
Two lines are drawn at the right angle, one being a tangent to \[{y^2} = 4ax\] and another to \[{x^2} = 4by\]. Show that the locus of their point of intersection is the curve \[ \ {\left( {bx - ay} \right)^2} + (by + ax)\left( {{x^2} + {y^2}} \right) = 0\]
Answer
621.9k+ views
Hint: Assume the equation of the general tangents to both the parabolas given in the equation. Then simply equate the product of their slopes to , and make the point whose locus needs to be found out, (let’s call it ) satisfy the equations of tangents you assumed.
Let’s assume two parabola
\[{y^2} = 4ax\] ……………… (1)
And
\[{x^2} = 4ay\]. ……………….. (2)
As lines are touching the parabola, therefore lines are tangents on the parabolas.
We are going to write the equation of tangents for both parabolas. As the question says that the lines intersect each other normally at a point. We have to write the equation in slope form.
For \[{y^2} = 4ax\]
Let slope of the tangent \[ = {m_1}\]
Therefore; the slope of tangent = slope of the parabola
\[\therefore \dfrac{{dy}}{{dx}} = {m_1}\] ……………. (A)
\[2y\dfrac{{dy}}{{dx}} = 4a\]
\[ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{dy}}{{dx}} = \dfrac{{2a}}{y}\] ………… (B)
Equating (A) and (B)
\[ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{dy}}{{dx}} = \dfrac{{2a}}{y} = {m_1}\]
\[ \Rightarrow y = \dfrac{{2a}}{{{m_1}}}\] Put this value in equation (1)
Form equation (1)
\[{\left( {\dfrac{{2a}}{{{m_1}}}} \right)^2} = 4ax\]
\[ \Rightarrow x = \dfrac{a}{{m_1^2}}\]
Therefore; co-ordinate of point of the tangent is
\[x = \dfrac{a}{{m_1^2}}\] And \[ \Rightarrow y = \dfrac{{2a}}{{{m_1}}}\]
Equation of tangent is
\[\left( {y - \dfrac{{2a}}{{{m_1}}}} \right) = {m_1}\left( {x - \dfrac{a}{{m_1^2}}} \right)\]
\[ \Rightarrow y = mx + \dfrac{a}{{{m_1}}}\] …….. (C) Equation of tangent of parabola\[{y^2} = 4ax\].
Equation of tangent for parabola \[{x^2} = 4ay\]
Just replace \[x \to y\,,\,\,y \to x\,,\,{m_1} \to {m_2}\,and \to b\]in equation (C)
\[ \Rightarrow x = {m_2}y + \dfrac{b}{{{m_2}}}\] …….. (D)
\[ \Rightarrow x{m_2} = m_{_2}^2y + b\]
\[ \Rightarrow y = \dfrac{x}{{{m_2}}} - \dfrac{b}{{m_{_2}^2}}\] ……….. (E)
Compare this equation (E) with the general equation of a straight line\[y = mx + c\].
Slope of tangent \[ = \dfrac{1}{{{m_2}}}\]
As tangents are intersecting perpendicular to each other.
Therefore, the product of slope\[ = - 1\].
\[{m_1} \cdot \dfrac{1}{{{m_2}}} = - 1\]
\[ \Rightarrow {m_2} = - {m_1}\] ……………… (3)
Assume tangents are intersecting with each other at a point\[P(h,k)\].
Therefore, equation (C) and (E) must satisfy the point ‘P’.
Put the value of ‘P’ in equations (C) and (E).
From equation (C)
\[ \Rightarrow y = {m_1}x + \dfrac{a}{{{m_1}}}\]
\[ \Rightarrow k = {m_1}h + \dfrac{a}{{{m_1}}}\]
\[ \Rightarrow m_1^2h - {m_1}k + a = 0\] ……………. (5)
From equation (E)
\[ \Rightarrow y = \dfrac{x}{{{m_2}}} - \dfrac{b}{{m_{_2}^2}}\]
\[ \Rightarrow k = \dfrac{h}{{{m_2}}} - \dfrac{b}{{m_{_2}^2}}\]
\[ \Rightarrow m_{_2}^2k - {m_2}h + b = 0\] …………….(6)
Put the value \[{m_2} = - {m_1}\] in equation (6)
From equation (6) and (3)
\[ \Rightarrow {\left( { - {m_1}} \right)^2}k - \left( { - {m_1}} \right)h + b = 0\]
\[ \Rightarrow m_{_1}^2k + {m_1}h + b = 0\] …………….. (7)
Apply the cross-multiplication method in equation (5) and (7)
\[m_1^2h - {m_1}k + a = 0\] ……………. (5)
\[m_{_1}^2k + {m_1}h + b = 0\] …………….. (7)
\[ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{m_1^2}}{{ - kb - ha}} = \dfrac{{( - ){m_1}}}{{hb - ak}} = \dfrac{1}{{{h^2} - ( - k)k}}\]
From above we can say that
\[ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{m_1^2}}{{ - kb - ha}} = \dfrac{1}{{{h^2} - ( - k)k}}\]
\[ \Rightarrow m_1^2 = \dfrac{{ - kb - ha}}{{{h^2} + {k^2}}}\] …………….. (8)
Again from above
\[ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{( - ){m_1}}}{{hb - ak}} = \dfrac{1}{{{h^2} + {k^2}}}\]
\[ \Rightarrow ( - ){m_1} = \dfrac{{hb - ak}}{{{h^2} + {k^2}}}\]
Squaring both sides
\[ \Rightarrow m_{_1}^2 = \left( {\dfrac{{hb - ak}}{{{h^2} + {k^2}}}} \right)\] ……… (9)
Comparing equation (8) and (9)
From equation (8) and (9)
\[ \Rightarrow m_1^2 = \dfrac{{ - kb - ha}}{{{h^2} + {k^2}}} = {\left( {\dfrac{{hb - ak}}{{{h^2} + {k^2}}}} \right)^2}\]
\[ \Rightarrow - (kb + ha) = \dfrac{{{{\left( {hb - ak} \right)}^2}}}{{{h^2} + {k^2}}}\]
\[ \Rightarrow - (kb + ha)\left( {{h^2} + {k^2}} \right) = {\left( {hb - ak} \right)^2}\]
\[ \Rightarrow {\left( {hb - ak} \right)^2} + (kb + ha)\left( {{h^2} + {k^2}} \right) = 0\] …….(10)
Equation (10) is in terms of\[\left( {h,y} \right)\].
