
What are synthetic fibres?
Answer
592.2k+ views
Hint: Polymers are macromolecules formed due to linkages between small repeating units called monomers. Some examples of polymers are wool, nylon, etc.
Complete answer:
Polymers are macromolecules with large molecular weight and are composed of a number of smaller repeating units called monomers. There are so many polymers around us like in our body we have DNA, nerve fibres, nails, hair, etc. Some other common polymers are wool, nylon, rubber, etc.
Polymers are classified into three types based on source.
-Natural polymers: They are obtained from natural sources like plants or animals and accordingly named as plant polymers or animal polymers respectively. For example, cellulose, jute, linen, wool, silk, natural rubber, etc.
-Semi-synthetic polymers: They are chemically modified natural polymers to improve their properties like appearance, tensile strength, luster, etc. For example, acetate rayon, vulcanized rubber, cuprammonium silk etc.
-Synthetic polymers: They are manmade and chemically synthesized in laboratories or industries. For example, nylon, terylene, polythene, etc.
Synthetic fibres are fibres of man made polymers having strong intermolecular forces due to hydrogen bonding. These fibres have high tensile strength. They are used in textile industries, strong ropes, tyre cords, etc.
For example, nylon, terylene.
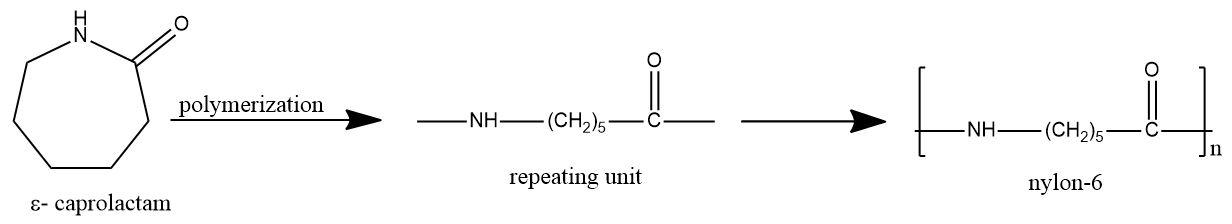
Nylon-6 is synthesized from $\text{ }\!\!\varepsilon\!\!\text{ -caprolactam}$. The lactum linkage is broken to form a straight chain which is the repeating unit. Many of these repeating units come together to form nylon-6.
Note: Synthetic fibres are polymers having high tensile strength as one of their important properties. Don’t get confused with synthetic polymers and synthetic fibres. Synthetic fibres are a class of synthetic polymers.
Complete answer:
Polymers are macromolecules with large molecular weight and are composed of a number of smaller repeating units called monomers. There are so many polymers around us like in our body we have DNA, nerve fibres, nails, hair, etc. Some other common polymers are wool, nylon, rubber, etc.
Polymers are classified into three types based on source.
-Natural polymers: They are obtained from natural sources like plants or animals and accordingly named as plant polymers or animal polymers respectively. For example, cellulose, jute, linen, wool, silk, natural rubber, etc.
-Semi-synthetic polymers: They are chemically modified natural polymers to improve their properties like appearance, tensile strength, luster, etc. For example, acetate rayon, vulcanized rubber, cuprammonium silk etc.
-Synthetic polymers: They are manmade and chemically synthesized in laboratories or industries. For example, nylon, terylene, polythene, etc.
Synthetic fibres are fibres of man made polymers having strong intermolecular forces due to hydrogen bonding. These fibres have high tensile strength. They are used in textile industries, strong ropes, tyre cords, etc.
For example, nylon, terylene.

Nylon-6 is synthesized from $\text{ }\!\!\varepsilon\!\!\text{ -caprolactam}$. The lactum linkage is broken to form a straight chain which is the repeating unit. Many of these repeating units come together to form nylon-6.
Note: Synthetic fibres are polymers having high tensile strength as one of their important properties. Don’t get confused with synthetic polymers and synthetic fibres. Synthetic fibres are a class of synthetic polymers.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




