
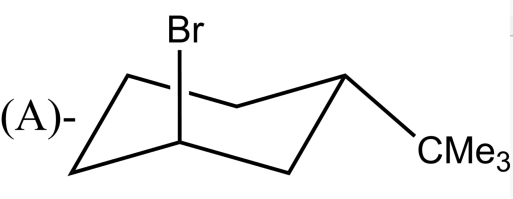
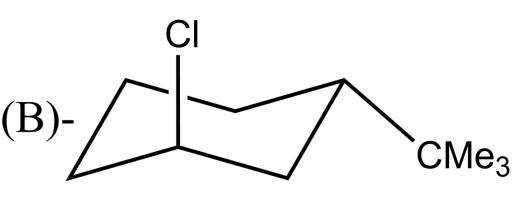
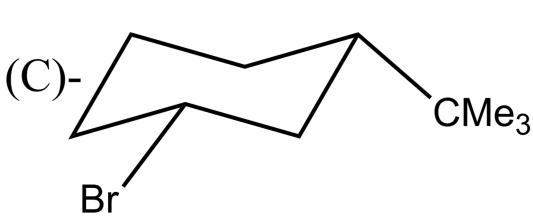
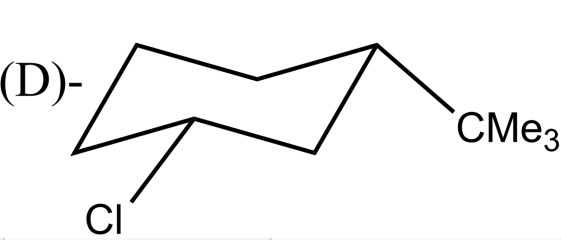
Which alkyl halide undergoes ${{E}_{2}}$ elimination?




Answer
591.9k+ views
Hint: ${{E}_{2}}$ reactions are a single step concerted reaction in which there is one transition state. ${{E}_{2}}$ reactions are seen typically with secondary and tertiary alkyl halides, but in the case of primary halide, there is a necessity of a hindered base.
Complete answer:
-${{E}_{2}}$ reactions, in order to proceed, must follow the following requirements-
(i) Secondary and tertiary alkyl halides will undergo ${{E}_{2}}$ reactions in the presence of a base like OH-, RO-, ${{R}_{2}}N-$ .
(ii) Both leaving groups must be present on the same plane. This will allow the formation of double bond giving stability to the complex.
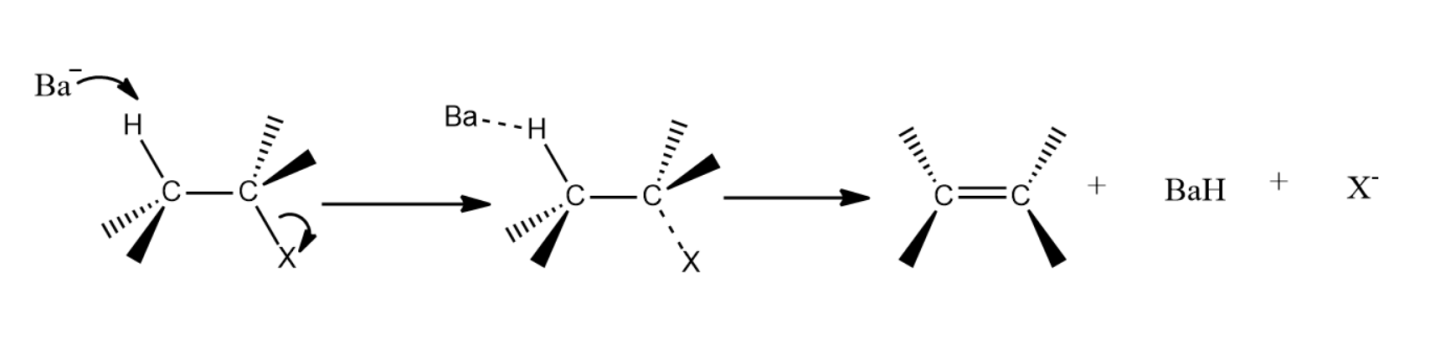
(iii) The complex must follow Zaitsev’s rule, which is a good predictor for simple elimination reactions of alkyl halide. The most substituted alkene is usually the major product at the end.
(iv) The complex must follow Hoffman rule, which says that when an elimination reaction takes place which can produce two or more alkenes (or alkyne) products, the product containing the less highly substituted pi bond is the major one.
-${{E}_{2}}$ reactions are anti elimination which means that there must be a proton in the beta position of the leaving group. In complexes (A) and (B) there Hydrogen atom is present in the anti position of the leaving group. After the removal of the leaving group, i.e Br and Cl respectively in option (A) and (B) an alkene will be formed. Whereas the complexes in (C) and (D) do not have Hydrogen atoms in the anti position of the leaving group.
So, the correct answer is “Option A and B”.
Note: ${{E}_{2}}$ elimination reactions of alkyl halides will dominate with most of the nucleophiles, even if they are weak bases. In high dielectric ionizing solvents, the products formed maybe ${{S}_{N}}1$ and ${{E}_{1}}$ .
Complete answer:
-${{E}_{2}}$ reactions, in order to proceed, must follow the following requirements-
(i) Secondary and tertiary alkyl halides will undergo ${{E}_{2}}$ reactions in the presence of a base like OH-, RO-, ${{R}_{2}}N-$ .
(ii) Both leaving groups must be present on the same plane. This will allow the formation of double bond giving stability to the complex.

(iii) The complex must follow Zaitsev’s rule, which is a good predictor for simple elimination reactions of alkyl halide. The most substituted alkene is usually the major product at the end.
(iv) The complex must follow Hoffman rule, which says that when an elimination reaction takes place which can produce two or more alkenes (or alkyne) products, the product containing the less highly substituted pi bond is the major one.
-${{E}_{2}}$ reactions are anti elimination which means that there must be a proton in the beta position of the leaving group. In complexes (A) and (B) there Hydrogen atom is present in the anti position of the leaving group. After the removal of the leaving group, i.e Br and Cl respectively in option (A) and (B) an alkene will be formed. Whereas the complexes in (C) and (D) do not have Hydrogen atoms in the anti position of the leaving group.
So, the correct answer is “Option A and B”.
Note: ${{E}_{2}}$ elimination reactions of alkyl halides will dominate with most of the nucleophiles, even if they are weak bases. In high dielectric ionizing solvents, the products formed maybe ${{S}_{N}}1$ and ${{E}_{1}}$ .
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




