
Two charges $5\times {{10}^{-8}}C$ and $-3\times {{10}^{-8}}C$ are placed $16cm$ apart. At what points on the line joining of the two charges will be the electric potential zero? Let us assume that the potential at infinity will be zero.
Answer
572.1k+ views
Hint: The electric potential at a point can be found by taking the ratio of the charge at this point to the product of the four-time the value of pi, the permittivity, and the distance to this point. Apply the conditions mentioned in the question and substitute the values in it. This will help you in answering this question.
Complete step-by-step solution
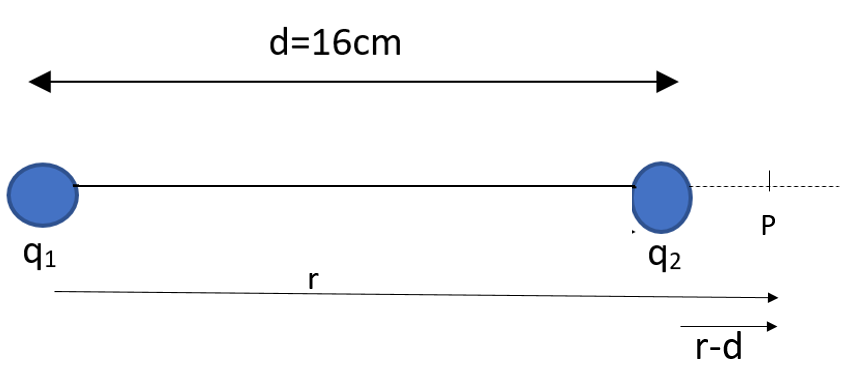
Let P be the point of zero potential at a distance \[r\] from the charge \[1\]. Let the distance between them be given as,
\[d=16cm\]
The electric potential at a point can be found by taking the ratio of the charge at this point to the product of the four time the value of pi, the permittivity and the distance to this point. This can be written as,
\[v=\dfrac{q}{4\pi {{\varepsilon }_{0}}d}\]
In this situation, we can write that,
\[v=\dfrac{{{q}_{1}}}{4\pi {{\varepsilon }_{0}}r}+\dfrac{{{q}_{2}}}{4\pi {{\varepsilon }_{0}}\left( d-r \right)}\]
As it is already mentioned that the potential at the mentioned point is zero. Therefore we can write that,
\[0=\dfrac{{{q}_{1}}}{4\pi {{\varepsilon }_{0}}r}+\dfrac{{{q}_{2}}}{4\pi {{\varepsilon }_{0}}\left( d-r \right)}\]
Simplifying this equation can be shown as,
\[\dfrac{{{q}_{1}}}{r}=\dfrac{-{{q}_{2}}}{\left( d-r \right)}\]
Substituting the values in this equation can be shown as,
\[\dfrac{5\times {{10}^{-8}}}{r}=\dfrac{-3\times {{10}^{-8}}}{\left( 0.16-r \right)}\]
From this equation, the value of \[r\] can be found as,
\[r=40cm\]

When the point P is outside the system, we can write the potential at this point as,
\[v=\dfrac{{{q}_{1}}}{4\pi {{\varepsilon }_{0}}r}+\dfrac{{{q}_{2}}}{4\pi {{\varepsilon }_{0}}\left( r-d \right)}\]
Simplifying this equation can be shown as,
\[\dfrac{{{q}_{1}}}{r}=\dfrac{{{q}_{2}}}{\left( r-d \right)}\]
Substituting the values in the equation will give,
\[\dfrac{5\times {{10}^{-8}}}{r}=\dfrac{-3\times {{10}^{-8}}}{\left( r-0.16 \right)}\]
Therefore the value of \[r\] can be written as,
\[r=10cm\]
Hence the answer for the question has been calculated.
Note: An electric potential is defined as the amount of work required in order to move a unit of electric charge from the reference position to a specific position in an electric field without creating an acceleration. In general, the reference points are taken as the Earth or a point at infinity.
Complete step-by-step solution
Let P be the point of zero potential at a distance \[r\] from the charge \[1\]. Let the distance between them be given as,
\[d=16cm\]
The electric potential at a point can be found by taking the ratio of the charge at this point to the product of the four time the value of pi, the permittivity and the distance to this point. This can be written as,
\[v=\dfrac{q}{4\pi {{\varepsilon }_{0}}d}\]
In this situation, we can write that,
\[v=\dfrac{{{q}_{1}}}{4\pi {{\varepsilon }_{0}}r}+\dfrac{{{q}_{2}}}{4\pi {{\varepsilon }_{0}}\left( d-r \right)}\]
As it is already mentioned that the potential at the mentioned point is zero. Therefore we can write that,
\[0=\dfrac{{{q}_{1}}}{4\pi {{\varepsilon }_{0}}r}+\dfrac{{{q}_{2}}}{4\pi {{\varepsilon }_{0}}\left( d-r \right)}\]
Simplifying this equation can be shown as,
\[\dfrac{{{q}_{1}}}{r}=\dfrac{-{{q}_{2}}}{\left( d-r \right)}\]
Substituting the values in this equation can be shown as,
\[\dfrac{5\times {{10}^{-8}}}{r}=\dfrac{-3\times {{10}^{-8}}}{\left( 0.16-r \right)}\]
From this equation, the value of \[r\] can be found as,
\[r=40cm\]

When the point P is outside the system, we can write the potential at this point as,
\[v=\dfrac{{{q}_{1}}}{4\pi {{\varepsilon }_{0}}r}+\dfrac{{{q}_{2}}}{4\pi {{\varepsilon }_{0}}\left( r-d \right)}\]
Simplifying this equation can be shown as,
\[\dfrac{{{q}_{1}}}{r}=\dfrac{{{q}_{2}}}{\left( r-d \right)}\]
Substituting the values in the equation will give,
\[\dfrac{5\times {{10}^{-8}}}{r}=\dfrac{-3\times {{10}^{-8}}}{\left( r-0.16 \right)}\]
Therefore the value of \[r\] can be written as,
\[r=10cm\]

Hence the answer for the question has been calculated.
Note: An electric potential is defined as the amount of work required in order to move a unit of electric charge from the reference position to a specific position in an electric field without creating an acceleration. In general, the reference points are taken as the Earth or a point at infinity.
Watch videos on
Two charges $5\times {{10}^{-8}}C$ and $-3\times {{10}^{-8}}C$ are placed $16cm$ apart. At what points on the line joining of the two charges will be the electric potential zero? Let us assume that the potential at infinity will be zero.

Electrostatic Potential and Capacitance Class 12 Physics - NCERT EXERCISE 2.1 | Vishal Kumar Sir
Subscribe
 Share
Share likes
390 Views
2 years ago
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

Draw ray diagrams each showing i myopic eye and ii class 12 physics CBSE

Giving reasons state the signs positive or negative class 12 physics CBSE

Explain esterification reaction with the help of a class 12 chemistry CBSE

What is defined as a solenoid Depict a diagram with class 12 physics CBSE



 Watch Video
Watch Video
