
Which is the correct statement about ${{\sigma }}$- and ${{\pi }}$-molecular orbitals? Statements are
(i) ${{\pi }}$-bonding orbitals are ungerade
(ii) ${{\pi }}$-antibonding orbitals are ungerade
(iii) ${{\sigma }}$-antibonding orbitals are gerade
(A) (i) only
(B) (ii) and (iii) only
(C) (iii) only
(D) (ii) only
Answer
573.6k+ views
Hint: To solve this we will consider the molecular orbital theory (MOT). MOT describes structure and properties of different molecules. MOT explains about the single bond and double bond in the resonating structure of molecules.
Complete Step by step answer: We can determine the symmetry of a molecule by rotating the molecule through the center of symmetry.
If we invert a molecule through the center of symmetry and the sign of the molecular orbital does not change then the molecular orbital is said to be gerade. It is denoted by g.
If we invert a molecule through the center of symmetry and the sign of the molecular orbital changes then the molecular orbital is said to be ungerade. It is denoted by u.
We know that the ${{\pi }}$-bonding orbitals are formed by the constructive interference of two electron waves of atomic orbitals. The formation of ${{\pi }}$-bonding orbitals is as follows:
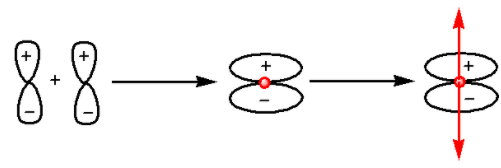
In the given diagram, above the point there is a positive wave function and below the point there is a negative wave function. Thus, there is no center of symmetry. Thus, ${{\pi }}$-bonding orbitals are ungerade.
We know that the ${{\pi }}$-antibonding orbitals are formed by the destructive interference of two electron waves of atomic orbitals. The formation of ${{\pi }}$- antibonding orbitals is as follows:
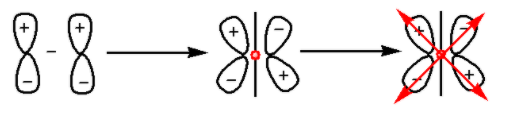
In the given diagram, there is a center of symmetry. Thus, ${{\pi }}$-antibonding orbitals are gerade.
We know that the ${{\sigma }}$-antibonding orbitals are formed by the destructive interference of head on overlapping atomic orbitals. The formation of ${{\sigma }}$-antibonding orbitals is as follows:
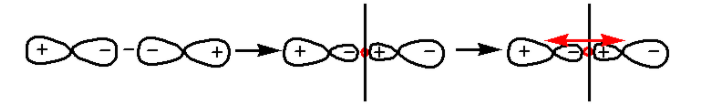
In the given diagram, there is no center of symmetry. Thus, ${{\sigma }}$-antibonding orbitals are ungerade.
Thus, the statement ‘${{\pi }}$-bonding orbitals are ungerade’ is correct.
Thus, the correct option is (A) (i) only.
Note: We know that the molecule has covalent bonds there are sigma bonds and pi bonds. The sigma bonds are represented by ${{\sigma }}$ and the pi bonds are represented by ${{\pi }}$. The bond formed between two atoms by the axial overlap of the atomic orbitals along the intermolecular axis is known as the sigma bond.
The bond formed by the lateral overlap of the atomic orbitals at right angles to the intermolecular axis is known as the pi bond.
Complete Step by step answer: We can determine the symmetry of a molecule by rotating the molecule through the center of symmetry.
If we invert a molecule through the center of symmetry and the sign of the molecular orbital does not change then the molecular orbital is said to be gerade. It is denoted by g.
If we invert a molecule through the center of symmetry and the sign of the molecular orbital changes then the molecular orbital is said to be ungerade. It is denoted by u.
We know that the ${{\pi }}$-bonding orbitals are formed by the constructive interference of two electron waves of atomic orbitals. The formation of ${{\pi }}$-bonding orbitals is as follows:

In the given diagram, above the point there is a positive wave function and below the point there is a negative wave function. Thus, there is no center of symmetry. Thus, ${{\pi }}$-bonding orbitals are ungerade.
We know that the ${{\pi }}$-antibonding orbitals are formed by the destructive interference of two electron waves of atomic orbitals. The formation of ${{\pi }}$- antibonding orbitals is as follows:

In the given diagram, there is a center of symmetry. Thus, ${{\pi }}$-antibonding orbitals are gerade.
We know that the ${{\sigma }}$-antibonding orbitals are formed by the destructive interference of head on overlapping atomic orbitals. The formation of ${{\sigma }}$-antibonding orbitals is as follows:

In the given diagram, there is no center of symmetry. Thus, ${{\sigma }}$-antibonding orbitals are ungerade.
Thus, the statement ‘${{\pi }}$-bonding orbitals are ungerade’ is correct.
Thus, the correct option is (A) (i) only.
Note: We know that the molecule has covalent bonds there are sigma bonds and pi bonds. The sigma bonds are represented by ${{\sigma }}$ and the pi bonds are represented by ${{\pi }}$. The bond formed between two atoms by the axial overlap of the atomic orbitals along the intermolecular axis is known as the sigma bond.
The bond formed by the lateral overlap of the atomic orbitals at right angles to the intermolecular axis is known as the pi bond.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




