
Which are position isomers?
(A)
(B)
(C)
(D)




Answer
584.7k+ views
Hint: Position isomers are structural isomers with the same number of atoms and different spatial arrangement of atoms. Changes in the functional group do not come under position isomers.
Complete step by step answer:
Isomers are molecules with identical molecular formulas, that is, they have the same number of atoms of each element, but distinct arrangements of atoms in space. Isomerism is the existence or possibility of isomers. Isomers do not necessarily share similar chemical or physical properties.
Position isomers are based on the movement of a functional group in the molecule. These are constitutional isomers that have the same carbon skeleton and the same functional groups but differ from each other in the location of the functional groups on or in the carbon chain.
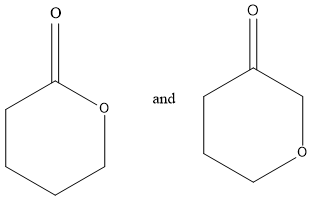
Considering option (A),
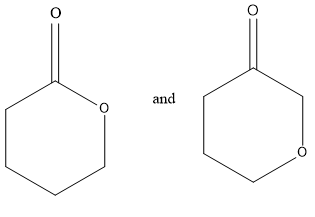
In this, first compounds have ester functional groups and other compounds have ether and ketone functional groups present. Therefore, these are functional group isomers.
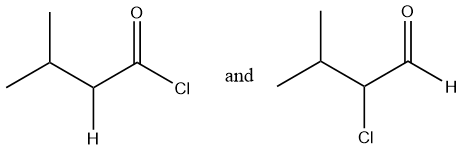
Considering option (B),
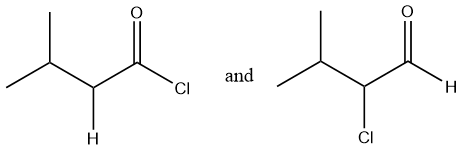
In this option, the first compound has an acyl chloride functional group and the second compound has an aldehyde functional group. Therefore, these are functional group isomers.
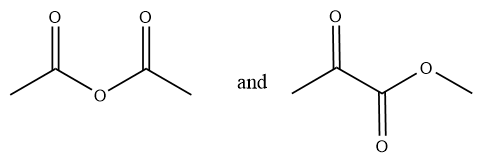
Considering option (C),

In this option, the first compound has anhydride functional group and the second compound has ketone and ester functional group. Therefore, these are functional group isomers.
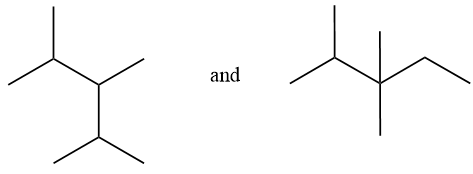
Considering option (D),
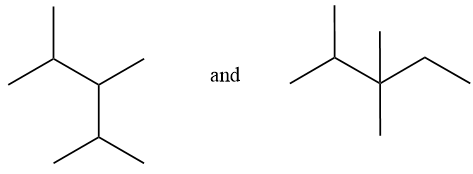
In this option, the first compound has substitution on 2,3,4 carbon numbers with 5 carbon chain length. And in the second compound, substitution is on 2 and 3 carbon atoms with 6 carbon chain length. Therefore, these are positional isomers.
So, the correct answer is “Option D”.
Note: There are different types of isomers. Two broad categories of isomers are – Structural isomers and Stereoisomers. Types of structural isomers are Chain isomers, position isomers, Functional isomers. Stereoisomers are of two types – Geometric isomers, optical isomers.
Complete step by step answer:
Isomers are molecules with identical molecular formulas, that is, they have the same number of atoms of each element, but distinct arrangements of atoms in space. Isomerism is the existence or possibility of isomers. Isomers do not necessarily share similar chemical or physical properties.
Position isomers are based on the movement of a functional group in the molecule. These are constitutional isomers that have the same carbon skeleton and the same functional groups but differ from each other in the location of the functional groups on or in the carbon chain.
Considering option (A),

In this, first compounds have ester functional groups and other compounds have ether and ketone functional groups present. Therefore, these are functional group isomers.
Considering option (B),

In this option, the first compound has an acyl chloride functional group and the second compound has an aldehyde functional group. Therefore, these are functional group isomers.
Considering option (C),

In this option, the first compound has anhydride functional group and the second compound has ketone and ester functional group. Therefore, these are functional group isomers.
Considering option (D),

In this option, the first compound has substitution on 2,3,4 carbon numbers with 5 carbon chain length. And in the second compound, substitution is on 2 and 3 carbon atoms with 6 carbon chain length. Therefore, these are positional isomers.
So, the correct answer is “Option D”.
Note: There are different types of isomers. Two broad categories of isomers are – Structural isomers and Stereoisomers. Types of structural isomers are Chain isomers, position isomers, Functional isomers. Stereoisomers are of two types – Geometric isomers, optical isomers.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




