
Two blocks A and B of masses 2m and m, respectively are connected by a massless and inextensible string. The whole system is suspended by a massless spring as shown in the figure. The magnitude of the acceleration of A and B immediately after the string is cut, are respectively:
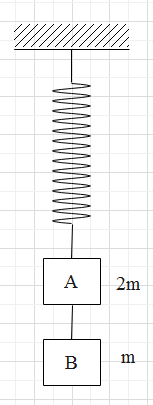
\[A.\,g,\dfrac{g}{2}\]
\[B.\,\dfrac{g}{2},g\]
\[C.\,g,g\]
\[D.\,\dfrac{g}{2},\dfrac{g}{2}\]

Answer
582.9k+ views
Hint: Using free body diagrams of blocks, the number of forces acting can be determined before and after cutting the string. Thus, equating the forces, the expression of acceleration can be obtained.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Consider the FBD of the blocks A and B.
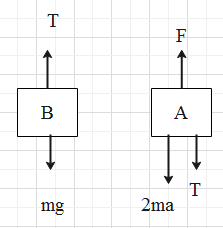
On block B, a normal force mg will be acting in the downward direction. A tension T will also be acting on block B, but, in the upward direction.
On block A, a normal force, that is, a net normal force 2mg will be acting in the downward direction. (One mg of block A and the other mg of block B), as the block B is connected next to block A. In this case, the tension T acts in the downward direction. Even a spring force F will also be acting on the block A, as the block is connected directly to the spring.
Consider the two blocks A and B to be a system.
The FBD of two blocks A and B to be a system
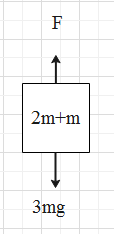
From the above FBD, we get a single force F acting in an upward direction and the normal force 3mg (2mg + mg) acting in the downward direction. So, we get,
\[F=3mg\]
After instant cutting of the string tied between the blocks A and B. The forces acting on the blocks are as discussed below.
Consider the FBD of the blocks A and B after cutting the string.
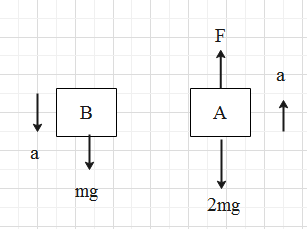
On block A, a force F acts in an upward direction and normal force 2mg acts in a downward direction. As the string is cut, there will be no tension acting on the block. The acceleration will be acting in an upward direction.
So, the equations are,
\[F-2mg=2ma\]
As we have obtained the value of F, so we will substitute the same here.
\[\begin{align}
& 3mg-2mg=2ma \\
& \Rightarrow mg=2ma \\
& \Rightarrow a={}^{g}/{}_{2} \\
\end{align}\]
Similarly, in the case of block B. The normal force mg will be acting in the downward direction and the acceleration a will be acting in the upward direction. As the string is cut, there will be no tension acting on the block.
Thus, the equations are,
\[\begin{align}
& mg=ma \\
& \Rightarrow a=g \\
\end{align}\]
Therefore, the acceleration of block A is \[{}^{g}/{}_{2}\] and that of block B is \[g\],
So, the correct answer is “Option B”.
Note: The direction of forces acting on the blocks should be taken care of. As, one wrong direction, will change the final result. Instead of the acceleration of blocks, the velocity can be asked by giving the value of time taken. In such a case, multiply the acceleration obtained by time.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Consider the FBD of the blocks A and B.

On block B, a normal force mg will be acting in the downward direction. A tension T will also be acting on block B, but, in the upward direction.
On block A, a normal force, that is, a net normal force 2mg will be acting in the downward direction. (One mg of block A and the other mg of block B), as the block B is connected next to block A. In this case, the tension T acts in the downward direction. Even a spring force F will also be acting on the block A, as the block is connected directly to the spring.
Consider the two blocks A and B to be a system.
The FBD of two blocks A and B to be a system

From the above FBD, we get a single force F acting in an upward direction and the normal force 3mg (2mg + mg) acting in the downward direction. So, we get,
\[F=3mg\]
After instant cutting of the string tied between the blocks A and B. The forces acting on the blocks are as discussed below.
Consider the FBD of the blocks A and B after cutting the string.

On block A, a force F acts in an upward direction and normal force 2mg acts in a downward direction. As the string is cut, there will be no tension acting on the block. The acceleration will be acting in an upward direction.
So, the equations are,
\[F-2mg=2ma\]
As we have obtained the value of F, so we will substitute the same here.
\[\begin{align}
& 3mg-2mg=2ma \\
& \Rightarrow mg=2ma \\
& \Rightarrow a={}^{g}/{}_{2} \\
\end{align}\]
Similarly, in the case of block B. The normal force mg will be acting in the downward direction and the acceleration a will be acting in the upward direction. As the string is cut, there will be no tension acting on the block.
Thus, the equations are,
\[\begin{align}
& mg=ma \\
& \Rightarrow a=g \\
\end{align}\]
Therefore, the acceleration of block A is \[{}^{g}/{}_{2}\] and that of block B is \[g\],
So, the correct answer is “Option B”.
Note: The direction of forces acting on the blocks should be taken care of. As, one wrong direction, will change the final result. Instead of the acceleration of blocks, the velocity can be asked by giving the value of time taken. In such a case, multiply the acceleration obtained by time.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




