
Two very long straight, parallel wires carry steady currents I and –I respectively. The distance between the wires is d. At a certain instant of time, a point charge q is at a point equidistant from the two wires, in the plane of the wires. Its instantaneous velocity v is perpendicular to this plane. The magnitude of the force due to the magnetic field acting on the charge at this instant is
A. $\dfrac{{{\mu }_{0}}Iqv}{2\pi d}$
B. $\dfrac{{{\mu }_{0}}Iqv}{\pi d}$
C. $\dfrac{2{{\mu }_{0}}Iqv}{\pi d}$
D. $0$
Answer
564.3k+ views
Hint:Draw a suitable figure with the given information for a better understanding. The magnetic force on a charge q due to the magnetic field at its position is given as $F=q\left(
\overrightarrow{v}\times \overrightarrow{B} \right)$. With the help of the right hand thumb rule
find the net magnetic field and find the force.
Formula used:
$F=q\left( \overrightarrow{v}\times \overrightarrow{B} \right)$
Complete step by step answer:
The magnetic force on a charge q due to the magnetic field at its position is given as $F=q\left(
\overrightarrow{v}\times \overrightarrow{B} \right)$ ….. (i),
where $\overrightarrow{v}$ is the velocity of the charge at that point and $\overrightarrow{B}$ is
the magnetic field at that point.
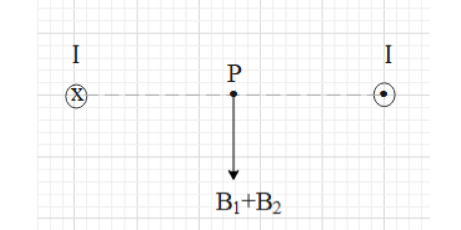
It is given that there are two straight wires carrying currents I and –I respectively. This means that the current both the wires are of same magnitude (i.e. I) but they are flowing in opposite direction to each other.
Let two wires be placed perpendicular to the plane of this page. Let the current in one wire be flowing inside the plane of this page and the current in the other wire be flowing outwards, as shown in the figure.
When a current flows in a conducting wire, it generates a magnetic field at every point. The direction of the magnetic field at a point is given by the right hand thumb rule.
By using the right hand thumb rule for wire 1, we get that the magnetic field (${{B}_{1}}$) at point P (where the charge q is placed) is directed downwards.
And the magnetic field (${{B}_{2}}$) at point P due to wire 2 is also directed downwards, as shown in the figure.
Therefore, the net magnetic field is equal $B={{B}_{1}}+{{B}_{2}}$ and is directed downwards.
Now it is given that the instantaneous velocity of the charge q is perpendicular to the plane of the two wires. This means that the velocity of the charge is either towards up or towards down. In both the cases, the velocity vector and the magnetic field will parallel or antiparallel to each other.
When the two vectors are parallel or antiparallel, the cross product of the two vectors is zero.
This means that $\left( \overrightarrow{v}\times \overrightarrow{B} \right)=0$
By substituting this value in (i) we get that $F=0$.
This means that the net force acting on the charge is zero.
Hence, the correct option is D.
Note:The magnitude of the magnetic force on charge q moving with velocity v at point where the magnitude of the magnetic field is B is equal to $F=qvB\sin \theta $, where $\theta $ is the angle between the velocity vector and the magnetic field.
We can solve the given question with formulas also. When the velocity and magnetic field are parallel, the angle between them is $\theta =0$. And $\sin 0=0$.
$\Rightarrow F=0$.
When the two are antiparallel, $\theta ={{180}^{\circ }}$ and $\sin {{180}^{\circ }}=0$.
$\Rightarrow F=0$.
\overrightarrow{v}\times \overrightarrow{B} \right)$. With the help of the right hand thumb rule
find the net magnetic field and find the force.
Formula used:
$F=q\left( \overrightarrow{v}\times \overrightarrow{B} \right)$
Complete step by step answer:
The magnetic force on a charge q due to the magnetic field at its position is given as $F=q\left(
\overrightarrow{v}\times \overrightarrow{B} \right)$ ….. (i),
where $\overrightarrow{v}$ is the velocity of the charge at that point and $\overrightarrow{B}$ is
the magnetic field at that point.
It is given that there are two straight wires carrying currents I and –I respectively. This means that the current both the wires are of same magnitude (i.e. I) but they are flowing in opposite direction to each other.
Let two wires be placed perpendicular to the plane of this page. Let the current in one wire be flowing inside the plane of this page and the current in the other wire be flowing outwards, as shown in the figure.
When a current flows in a conducting wire, it generates a magnetic field at every point. The direction of the magnetic field at a point is given by the right hand thumb rule.
By using the right hand thumb rule for wire 1, we get that the magnetic field (${{B}_{1}}$) at point P (where the charge q is placed) is directed downwards.
And the magnetic field (${{B}_{2}}$) at point P due to wire 2 is also directed downwards, as shown in the figure.
Therefore, the net magnetic field is equal $B={{B}_{1}}+{{B}_{2}}$ and is directed downwards.

Now it is given that the instantaneous velocity of the charge q is perpendicular to the plane of the two wires. This means that the velocity of the charge is either towards up or towards down. In both the cases, the velocity vector and the magnetic field will parallel or antiparallel to each other.
When the two vectors are parallel or antiparallel, the cross product of the two vectors is zero.
This means that $\left( \overrightarrow{v}\times \overrightarrow{B} \right)=0$
By substituting this value in (i) we get that $F=0$.
This means that the net force acting on the charge is zero.
Hence, the correct option is D.
Note:The magnitude of the magnetic force on charge q moving with velocity v at point where the magnitude of the magnetic field is B is equal to $F=qvB\sin \theta $, where $\theta $ is the angle between the velocity vector and the magnetic field.
We can solve the given question with formulas also. When the velocity and magnetic field are parallel, the angle between them is $\theta =0$. And $\sin 0=0$.
$\Rightarrow F=0$.
When the two are antiparallel, $\theta ={{180}^{\circ }}$ and $\sin {{180}^{\circ }}=0$.
$\Rightarrow F=0$.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




