
Which among the following are the correct statements?
Statement 1: Ethylamine is soluble in water, whereas aniline is not.
Statement 2: Ethylamine forms hydrogen bonds with water molecules.
a.) Assertion is correct, reason is incorrect.
b.) Assertion is incorrect, reason is correct.
c.) Both assertion and reason are correct, reason is correct for assertion.
d.) Both assertion and reason are correct but reason is not correct for assertion.
Answer
587.7k+ views
Hint: Lower aliphatic amines are soluble in water because they can form hydrogen bonds with water molecules. Aniline has a presence in the benzene group. Benzene group is hydrophobic. Solubility is dependent on formation of hydrogen bonds. When small alkyl groups like methyl are present, there is no steric hindrance in formation of hydrogen bonds.
Complete step by step answer:
-Intermolecular forces are forces of attraction and repulsion between neighboring molecules.
-Hydrogen bond is a type of intermolecular force. It exists in molecules in which highly polar bonds such as N-H, O-H, H-F are present.
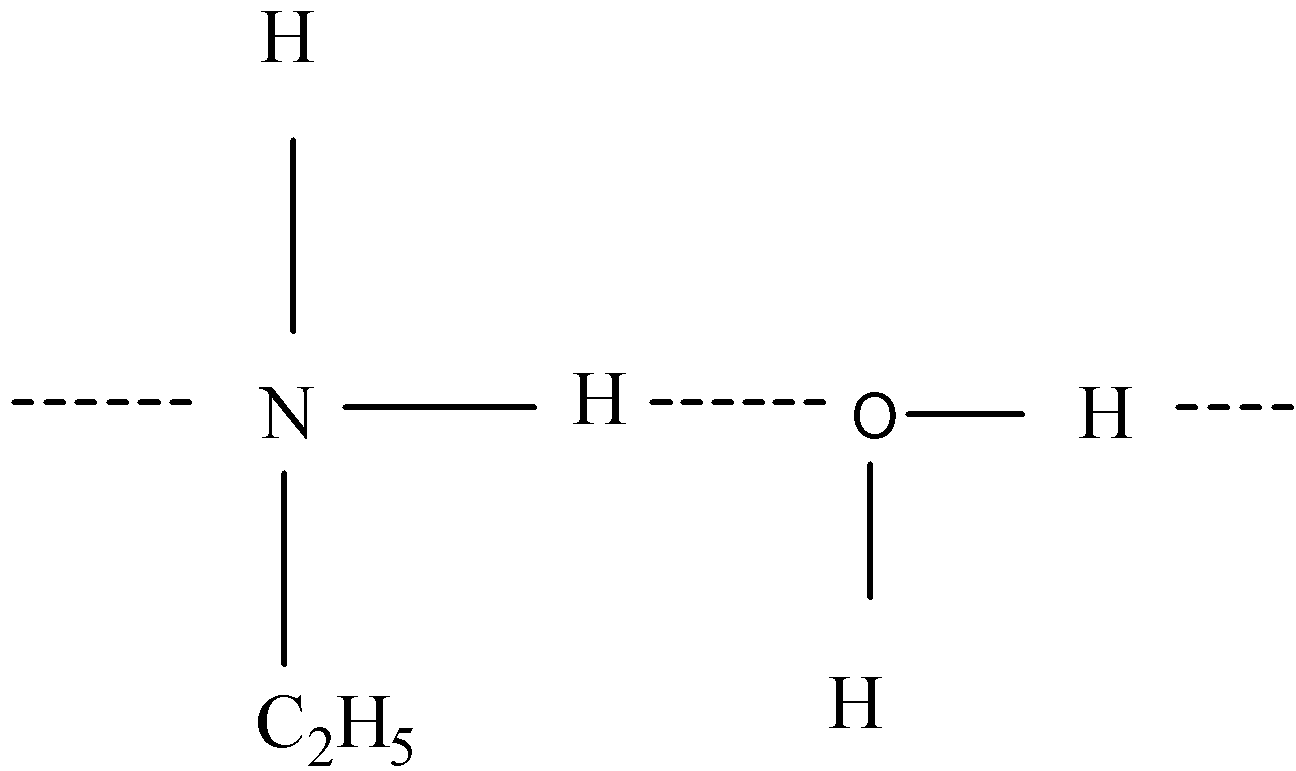
-Strength of hydrogen bond is determined by interaction between lone pairs of electronegative atoms and hydrogen atoms.
-In primary amines, intermolecular associations are more as there are two hydrogen atoms available for hydrogen bonds.
-Steric hindrance plays an important role in formation of hydrogen bonds. When small alkyl groups like methyl are present, there is no steric hindrance in formation of hydrogen bonds. In case of a bigger alkyl group like ethyl, there will be steric hindrance to hydrogen bonding.
-As in ethylamine, there is no steric hindrance, it can form hydrogen bonds with water molecules and is soluble in water. In Aniline, a hydrophobic group like benzene is present so it is moderately soluble in water.
So, the correct answer is “Option C”.
Note: primary and secondary amines are involved in intermolecular association due to hydrogen bond. In secondary amines, there are hydrogen atoms available for hydrogen bonds. In tertiary amine, no hydrogen atom is available for hydrogen bonds so there is no intermolecular association.
Complete step by step answer:
-Intermolecular forces are forces of attraction and repulsion between neighboring molecules.
-Hydrogen bond is a type of intermolecular force. It exists in molecules in which highly polar bonds such as N-H, O-H, H-F are present.

-Strength of hydrogen bond is determined by interaction between lone pairs of electronegative atoms and hydrogen atoms.
-In primary amines, intermolecular associations are more as there are two hydrogen atoms available for hydrogen bonds.
-Steric hindrance plays an important role in formation of hydrogen bonds. When small alkyl groups like methyl are present, there is no steric hindrance in formation of hydrogen bonds. In case of a bigger alkyl group like ethyl, there will be steric hindrance to hydrogen bonding.
-As in ethylamine, there is no steric hindrance, it can form hydrogen bonds with water molecules and is soluble in water. In Aniline, a hydrophobic group like benzene is present so it is moderately soluble in water.
So, the correct answer is “Option C”.
Note: primary and secondary amines are involved in intermolecular association due to hydrogen bond. In secondary amines, there are hydrogen atoms available for hydrogen bonds. In tertiary amine, no hydrogen atom is available for hydrogen bonds so there is no intermolecular association.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