Substitute
\[\begin{gathered}
h \to x \\
k \to y \\
\end{gathered} \]
Locus of point of intersection in term of ‘x’ and ‘y’
\[ \Rightarrow {\left( {bx - ay} \right)^2} + (by + ax)\left( {{x^2} + {y^2}} \right) = 0\]
Note: Cross multiplication
Assume two equation be
\[{A_{1\;}}{x^2}{\text{ }} + {\text{ }}{B_1}{\text{x }} + {\text{ }}{C_{1\;}} = {\text{ }}0\], and
\[{A_2}{x^2}{\text{ }} + {\text{ }}{B_2}{\text{x }} + {\text{ }}{C_{2\;}} = {\text{ }}0\].
The coefficients of \[{x^2}\] are: \[{A_1}\] and\[{A_2}\].
The coefficients of \[x\] are: \[{B_1}\;and{\text{ }}{B_2}\].
The constant terms are: \[{C_1}\;and{\text{ }}\;{C_2}\]
To solve the equations in a simplified way,
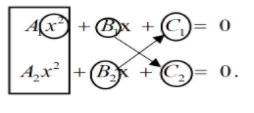
\[\dfrac{{{x^2}}}{{{B_1}{C_2} - {B_2}{C_1}}} = \dfrac{x}{{{C_1}{A_2} - {C_2}{A_1}}} = \dfrac{1}{{{A_1}{C_2} - {A_2}{B_1}}}\]
Let’s assume two parabola
\[{y^2} = 4ax\] ……………… (1)
And
\[{x^2} = 4ay\]. ……………….. (2)
As lines are touching the parabola, therefore lines are tangents on the parabolas.
We are going to write the equation of tangents for both parabolas. As the question says that the lines intersect each other normally at a point. We have to write the equation in slope form.
For \[{y^2} = 4ax\]
Let slope of the tangent \[ = {m_1}\]
Therefore; the slope of tangent = slope of the parabola
\[\therefore \dfrac{{dy}}{{dx}} = {m_1}\] ……………. (A)
\[2y\dfrac{{dy}}{{dx}} = 4a\]
\[ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{dy}}{{dx}} = \dfrac{{2a}}{y}\] ………… (B)
Equating (A) and (B)
\[ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{dy}}{{dx}} = \dfrac{{2a}}{y} = {m_1}\]
\[ \Rightarrow y = \dfrac{{2a}}{{{m_1}}}\] Put this value in equation (1)
Form equation (1)
\[{\left( {\dfrac{{2a}}{{{m_1}}}} \right)^2} = 4ax\]
\[ \Rightarrow x = \dfrac{a}{{m_1^2}}\]
Therefore; co-ordinate of point of the tangent is
\[x = \dfrac{a}{{m_1^2}}\] And \[ \Rightarrow y = \dfrac{{2a}}{{{m_1}}}\]
Equation of tangent is
\[\left( {y - \dfrac{{2a}}{{{m_1}}}} \right) = {m_1}\left( {x - \dfrac{a}{{m_1^2}}} \right)\]
\[ \Rightarrow y = mx + \dfrac{a}{{{m_1}}}\] …….. (C) Equation of tangent of parabola\[{y^2} = 4ax\].
Equation of tangent for parabola \[{x^2} = 4ay\]
Just replace \[x \to y\,,\,\,y \to x\,,\,{m_1} \to {m_2}\,and \to b\]in equation (C)
\[ \Rightarrow x = {m_2}y + \dfrac{b}{{{m_2}}}\] …….. (D)
\[ \Rightarrow x{m_2} = m_{_2}^2y + b\]
\[ \Rightarrow y = \dfrac{x}{{{m_2}}} - \dfrac{b}{{m_{_2}^2}}\] ……….. (E)
Compare this equation (E) with the general equation of a straight line\[y = mx + c\].
