
What is the aromaticity of \[C{H_4}\] ?
Answer
560.7k+ views
Hint:We need to know that the benzene has a high degree of unsaturation, but it also have a remarkable stability, and shows some unexpected behavior, those compounds having benzene type chemistry are conventionally known as the aromaticity of such compounds or aromatic character or aromaticity. Stability is due to delocalization of electrons present in $\pi - \pi $ orbitals.
Complete step by step answer:
We need to remember that if a compound should to be an aromatic, then it must follow the below criteria:
1.That compound must be a cyclic compound and it has some number of conjugated $\pi $ bonds.
2.The ring atoms usually have an unhybridized $p$ orbital.
3.The unhybridized $p$ orbital necessarily overlaps to form a continuous ring of parallel orbitals. The structure of that compound must be planar or nearly planar, because of an effective overlap to occur.
4.The delocalization of the $\pi $ electrons must decrease electronic energy over the ring.
For example: Benzene (Kekule’s structure$(cyclohexatriene)$)
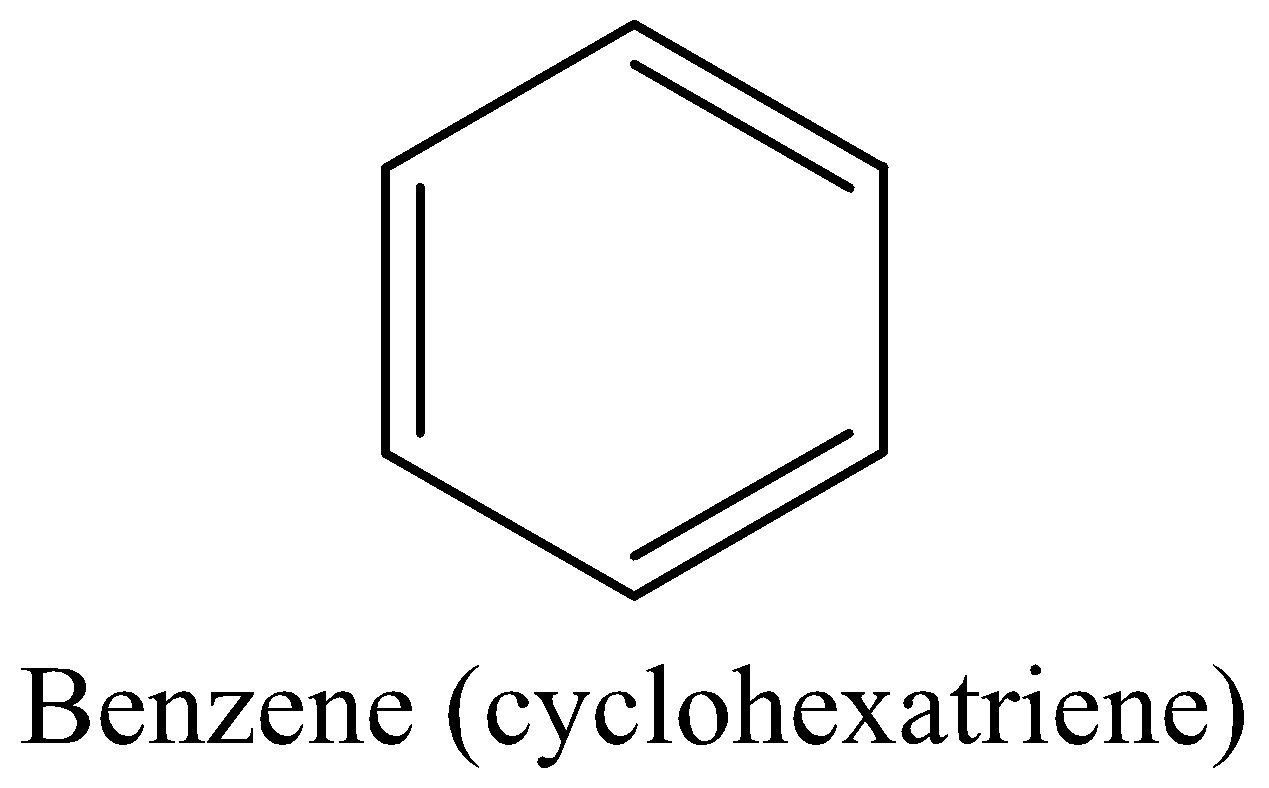
Benzene meets all the above four criteria. And actually, is aromatic and more stable.
