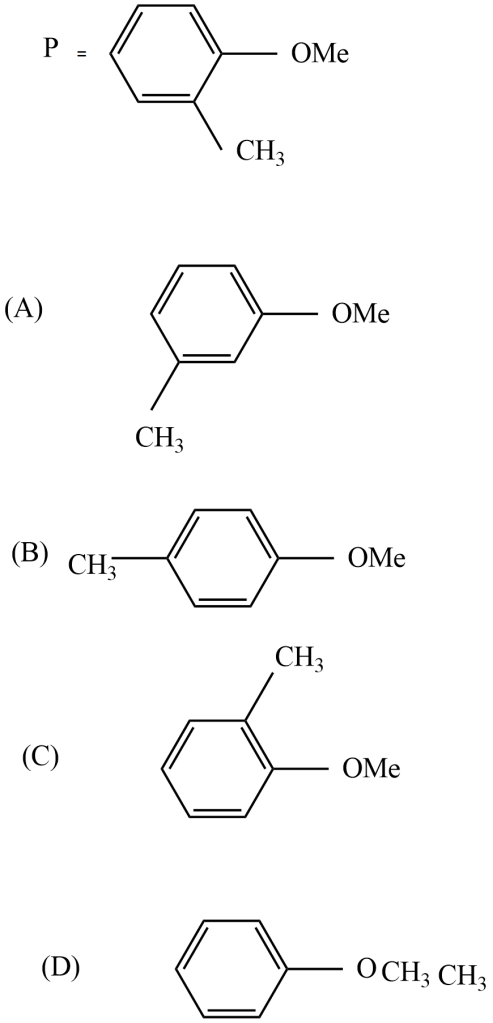
Which is the metamer of compound P?