Slope of tangent \[ = \dfrac{1}{{{m_2}}}\]
As tangents are intersecting perpendicular to each other.
Therefore, the product of slope\[ = - 1\].
\[{m_1} \cdot \dfrac{1}{{{m_2}}} = - 1\]
\[ \Rightarrow {m_2} = - {m_1}\] ……………… (3)
Assume tangents are intersecting with each other at a point\[P(h,k)\].
Therefore, equation (C) and (E) must satisfy the point ‘P’.
Put the value of ‘P’ in equations (C) and (E).
From equation (C)
\[ \Rightarrow y = {m_1}x + \dfrac{a}{{{m_1}}}\]
\[ \Rightarrow k = {m_1}h + \dfrac{a}{{{m_1}}}\]
\[ \Rightarrow m_1^2h - {m_1}k + a = 0\] ……………. (5)
From equation (E)
\[ \Rightarrow y = \dfrac{x}{{{m_2}}} - \dfrac{b}{{m_{_2}^2}}\]
\[ \Rightarrow k = \dfrac{h}{{{m_2}}} - \dfrac{b}{{m_{_2}^2}}\]
\[ \Rightarrow m_{_2}^2k - {m_2}h + b = 0\] …………….(6)
Put the value \[{m_2} = - {m_1}\] in equation (6)
From equation (6) and (3)
\[ \Rightarrow {\left( { - {m_1}} \right)^2}k - \left( { - {m_1}} \right)h + b = 0\]
\[ \Rightarrow m_{_1}^2k + {m_1}h + b = 0\] …………….. (7)
Apply the cross-multiplication method in equation (5) and (7)
\[m_1^2h - {m_1}k + a = 0\] ……………. (5)
\[m_{_1}^2k + {m_1}h + b = 0\] …………….. (7)
\[ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{m_1^2}}{{ - kb - ha}} = \dfrac{{( - ){m_1}}}{{hb - ak}} = \dfrac{1}{{{h^2} - ( - k)k}}\]
From above we can say that
\[ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{m_1^2}}{{ - kb - ha}} = \dfrac{1}{{{h^2} - ( - k)k}}\]
\[ \Rightarrow m_1^2 = \dfrac{{ - kb - ha}}{{{h^2} + {k^2}}}\] …………….. (8)
Again from above
\[ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{( - ){m_1}}}{{hb - ak}} = \dfrac{1}{{{h^2} + {k^2}}}\]
\[ \Rightarrow ( - ){m_1} = \dfrac{{hb - ak}}{{{h^2} + {k^2}}}\]
Squaring both sides
\[ \Rightarrow m_{_1}^2 = \left( {\dfrac{{hb - ak}}{{{h^2} + {k^2}}}} \right)\] ……… (9)
Comparing equation (8) and (9)
From equation (8) and (9)
\[ \Rightarrow m_1^2 = \dfrac{{ - kb - ha}}{{{h^2} + {k^2}}} = {\left( {\dfrac{{hb - ak}}{{{h^2} + {k^2}}}} \right)^2}\]
\[ \Rightarrow - (kb + ha) = \dfrac{{{{\left( {hb - ak} \right)}^2}}}{{{h^2} + {k^2}}}\]
\[ \Rightarrow - (kb + ha)\left( {{h^2} + {k^2}} \right) = {\left( {hb - ak} \right)^2}\]
\[ \Rightarrow {\left( {hb - ak} \right)^2} + (kb + ha)\left( {{h^2} + {k^2}} \right) = 0\] …….(10)
Equation (10) is in terms of\[\left( {h,y} \right)\].
Substitute
\[\begin{gathered}
h \to x \\
k \to y \\
\end{gathered} \]
Locus of point of intersection in term of ‘x’ and ‘y’
\[ \Rightarrow {\left( {bx - ay} \right)^2} + (by + ax)\left( {{x^2} + {y^2}} \right) = 0\]
Note: Cross multiplication
Assume two equation be
\[{A_{1\;}}{x^2}{\text{ }} + {\text{ }}{B_1}{\text{x }} + {\text{ }}{C_{1\;}} = {\text{ }}0\], and
\[{A_2}{x^2}{\text{ }} + {\text{ }}{B_2}{\text{x }} + {\text{ }}{C_{2\;}} = {\text{ }}0\].
The coefficients of \[{x^2}\] are: \[{A_1}\] and\[{A_2}\].
The coefficients of \[x\] are: \[{B_1}\;and{\text{ }}{B_2}\].
The constant terms are: \[{C_1}\;and{\text{ }}\;{C_2}\]
To solve the equations in a simplified way,

\[\dfrac{{{x^2}}}{{{B_1}{C_2} - {B_2}{C_1}}} = \dfrac{x}{{{C_1}{A_2} - {C_2}{A_1}}} = \dfrac{1}{{{A_1}{C_2} - {A_2}{B_1}}}\]
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




