
Two masses, 2 kg and 3 kg are placed on the floor of a lift as shown in the figure below. The force of normal reaction applied by a 3 kg block on the floor of the lift is 40 N. Which of the following statements is/are correct? [$g = 10m/{s^2}$ ]
A. The lift is moving with an upward acceleration.
B. The lift is moving with a downward acceleration
C. The lift is either at rest of moving with uniform speed
D. Force of normal reaction applied by the 2 kg block on the 3 kg block is 16 N.

Answer
573.6k+ views
Hint: while we travel in a lift that goes down we feel that we have lost some weight and when lift goes up we feel weight gain. But the actual mass of us is the same in both cases. It's all due to the variation of normal reactions in both the cases. This can be solved from the ground reference frame by using pseudo force which causes variation in normal force.
Formula used:
$\eqalign{
& mg - N = ma \cr
& N = mg - ma \cr
& N = W - ma \cr} $
Complete answer:
When lift is not moving let the weight of the blocks be W
$W = mg$
Where m is the mass of two blocks combined and g is the acceleration due to gravity
Now when lift starts moving down with acceleration ‘a’
Normal reaction N acts upward
Weight W acts downward
Force $m \times a$ acts downward
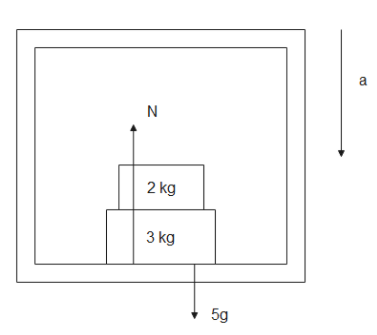
From ground frame of reference
Balancing the forces gives us
$\eqalign{
& mg - N = ma \cr
& \Rightarrow N = mg - ma \cr
& \Rightarrow N = W - ma \cr
& \Rightarrow 40 = 5g - 5a \cr
& \Rightarrow 40 = 50 - 5a \cr
& \therefore a = 2m/{s^2} \cr} $
So the lift is moving down with acceleration 2 meter per second square
Now normal reaction between 2kg and 3kg block will be
$\eqalign{
& {m_2}g - N = {m_2}a \cr
& \Rightarrow N = W - {m_2}a \cr
& \Rightarrow N = 2g - 2a \cr
& \Rightarrow N = 20 - 4 \cr
& \therefore N = 16newton \cr} $
Hence options B and D are correct.
Additional information:
Same question can be solved by the Lift frame of reference. Here pseudo force comes into action. Since lift blocks system is moving down with acceleration ‘a’ pseudo force will be acting upward and it will be $m \times a$
Upward forces = $N + ma$
Downward forces = $mg$
Equating both the forces we get
$N = W - ma$
Hence both methods will give us the same answer
Note:
It is to be noted that only weight seems to be increased but not mass. Because mass is always constant wherever we go but weights vary as resultant acceleration varies. A freely falling body feels no weight due to the same property as resultant acceleration would be (g-g =0) zero. This is called weightlessness. Same applies with the astronaut in the satellite where he feels weightlessness.
Formula used:
$\eqalign{
& mg - N = ma \cr
& N = mg - ma \cr
& N = W - ma \cr} $
Complete answer:
When lift is not moving let the weight of the blocks be W
$W = mg$
Where m is the mass of two blocks combined and g is the acceleration due to gravity
Now when lift starts moving down with acceleration ‘a’
Normal reaction N acts upward
Weight W acts downward
Force $m \times a$ acts downward

From ground frame of reference
Balancing the forces gives us
$\eqalign{
& mg - N = ma \cr
& \Rightarrow N = mg - ma \cr
& \Rightarrow N = W - ma \cr
& \Rightarrow 40 = 5g - 5a \cr
& \Rightarrow 40 = 50 - 5a \cr
& \therefore a = 2m/{s^2} \cr} $
So the lift is moving down with acceleration 2 meter per second square
Now normal reaction between 2kg and 3kg block will be
$\eqalign{
& {m_2}g - N = {m_2}a \cr
& \Rightarrow N = W - {m_2}a \cr
& \Rightarrow N = 2g - 2a \cr
& \Rightarrow N = 20 - 4 \cr
& \therefore N = 16newton \cr} $
Hence options B and D are correct.
Additional information:
Same question can be solved by the Lift frame of reference. Here pseudo force comes into action. Since lift blocks system is moving down with acceleration ‘a’ pseudo force will be acting upward and it will be $m \times a$
Upward forces = $N + ma$
Downward forces = $mg$
Equating both the forces we get
$N = W - ma$
Hence both methods will give us the same answer
Note:
It is to be noted that only weight seems to be increased but not mass. Because mass is always constant wherever we go but weights vary as resultant acceleration varies. A freely falling body feels no weight due to the same property as resultant acceleration would be (g-g =0) zero. This is called weightlessness. Same applies with the astronaut in the satellite where he feels weightlessness.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