Answer
589.5k+ views
Hint: Aromatic hydrocarbons show structural isomerism due to the attachment to various functional groups. Metamerism is one of the types of chain isomerism or position isomerism which is observed with the same functional group and different alkyl groups attached to hetero atom or a benzene ring.
Complete step by step solution:
The phenomenon of existence with the same molecule formula of two or more compounds but different properties is known as isomerism and which compounds exhibit this phenomenon is called isomers.
The following flow chart shows different types of isomerism,
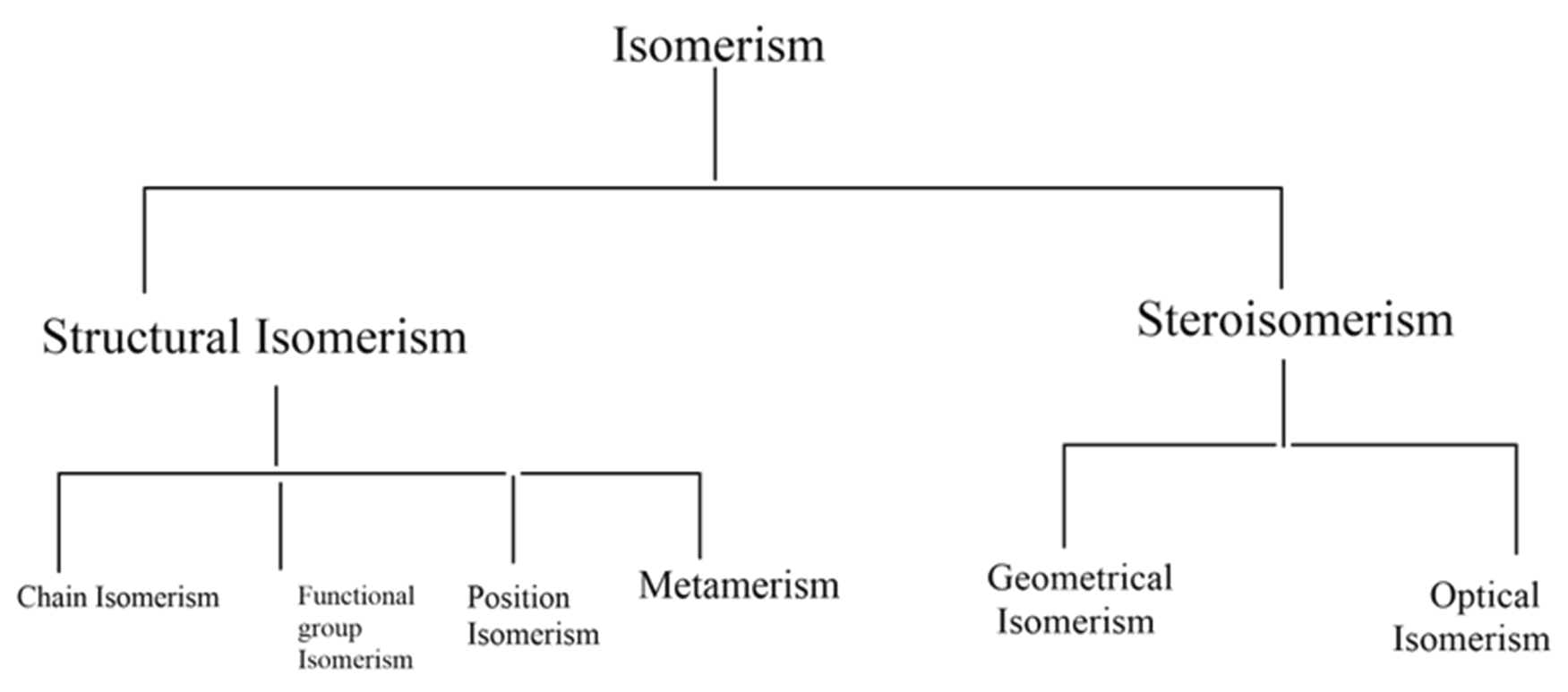
Structural isomerism: compounds with different structures with the same molecular formula are classified as structural isomers. Different types of structural isomerism shown in the flow chart are,
(1) Chain isomerism
(2) Position isomerism
(3) Functional group isomerism
(4) Metamerism
Chain isomerism: when compounds exhibit the same formula with different carbon skeleton are formed this isomerism. Mostly alkenes exhibit this type of isomerism
Position isomerism: when a substituted atom differs in the position in the carbon skeleton exhibits this type of isomerism. When alkenes or alkynes are involved besides reaction, the products show this isomerism.
Functional group isomerism: The compound with different functional groups having the same molecular formula exhibits this type of isomerism. For example, aldehyde, and ketones exhibit this isomerism with the same molecular formula.
Metamerism: this isomerism observed in compounds having the same molecular formula but different alkyl chains on either side of the functional group of the molecule.
The metamer of the given compound ‘P’ is,
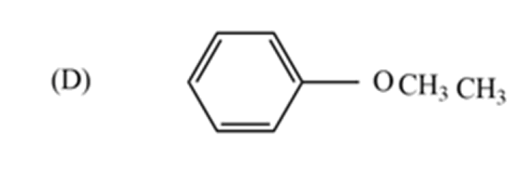
Because all other options are functional group isomers. In option (D), the given compound $-C{{H}_{3}}\ And -OC{{H}_{3}}$ functional groups exhibit metamerism.
Note: Metamerism occurs among the members of the same homologous family. Sometimes metamers are also called position isomers. The compound which exhibits the metamerism having the same molecular weight but the difference in their chemical properties.
Complete step by step solution:
The phenomenon of existence with the same molecule formula of two or more compounds but different properties is known as isomerism and which compounds exhibit this phenomenon is called isomers.
The following flow chart shows different types of isomerism,

Structural isomerism: compounds with different structures with the same molecular formula are classified as structural isomers. Different types of structural isomerism shown in the flow chart are,
(1) Chain isomerism
(2) Position isomerism
(3) Functional group isomerism
(4) Metamerism
Chain isomerism: when compounds exhibit the same formula with different carbon skeleton are formed this isomerism. Mostly alkenes exhibit this type of isomerism
Position isomerism: when a substituted atom differs in the position in the carbon skeleton exhibits this type of isomerism. When alkenes or alkynes are involved besides reaction, the products show this isomerism.
Functional group isomerism: The compound with different functional groups having the same molecular formula exhibits this type of isomerism. For example, aldehyde, and ketones exhibit this isomerism with the same molecular formula.
Metamerism: this isomerism observed in compounds having the same molecular formula but different alkyl chains on either side of the functional group of the molecule.
The metamer of the given compound ‘P’ is,

Because all other options are functional group isomers. In option (D), the given compound $-C{{H}_{3}}\ And -OC{{H}_{3}}$ functional groups exhibit metamerism.
Note: Metamerism occurs among the members of the same homologous family. Sometimes metamers are also called position isomers. The compound which exhibits the metamerism having the same molecular weight but the difference in their chemical properties.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Chemistry: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Draw a diagram of nephron and explain its structur class 11 biology CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

Chemical formula of Bleaching powder is A Ca2OCl2 B class 11 chemistry CBSE

Name the part of the brain responsible for the precision class 11 biology CBSE

The growth of tendril in pea plants is due to AEffect class 11 biology CBSE

One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE




