
Which indicator produces a pink colour in an alkaline solution?
(A) Methyl orange
(B) Turmeric paper
(C) Phenolphthalein
(D) Litmus paper
Answer
582.9k+ views
Hint: The indicator shows the change in colour as the acidic condition changes to basic. This leads to neutralization of the proton (from the indicator) and leaving behind the anion part, which absorbs the visible light.
Complete step by step solution:
The indicators are often used in the acid-base titration as their colour varies with the change in the pH of the solution. Thus, indicating the endpoints of the acid or base in the solution.
One of the indicators which produce a pink colour in the alkaline solution is the Phenolphthalein indicator. It is colourless in acidic medium, but on adding base it changes to dark pink colour. Hence, used in acid-base titrations.
This happens because phenolphthalein $(HIn)$ being a weak acid, it dissociates partially on dissolving in the water giving ${{H}^{+}}$ ions and anion $I{{n}^{-}}$, with the colour change from colourless to pink.
$HIn(aq)+{{H}_{2}}O(l)\rightleftharpoons I{{n}^{-}}(aq)+{{H}_{3}}{{O}^{+}}(aq)$
But when the base is added to this solution, these protons are neutralised by it, thus shifting the equilibrium towards the right side, due to which more anions are formed in the solution and it becomes visibly pink.
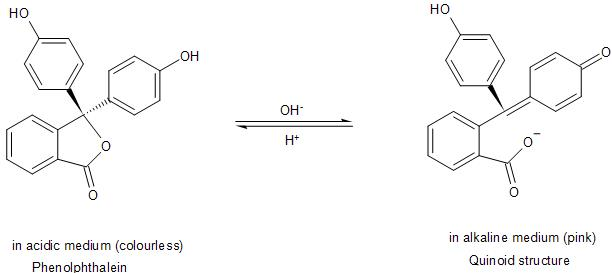
The anion is stabilised through resonance to form the quinoid structure. Thus, it is due to this quinoid structure formed by the breaking of a C-O bond, after the dissociation of the proton, that the Phenolphthalein shows pink colour.
Hence, answer is option (C).
Note: In the alkaline solution, the methyl orange indicator shows a yellow colour; the turmeric paper shows a red colour and the red litmus changes to blue. For the equilibrium, Le Chatelier’s principle is followed and the pink colour can be seen because the quinoid structure formed absorbs the visible light.
Complete step by step solution:
The indicators are often used in the acid-base titration as their colour varies with the change in the pH of the solution. Thus, indicating the endpoints of the acid or base in the solution.
One of the indicators which produce a pink colour in the alkaline solution is the Phenolphthalein indicator. It is colourless in acidic medium, but on adding base it changes to dark pink colour. Hence, used in acid-base titrations.
This happens because phenolphthalein $(HIn)$ being a weak acid, it dissociates partially on dissolving in the water giving ${{H}^{+}}$ ions and anion $I{{n}^{-}}$, with the colour change from colourless to pink.
$HIn(aq)+{{H}_{2}}O(l)\rightleftharpoons I{{n}^{-}}(aq)+{{H}_{3}}{{O}^{+}}(aq)$
But when the base is added to this solution, these protons are neutralised by it, thus shifting the equilibrium towards the right side, due to which more anions are formed in the solution and it becomes visibly pink.

The anion is stabilised through resonance to form the quinoid structure. Thus, it is due to this quinoid structure formed by the breaking of a C-O bond, after the dissociation of the proton, that the Phenolphthalein shows pink colour.
Hence, answer is option (C).
Note: In the alkaline solution, the methyl orange indicator shows a yellow colour; the turmeric paper shows a red colour and the red litmus changes to blue. For the equilibrium, Le Chatelier’s principle is followed and the pink colour can be seen because the quinoid structure formed absorbs the visible light.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




