
2-Bromopentane is treated with an alcoholic KOH solution. What will be the major product formed in this reaction and what is this type of elimination called?
(A.) Pent-1-ene, $\beta$- Elimination
(B.) Pent-2-ene, $\beta$- Elimination
(C.) Pent-1-ene, Nucleophilic substitution
(D.) Pent-2-ene, Nucleophilic substitution
Answer
601.2k+ views
Hint: First, you have to the structure of 2-Bromopentane. This compound reacting with alcoholic KOH solution gives dehydrohalogenation products. Now try to find the correct answer to this question.
Complete step by step solution:
Let’s find the correct answer to this question -
First, we will draw the structure of 2-Bromopentane.
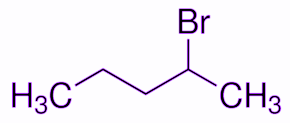
As given in the question this 2-Bromopentane reacts with alcoholic KOH. The products will be formed according to the dehydrohalogenation reaction. In the structure below we have assigned the position of halogen and nearby carbon atoms by greek letters. Since hydrogen will be removed from $\beta$ the position, this reaction is known as $\beta$-dehydrohalogenation.
Now, there are two $\beta$ positions in this molecule, so we have to remove the hydrogen where alkene (the final product) formed is stable.
According to Saytzeff’s rule "In dehydrohalogenation reactions, the preferred product is that alkene which has the greater number of alkyl groups attached to the doubly bonded carbon atoms."
So, hydrogen atoms from internal carbon will be removed and Pent-2-ene will be formed as a major product (also known as Saytzeff's Product).
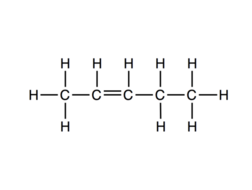
As we already know The process is known as $\beta$− elimination as it involves the elimination of $\beta$− Hydrogen.
Therefore, we can conclude that the correct answer to this question is option B.
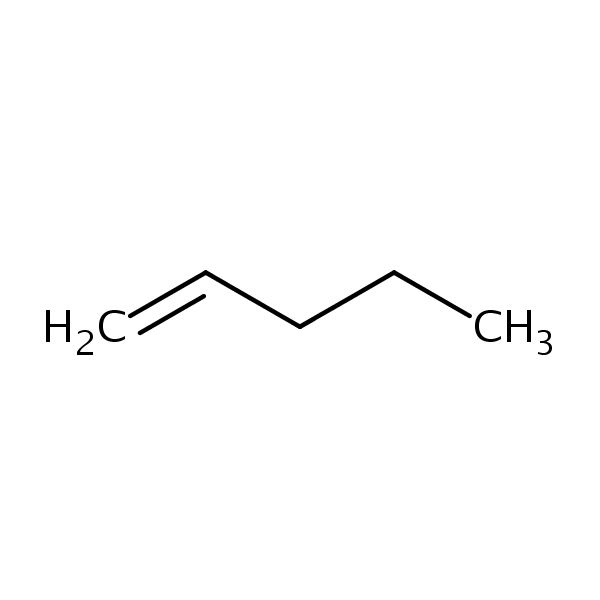
Note: We should also know that, If the product containing the less highly substituted pi bond is major. This is known as Hoffmann alkene. For example, pent-1-ene is Hoffman product (but it is not major)
Complete step by step solution:
Let’s find the correct answer to this question -
First, we will draw the structure of 2-Bromopentane.

As given in the question this 2-Bromopentane reacts with alcoholic KOH. The products will be formed according to the dehydrohalogenation reaction. In the structure below we have assigned the position of halogen and nearby carbon atoms by greek letters. Since hydrogen will be removed from $\beta$ the position, this reaction is known as $\beta$-dehydrohalogenation.
Now, there are two $\beta$ positions in this molecule, so we have to remove the hydrogen where alkene (the final product) formed is stable.
According to Saytzeff’s rule "In dehydrohalogenation reactions, the preferred product is that alkene which has the greater number of alkyl groups attached to the doubly bonded carbon atoms."
So, hydrogen atoms from internal carbon will be removed and Pent-2-ene will be formed as a major product (also known as Saytzeff's Product).

As we already know The process is known as $\beta$− elimination as it involves the elimination of $\beta$− Hydrogen.
Therefore, we can conclude that the correct answer to this question is option B.
Note: We should also know that, If the product containing the less highly substituted pi bond is major. This is known as Hoffmann alkene. For example, pent-1-ene is Hoffman product (but it is not major)

Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

How is the angle of emergence e related to the angle class 12 physics CBSE

Differentiate between lanthanoids and actinoids class 12 chemistry CBSE

Derive Lens Makers formula for a convex lens class 12 physics CBSE

a Draw Labelled diagram of Standard Hydrogen Electrode class 12 chemistry CBSE




