
Which glycosidic linkage is present in maltose?
A. $\alpha $ -D – (+) - Glucose (${{C}_{1}}$ ) – O – (${{C}_{2}}$ ) - $\beta $ - D- (-) – glucose
B. $\beta $ -D – (+) - Glucose (${{C}_{1}}$ ) – O – (${{C}_{4}}$ ) - D- (+) – glucose
C. $\alpha $ -D – (+) - Glucose (${{C}_{1}}$ ) – O – (${{C}_{4}}$ ) - D- (+) – glucose
D. $\beta $ -D – (+) - Glucose (${{C}_{1}}$ ) – O – (${{C}_{4}}$) - D- (-) – glucose
Answer
531.9k+ views
Hint: The linkage which is going to join one carbohydrate with the other is called glycosidic linkage. Glycosidic bond or glycosidic linkage both are the same and it is one type of covalent bond which is present in molecules like carbohydrates.
Complete answer:
- In the question it is asked which glycosidic linkage is present in maltose.
- First we should know the structure of the maltose to find the type of glycosidic linkage which is present in it.
- We know that the structure of maltose contains two glucose units and the structure is as follows.
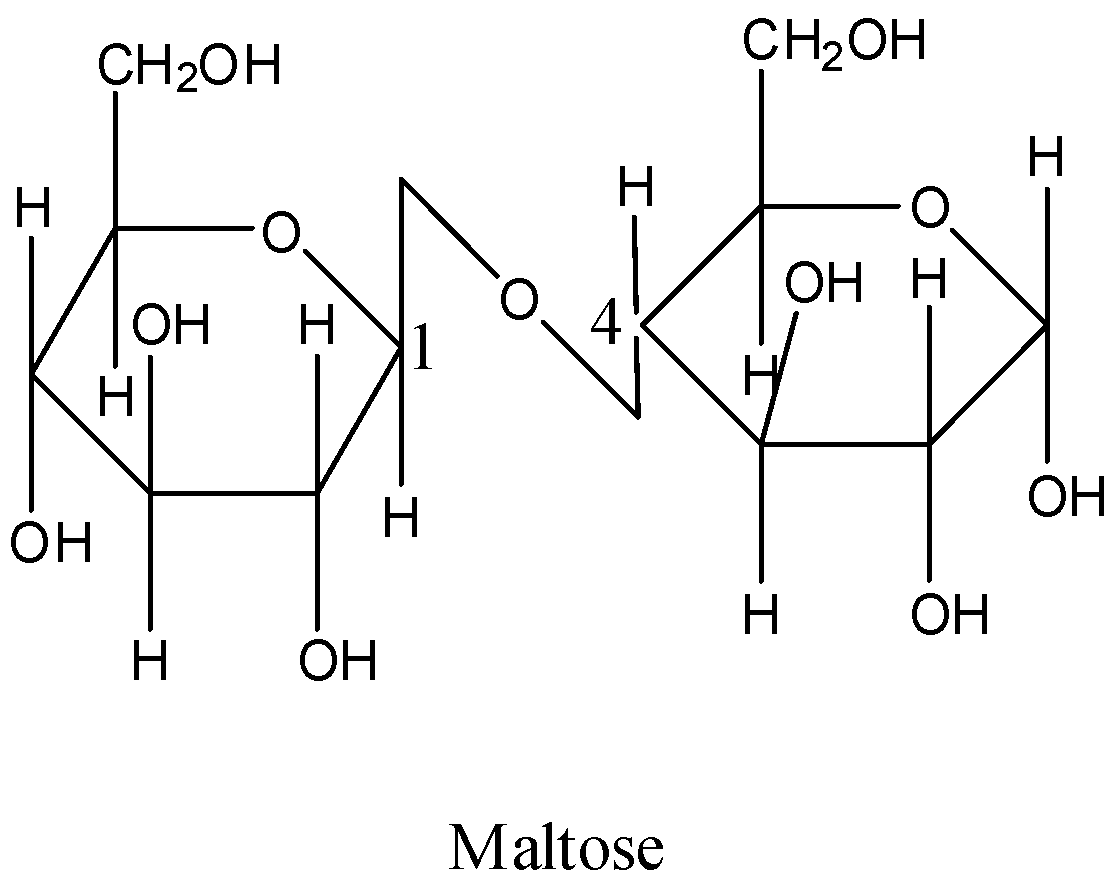
- In the structure of maltose we can see that there are two glucose units.
- The carbon one of the first glucose unit linked to carbon 4 of another glucose unit.
- Therefore the linkage between the two glucose units in maltose $\alpha $ -D – (+) - Glucose (${{C}_{1}}$ ) – O – (${{C}_{4}}$ ) - D- (+) – glucose.
So, the correct option is C.
Note:
The glycosidic covalent linkage is going to hold the two glucose units together and form a stable carbohydrate called maltose. Maltose carbohydrate is an example for disaccharide containing two glucose monosaccharides in its structure.
Complete answer:
- In the question it is asked which glycosidic linkage is present in maltose.
- First we should know the structure of the maltose to find the type of glycosidic linkage which is present in it.
- We know that the structure of maltose contains two glucose units and the structure is as follows.

- In the structure of maltose we can see that there are two glucose units.
- The carbon one of the first glucose unit linked to carbon 4 of another glucose unit.
- Therefore the linkage between the two glucose units in maltose $\alpha $ -D – (+) - Glucose (${{C}_{1}}$ ) – O – (${{C}_{4}}$ ) - D- (+) – glucose.
So, the correct option is C.
Note:
The glycosidic covalent linkage is going to hold the two glucose units together and form a stable carbohydrate called maltose. Maltose carbohydrate is an example for disaccharide containing two glucose monosaccharides in its structure.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

What is a transformer Explain the principle construction class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE




