
Which is meant by electric current? Name and define S.I unit. In a conductor if electrons are flowing from $ \text{B} $ to $ \text{A} $ . What is the direction of conventional current? Give justification of your answer.
Answer
554.1k+ views
Hint: The net flow of charge in a direction through a metallic wire constitutes an electric current. The branch of physics which deals with study of charge in motion is called current electricity. Discuss the electric currents in conductors (solid conductor and liquid conductor. Conventional current and electric current can be easily understood by this.
Complete step by step solution
Electric Current: The flow of charge in a definite direction constitutes the electric current and time rate of flow of charge through any cross-section of conductor is measure of current.
$ \text{Electric current = }\dfrac{\text{Total charge flown}}{\text{Time taken}}=\dfrac{q}{t} $
In a solid conductor, $ n $ number of free electrons each of charge moves towards the positive end of conductor at time $ t $ , when net charge flown,
$ q=ne $
$ I=\dfrac{q}{t}=\dfrac{ne}{t} $
If $ q $ is positive, then direction of current is forward
If $ q $ is negative, then direction of current is negative
Sometimes charges flowing normally through an area may not be steady but varying with time, we can define:
The triangle $ \Delta Q $ is the net amount of charge flowing normally across a cross-section of conductor in a particular interval from $ t+\Delta t $ .
Then at time $ t $ ,
$ I=\underset{\Delta t\to 0}{\mathop{\lim }}\,\dfrac{\Delta Q}{\Delta t}=\dfrac{dQ}{dt} $
It means, current through a conductor at a time is dependent as first derivative of charge with respect of charge with respect to time passing through a cross-section of the conductor in a particular direction.
Unit of Electric current:
S.I unit of current is Ampere; It is also a practical unit of current.
$ 1\text{ ampere}\left( \text{A} \right)=\dfrac{1\text{ Coulomb}}{1\text{ Second}}=1\text{C}{{\text{s}}^{-1}} $
Thus, the current through a wire is said to be 1 ampere, if one coulomb of charge is flowing per second through any section of wire.
Direction of Electric Current: We have a conductor AB which is connected to battery/cell.
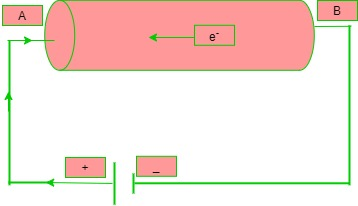
The direction of flow of positive charge gives the direction of current. This is called conventional current.
The direction of flow of electrons gives the direction of electric current.
The direction of electric current is opposite to that of conventional current. End A of the conductor is connected to the positive terminal of the cell, the electrons will be flowing through the conductor from B to A. The direction of electric current will be from B to A. Hence, direction of conventional current is from A to B.
Note
The current is scalar quantity, not a vector quantity.
Through a cross-section of conductor in a time t, if the total charge $ {{q}_{2}} $ is flowing from B to A. Then, total current through a conductor is,
The currents in our nerves are in microampere $ \left( \mu \text{A} \right) $ .
Complete step by step solution
Electric Current: The flow of charge in a definite direction constitutes the electric current and time rate of flow of charge through any cross-section of conductor is measure of current.
$ \text{Electric current = }\dfrac{\text{Total charge flown}}{\text{Time taken}}=\dfrac{q}{t} $
In a solid conductor, $ n $ number of free electrons each of charge moves towards the positive end of conductor at time $ t $ , when net charge flown,
$ q=ne $
$ I=\dfrac{q}{t}=\dfrac{ne}{t} $
If $ q $ is positive, then direction of current is forward
If $ q $ is negative, then direction of current is negative
Sometimes charges flowing normally through an area may not be steady but varying with time, we can define:
The triangle $ \Delta Q $ is the net amount of charge flowing normally across a cross-section of conductor in a particular interval from $ t+\Delta t $ .
Then at time $ t $ ,
$ I=\underset{\Delta t\to 0}{\mathop{\lim }}\,\dfrac{\Delta Q}{\Delta t}=\dfrac{dQ}{dt} $
It means, current through a conductor at a time is dependent as first derivative of charge with respect of charge with respect to time passing through a cross-section of the conductor in a particular direction.
Unit of Electric current:
S.I unit of current is Ampere; It is also a practical unit of current.
$ 1\text{ ampere}\left( \text{A} \right)=\dfrac{1\text{ Coulomb}}{1\text{ Second}}=1\text{C}{{\text{s}}^{-1}} $
Thus, the current through a wire is said to be 1 ampere, if one coulomb of charge is flowing per second through any section of wire.
Direction of Electric Current: We have a conductor AB which is connected to battery/cell.

The direction of flow of positive charge gives the direction of current. This is called conventional current.
The direction of flow of electrons gives the direction of electric current.
The direction of electric current is opposite to that of conventional current. End A of the conductor is connected to the positive terminal of the cell, the electrons will be flowing through the conductor from B to A. The direction of electric current will be from B to A. Hence, direction of conventional current is from A to B.
Note
The current is scalar quantity, not a vector quantity.
Through a cross-section of conductor in a time t, if the total charge $ {{q}_{2}} $ is flowing from B to A. Then, total current through a conductor is,
The currents in our nerves are in microampere $ \left( \mu \text{A} \right) $ .
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




