
What is the acceleration of the box?

Answer
565.2k+ views
Hint: We know that total force on an object remains zero. Here, we will take the box as the object and then will equate all the forces acting on it.
Formulae Used: $ F = ma $
Where, $ F $ is the force on the object, $ m $ is its mass and $ a $ is its acceleration.
$ tan\theta = p/b $
Where, $ \theta $ is the angle of inclination, $ p $ is the perpendicular height and $ b $ is the base length.
Complete Step By Step Solution
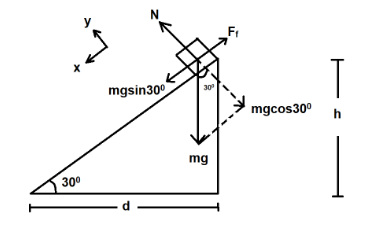
Let us assume that the box accelerate down the slope,
Then, We know that Frictional Constant, $ \mu = tan\theta $
Here, $ \theta = {30^0} $
Thus, After calculating, we get
$ \mu = 1/\surd 3 $
Now, $ mgsin{30^0} = {F_f} $
Also, $ {F_f} = \mu N $
But, N=mgcos300
$ N = \surd 3mg $
Now, $ ma = {F_f} $
Thus, $ mgsin{30^0} = ma $
We know, $ g = 9.81m{s^{ - 2}} $
Thus, $ a = g \times \left( {1/2} \right) $
After calculating, we get
$ a = 4.905m{s^{ - 2}} $
Thus, the acceleration of the box is $ 4.905{\text{ }}m{s^{ - 2}} $ .
Additional Information
The diagram we dealt upon is known as free body diagram in scientific terminology. It is actually a schematic representation of a real life problem taking into account the relative magnitudes and force acting on an object in a given situation.
The frictional constant $ \mu $ multiplied by the mass of the target object is the value up till which the object is acted upon by static friction and beyond this barrier the friction gets converted into kinetic friction. The value of kinetic friction is a bit lower than that of the static friction. In other words, we can say that the barrier is after which a body starts to move.
Note
The value we calculated is by taking $ g = 9.81m{s^{ - 2}} $ , but we could also approximate and take $ g = 10m{s^{ - 2}} $ . For that the value of acceleration comes out to be $ 5m{s^{ - 2}} $ .
Formulae Used: $ F = ma $
Where, $ F $ is the force on the object, $ m $ is its mass and $ a $ is its acceleration.
$ tan\theta = p/b $
Where, $ \theta $ is the angle of inclination, $ p $ is the perpendicular height and $ b $ is the base length.
Complete Step By Step Solution
Let us assume that the box accelerate down the slope,
Then, We know that Frictional Constant, $ \mu = tan\theta $
Here, $ \theta = {30^0} $
Thus, After calculating, we get
$ \mu = 1/\surd 3 $
Now, $ mgsin{30^0} = {F_f} $
Also, $ {F_f} = \mu N $
But, N=mgcos300
$ N = \surd 3mg $
Now, $ ma = {F_f} $
Thus, $ mgsin{30^0} = ma $
We know, $ g = 9.81m{s^{ - 2}} $
Thus, $ a = g \times \left( {1/2} \right) $
After calculating, we get
$ a = 4.905m{s^{ - 2}} $
Thus, the acceleration of the box is $ 4.905{\text{ }}m{s^{ - 2}} $ .
Additional Information
The diagram we dealt upon is known as free body diagram in scientific terminology. It is actually a schematic representation of a real life problem taking into account the relative magnitudes and force acting on an object in a given situation.
The frictional constant $ \mu $ multiplied by the mass of the target object is the value up till which the object is acted upon by static friction and beyond this barrier the friction gets converted into kinetic friction. The value of kinetic friction is a bit lower than that of the static friction. In other words, we can say that the barrier is after which a body starts to move.
Note
The value we calculated is by taking $ g = 9.81m{s^{ - 2}} $ , but we could also approximate and take $ g = 10m{s^{ - 2}} $ . For that the value of acceleration comes out to be $ 5m{s^{ - 2}} $ .
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




