
Which is the correct genotypic ratio of mendel dihybrid cross among 1:2:1:2:4:2:1:2:1 and 1:2:2:4:1:2:1:2:1?
Answer
488.1k+ views
Hint: A dihybrid cross is a cross between two individuals who differ in two features controlled by two separate genes. If both parents are homozygous for both genes, the offspring of the F1 generation will be uniformly heterozygous for both genes and will have the dominant phenotype for both qualities.
Complete answer:
The phenotypic ratio of Mendel's dihybrids is 9:3:3:1.
Let us explain using the pea plant as an example. A pea plant with yellow coloured cotyledons and spherical seeds is crossed with a pea plant with green coloured cotyledons and wrinkled seeds.
The hue yellow (Y) dominates the green colour of cotyledons (y). Seeds with a round shape (R) have an advantage over wrinkled seeds (r). Yellow coloured cotyledons and spherical seeds will be found on all F1 generation plants.
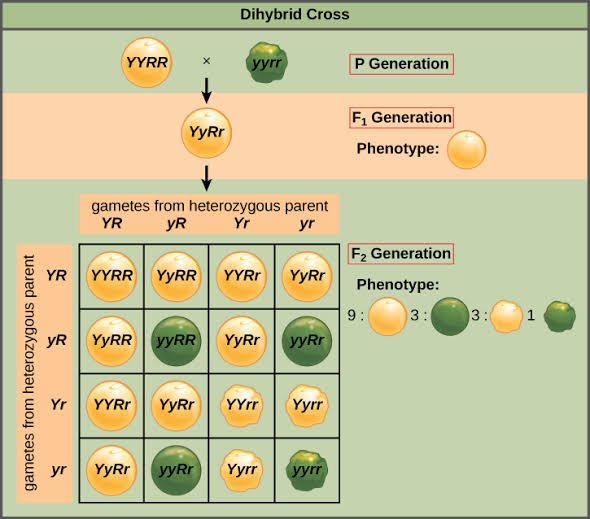
We obtain F2 generation by enabling pollination of F1 generation plants. In the F2 generation, the offspring will be yellow round: yellow wrinkled: green round: green wrinkled in a 9:3:3:1 ratio.
Plants of yellow round peas (9) will have four genotypes: YYRR, YYRr, Yy RR, and YyRr.
Yellow wrinkly will have two genotypes: YYrr and Yyrr. There will be two genotypes in the green round: yyRR and yyRr. Only one genotype will be found in green wrinkled : yyrr.
As a result, the genotypic ratio of F2 dihybrids will be 1:2:2:4:1:2:1:2:1:2
Note:
When Mendel constructed this hybrid, he already knew the dominant relationship between alleles for each trait. The dihybrid cross was used to see if there was any association between distinct allelic pairs. Through a test cross, genotypes can be used to determine the phenotypes of an organism's progeny and, as a result, the phenotypic ratio. If a red bug and a blue bug mate, their offspring may be red, blue, or purple in colour (a mixture of both colors).
Complete answer:
The phenotypic ratio of Mendel's dihybrids is 9:3:3:1.
Let us explain using the pea plant as an example. A pea plant with yellow coloured cotyledons and spherical seeds is crossed with a pea plant with green coloured cotyledons and wrinkled seeds.
The hue yellow (Y) dominates the green colour of cotyledons (y). Seeds with a round shape (R) have an advantage over wrinkled seeds (r). Yellow coloured cotyledons and spherical seeds will be found on all F1 generation plants.

We obtain F2 generation by enabling pollination of F1 generation plants. In the F2 generation, the offspring will be yellow round: yellow wrinkled: green round: green wrinkled in a 9:3:3:1 ratio.
Plants of yellow round peas (9) will have four genotypes: YYRR, YYRr, Yy RR, and YyRr.
Yellow wrinkly will have two genotypes: YYrr and Yyrr. There will be two genotypes in the green round: yyRR and yyRr. Only one genotype will be found in green wrinkled : yyrr.
As a result, the genotypic ratio of F2 dihybrids will be 1:2:2:4:1:2:1:2:1:2
Note:
When Mendel constructed this hybrid, he already knew the dominant relationship between alleles for each trait. The dihybrid cross was used to see if there was any association between distinct allelic pairs. Through a test cross, genotypes can be used to determine the phenotypes of an organism's progeny and, as a result, the phenotypic ratio. If a red bug and a blue bug mate, their offspring may be red, blue, or purple in colour (a mixture of both colors).
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

Draw ray diagrams each showing i myopic eye and ii class 12 physics CBSE

Giving reasons state the signs positive or negative class 12 physics CBSE

Explain esterification reaction with the help of a class 12 chemistry CBSE

What is defined as a solenoid Depict a diagram with class 12 physics CBSE