The given compound \[C{H_4}\],
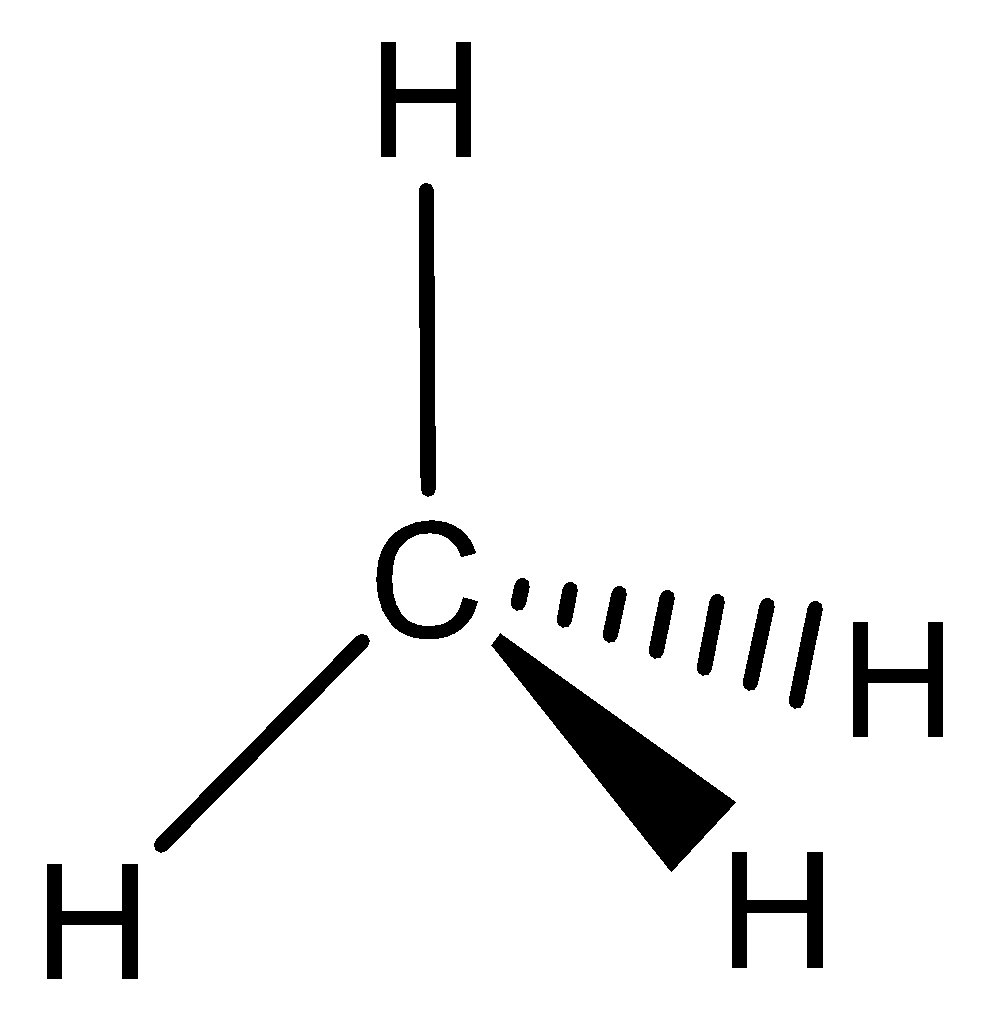
This compound does not have a continuous overlapping of $p$ orbitals as required from above rule $(3),$ it cannot be aromatic. It has $s{p^3}$ hybridized carbon and does not planar structure. It is a nonaromatic or aliphatic compound.
Note:
We should need to know that if a compound does not contain benzene but shows aromatic characters then they are called non benzenoid aromatic compounds. And also we have terms such as antiaromatic compounds. Huckel was a German chemical physicist, he proposed a rule, states that if the number of $\pi $ electrons in the system is $(4n + 2)$ , the system is aromatic, and if it is $(4n)$ , that system is nonaromatic or antiaromatic.
Complete step by step answer:
We need to remember that if a compound should to be an aromatic, then it must follow the below criteria:
1.That compound must be a cyclic compound and it has some number of conjugated $\pi $ bonds.
2.The ring atoms usually have an unhybridized $p$ orbital.
3.The unhybridized $p$ orbital necessarily overlaps to form a continuous ring of parallel orbitals. The structure of that compound must be planar or nearly planar, because of an effective overlap to occur.
4.The delocalization of the $\pi $ electrons must decrease electronic energy over the ring.
For example: Benzene (Kekule’s structure$(cyclohexatriene)$)

Benzene meets all the above four criteria. And actually, is aromatic and more stable.
The given compound \[C{H_4}\],

This compound does not have a continuous overlapping of $p$ orbitals as required from above rule $(3),$ it cannot be aromatic. It has $s{p^3}$ hybridized carbon and does not planar structure. It is a nonaromatic or aliphatic compound.
Note:
We should need to know that if a compound does not contain benzene but shows aromatic characters then they are called non benzenoid aromatic compounds. And also we have terms such as antiaromatic compounds. Huckel was a German chemical physicist, he proposed a rule, states that if the number of $\pi $ electrons in the system is $(4n + 2)$ , the system is aromatic, and if it is $(4n)$ , that system is nonaromatic or antiaromatic.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




