
Under the influence of the Coulomb field of charge +Q, a charge q is moving around it in an elliptical orbit. Find out the correct statement(s).
A. The angular momentum of the charge q is constant
B. The linear momentum of the charge q is constant.
C. The angular velocity of the charge q is constant
D. The linear speed of the charge q is constant
Answer
583.5k+ views
Hint: Check whether the torque on the charge q due the force exerted by charge +Q about a point on charge +Q is zero. Note that torque is defined as the rate of change in angular momentum of the particle with respect to time.
Formula used:
$\tau =Fr$
$\tau =\dfrac{dL}{dt}$
$L=I\omega $
Complete answer:
For a particle to revolve around another particle, there must be a force attraction between the two particles. It is given that a charge q is revolving around a charge +Q in an elliptical orbit. We know that unlike charges, they attract each other. Therefore, the revolving charge q must be a negative charge.
Therefore, the +Q charge will exert a force of attraction on the charge q. The electrostatic force of attraction is always towards the charge that exerts the force. This means that the direction of the force on charge q is towards charge +Q.
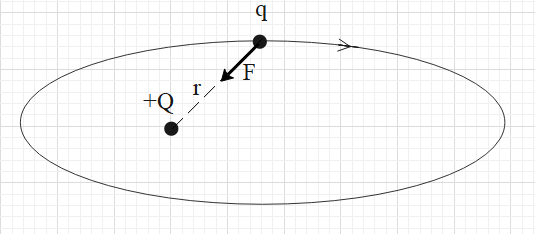
The magnitude of torque on the charge about a point is equal to the product of the distance (r) between the two charges and the component of the force that is normal to r.
i.e. $\tau =Fr$.
In this case, torque about charge +Q is zero because the component of the force normal to r is zero.
i.e. $\tau =0$
And torque is defined as the rate of change in the angular momentum about the same point with respect to time.
i.e. $\tau =\dfrac{dL}{dt}$.
This means that the change in the angular momentum of charge q is zero. In other words, the angular momentum of charge q is constant.
So, the correct answer is “Option A”.
Note:
Angular momentum is given as the product of the momentum of inertia (I) and the angular velocity ($\omega $) of the particle about the same point.
i.e. $L=I\omega $.
When the charge q is moving in the elliptical path, its momentum of inertia is continuously changing because the distance of the charge q from charge Q is changing. We know that L is constant. Therefore, if I is changing then $\omega $ is also changing.
When a particle revolves in an elliptical orbit, its linear speed changes. Since the linear speed changes, the linear momentum also changes.
Formula used:
$\tau =Fr$
$\tau =\dfrac{dL}{dt}$
$L=I\omega $
Complete answer:
For a particle to revolve around another particle, there must be a force attraction between the two particles. It is given that a charge q is revolving around a charge +Q in an elliptical orbit. We know that unlike charges, they attract each other. Therefore, the revolving charge q must be a negative charge.
Therefore, the +Q charge will exert a force of attraction on the charge q. The electrostatic force of attraction is always towards the charge that exerts the force. This means that the direction of the force on charge q is towards charge +Q.

The magnitude of torque on the charge about a point is equal to the product of the distance (r) between the two charges and the component of the force that is normal to r.
i.e. $\tau =Fr$.
In this case, torque about charge +Q is zero because the component of the force normal to r is zero.
i.e. $\tau =0$
And torque is defined as the rate of change in the angular momentum about the same point with respect to time.
i.e. $\tau =\dfrac{dL}{dt}$.
This means that the change in the angular momentum of charge q is zero. In other words, the angular momentum of charge q is constant.
So, the correct answer is “Option A”.
Note:
Angular momentum is given as the product of the momentum of inertia (I) and the angular velocity ($\omega $) of the particle about the same point.
i.e. $L=I\omega $.
When the charge q is moving in the elliptical path, its momentum of inertia is continuously changing because the distance of the charge q from charge Q is changing. We know that L is constant. Therefore, if I is changing then $\omega $ is also changing.
When a particle revolves in an elliptical orbit, its linear speed changes. Since the linear speed changes, the linear momentum also changes.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




