
What is a direct variation?
Answer
518.4k+ views
Hint: First we need to know about the term direct variation. We will take some examples of equations that represent direct variation relations. Here we will know about the term constant of proportionality and why it is introduced in the relationship. We will take examples of linear equations in direct variation.
Complete step by step solution:
Here we have asked to define the term direct variation. Let us understand it using some examples.
Now, in mathematics a direct variation is a relation between two variables (say x and y) such that the ratio of the two variables is always a constant. It is a linear relation between the two variables. The general representation of a direct variation is given as $y\propto x$. Here the sign $\propto $ means proportional. When we remove the proportionality sign then a constant (k) is introduced such that the relation becomes $y=kx$, here k can be any real value other than 0. For example: -
(1) $y=5x$. Here we can see that y varies linearly as x and the constant of proportionality is 5, so it is a direct variation.

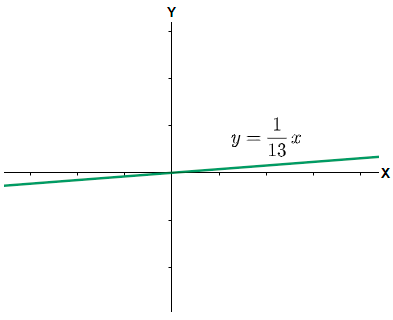
(2) $x=13y$. Here we can write the equation as $y=\dfrac{1}{13}x$, so the constant of proportionality is $\dfrac{1}{13}$ and therefore it is also a direct variation.
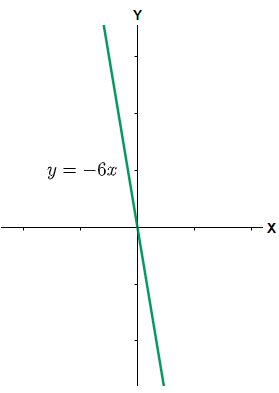
(3) $y=-6x$. Here when we will take the ratio of y and x it will be equal to –6 which is a constant, so the given relation is also a direct variation.
Note: Note that the exponent of the two variables in a direct variation will always be 1 and they will always form a straight line. The proportionality constant is also the slope of the line. One more important variation is known as the Inverse variation. In this type of variation the product of the two variables is a constant. It forms a rectangular hyperbolic relation given as $xy=k$.
Complete step by step solution:
Here we have asked to define the term direct variation. Let us understand it using some examples.
Now, in mathematics a direct variation is a relation between two variables (say x and y) such that the ratio of the two variables is always a constant. It is a linear relation between the two variables. The general representation of a direct variation is given as $y\propto x$. Here the sign $\propto $ means proportional. When we remove the proportionality sign then a constant (k) is introduced such that the relation becomes $y=kx$, here k can be any real value other than 0. For example: -
(1) $y=5x$. Here we can see that y varies linearly as x and the constant of proportionality is 5, so it is a direct variation.

(2) $x=13y$. Here we can write the equation as $y=\dfrac{1}{13}x$, so the constant of proportionality is $\dfrac{1}{13}$ and therefore it is also a direct variation.

(3) $y=-6x$. Here when we will take the ratio of y and x it will be equal to –6 which is a constant, so the given relation is also a direct variation.

Note: Note that the exponent of the two variables in a direct variation will always be 1 and they will always form a straight line. The proportionality constant is also the slope of the line. One more important variation is known as the Inverse variation. In this type of variation the product of the two variables is a constant. It forms a rectangular hyperbolic relation given as $xy=k$.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 9 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Class 9 Question and Answer - Your Ultimate Solutions Guide

Trending doubts
Find the mode and median of the data 13 16 12 14 1-class-9-maths-CBSE

What were the main changes brought about by the Bolsheviks class 9 social science CBSE

What is the theme or message of the poem The road not class 9 english CBSE

What are the major achievements of the UNO class 9 social science CBSE

Explain the importance of pH in everyday life class 9 chemistry CBSE

Differentiate between parenchyma collenchyma and sclerenchyma class 9 biology CBSE





