
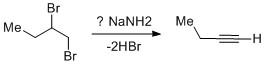
Vicinal dihalides undergo double dehydrohalogenation to give terminal alkyne. How many moles of\[NaN{H_2}\] are used in the overall reaction?
A.One
B.Two
C.Three
D.Four

Answer
601.2k+ views
Hint: The dehydrohalogenation is the removal of \[HX\] from the molecule where \[H\] is hydrogen atom and \[X\] is halogen atom. \[NaN{H_2}\] acts as a strong base that has the ability to abstract protons.
Complete step by step answer:
The vicinal dihalides undergo dehydrohalogenation to generate terminal alkynes. The reaction goes through a stepwise manner.
In the first step, one mole of \[NaN{H_2}\] abstracts the acidic proton from the dihalide to yield an alkenyl bromide. The protons flanked between the two bromo attached carbons are mildly acidic in nature. Due to the use of \[NaN{H_2}\] which is a very strong base allows the proton to abstract and leads to the alkene intermediate.
In the second step, the alkene intermediate consumes a second-mole \[NaN{H_2}\] to give an alkyne by dehydrohalogenation. The proton abstraction from alkene is easier than in the first step as alkenes are more acidic than alkanes.
Due to the generation of terminal alkynes which are very much acidic in nature the proton from the alkyne gets easily abstracted. But the reaction after aqueous workup yields the desired alkyne compound. From alkane to alkene to alkyne the percentage of s-character increases. As a result the electronegativity increases and the acidic nature increases. Hence alkynes are highly acidic in nature and the third mole of \[NaN{H_2}\] will be consumed during the reaction course.
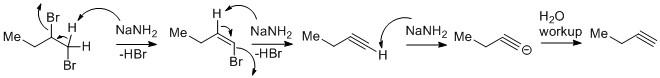
Thus three moles of \[NaN{H_2}\]are used in the overall reaction.
Note:
The proton on the left side is not abstracted by \[NaN{H_2}\] as it is attached to a carbon that is attached to the methyl group. As methyl groups are electron donating in nature so the acidity of the proton decreases.
Complete step by step answer:
The vicinal dihalides undergo dehydrohalogenation to generate terminal alkynes. The reaction goes through a stepwise manner.
In the first step, one mole of \[NaN{H_2}\] abstracts the acidic proton from the dihalide to yield an alkenyl bromide. The protons flanked between the two bromo attached carbons are mildly acidic in nature. Due to the use of \[NaN{H_2}\] which is a very strong base allows the proton to abstract and leads to the alkene intermediate.
In the second step, the alkene intermediate consumes a second-mole \[NaN{H_2}\] to give an alkyne by dehydrohalogenation. The proton abstraction from alkene is easier than in the first step as alkenes are more acidic than alkanes.
Due to the generation of terminal alkynes which are very much acidic in nature the proton from the alkyne gets easily abstracted. But the reaction after aqueous workup yields the desired alkyne compound. From alkane to alkene to alkyne the percentage of s-character increases. As a result the electronegativity increases and the acidic nature increases. Hence alkynes are highly acidic in nature and the third mole of \[NaN{H_2}\] will be consumed during the reaction course.

Thus three moles of \[NaN{H_2}\]are used in the overall reaction.
Note:
The proton on the left side is not abstracted by \[NaN{H_2}\] as it is attached to a carbon that is attached to the methyl group. As methyl groups are electron donating in nature so the acidity of the proton decreases.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Draw a diagram of nephron and explain its structur class 11 biology CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

Chemical formula of Bleaching powder is A Ca2OCl2 B class 11 chemistry CBSE

Name the part of the brain responsible for the precision class 11 biology CBSE

The growth of tendril in pea plants is due to AEffect class 11 biology CBSE

One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE




