
The values of \[\alpha \] if \[(\alpha ,2\alpha )\]lies inside the \[\Delta ABC\] if
\[A(0,2),B(2,0)\]and \[C(4,4)\]
(a) \[\alpha \in \left( \dfrac{1}{3},\dfrac{2}{3} \right)\]
(b) \[\alpha \in \left( \dfrac{2}{3},1 \right)\]
(c) \[\alpha \in \left( \dfrac{2}{3},\dfrac{4}{3} \right)\]
(d) \[\alpha \in \left( \dfrac{1}{3},1 \right)\]
Answer
625.5k+ views
Hint: Find the equation of the lines which are forming the triangle.
The figure for the given problem is as follows:
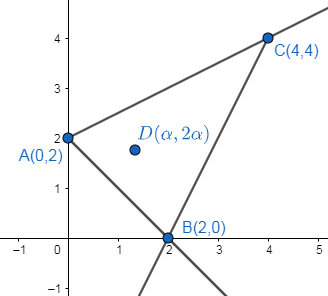
Now we will find the equations of all the three sides of the triangle.
We know equation of line between the two points \[({{x}_{1}},{{y}_{1}})\] and \[({{x}_{2}},{{y}_{2}})\]can be written as,
\[\dfrac{y-{{y}_{1}}}{{{y}_{2}}-{{y}_{1}}}=\dfrac{x-{{x}_{1}}}{{{x}_{2}}-{{x}_{1}}}\]
Applying the above formula, the equation of side AB is,
\[\dfrac{y-2}{0-2}=\dfrac{x-0}{2-0}\]
\[\dfrac{y-2}{-2}=\dfrac{x}{2}\]
\[\dfrac{y-2}{-1}=\dfrac{x}{1}\]
On cross multiplication, we get
\[y-2=-x\]
\[x+y-2=0........(i)\]
Similarly, the equation of side BC is,
\[\dfrac{y-0}{4-0}=\dfrac{x-2}{4-2}\]
\[\dfrac{y}{4}=\dfrac{x-2}{2}\]
\[\dfrac{y}{2}=\dfrac{x-2}{1}\]
On cross multiplication, we get
\[y=2x-4\]
\[2x-y-4=0........(ii)\]
And, the equation of side AC is,
\[\dfrac{y-2}{4-2}=\dfrac{x-0}{4-0}\]
\[\dfrac{y-2}{2}=\dfrac{x}{4}\]
\[\dfrac{y-2}{1}=\dfrac{x}{2}\]
On cross multiplication, we get
\[2y-4=x\]
\[x-2y+4=0........(iii)\]
Therefore the figure with equations is,
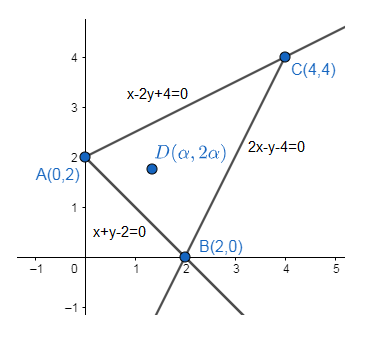
Two given points \[\left( {{x}_{1}},\text{ }{{y}_{1}} \right)\]and \[\left( {{x}_{2}},\text{ }{{y}_{2}} \right)\]will lie on the same side of the line \[ax+by+c=0\] if \[a{{x}_{1}}+b{{y}_{1}}+c\] and \[a{{x}_{2}}+b{{y}_{2}}+c\] will have same signs.
From the above figure it is clear that the points B and D lie on the same side of the line AC. So, it should satisfy the above condition, i.e.,
\[2-2(0)+4=6>0\]
So, when we substitute the value of point D in line AC, it should be greater than zero, i.e.,
\[\alpha -2(2\alpha )+4>0\]
\[\alpha -4\alpha +4>0\]
\[-3\alpha +4>0\]
\[4>3\alpha \]
\[\Rightarrow \alpha <\dfrac{4}{3}.........(iv)\]
Now from the above figure it is clear that the points C and D lie on the same side of the line AB. Substitute value of point C in equation of line AB, we get
\[4+4-2=6>0\]
So, when we substitute the value of point D in line AB, it should be greater than zero, i.e.,
\[\alpha +2\alpha -2>0\]
\[3\alpha -2>0\]
\[3\alpha >2\]
\[\Rightarrow \alpha >\dfrac{2}{3}.........(v)\]
So, from equation (iv) and (v), we get
\[\alpha \in \left( \dfrac{2}{3},\dfrac{4}{3} \right)\]
Hence the correct answer is option (c).
Note: We can solve this by finding boundaries of x and y. But the options are given in fraction form, using this method it gives the exact answer.
The figure for the given problem is as follows:

Now we will find the equations of all the three sides of the triangle.
We know equation of line between the two points \[({{x}_{1}},{{y}_{1}})\] and \[({{x}_{2}},{{y}_{2}})\]can be written as,
\[\dfrac{y-{{y}_{1}}}{{{y}_{2}}-{{y}_{1}}}=\dfrac{x-{{x}_{1}}}{{{x}_{2}}-{{x}_{1}}}\]
Applying the above formula, the equation of side AB is,
\[\dfrac{y-2}{0-2}=\dfrac{x-0}{2-0}\]
\[\dfrac{y-2}{-2}=\dfrac{x}{2}\]
\[\dfrac{y-2}{-1}=\dfrac{x}{1}\]
On cross multiplication, we get
\[y-2=-x\]
\[x+y-2=0........(i)\]
Similarly, the equation of side BC is,
\[\dfrac{y-0}{4-0}=\dfrac{x-2}{4-2}\]
\[\dfrac{y}{4}=\dfrac{x-2}{2}\]
\[\dfrac{y}{2}=\dfrac{x-2}{1}\]
On cross multiplication, we get
\[y=2x-4\]
\[2x-y-4=0........(ii)\]
And, the equation of side AC is,
\[\dfrac{y-2}{4-2}=\dfrac{x-0}{4-0}\]
\[\dfrac{y-2}{2}=\dfrac{x}{4}\]
\[\dfrac{y-2}{1}=\dfrac{x}{2}\]
On cross multiplication, we get
\[2y-4=x\]
\[x-2y+4=0........(iii)\]
Therefore the figure with equations is,

Two given points \[\left( {{x}_{1}},\text{ }{{y}_{1}} \right)\]and \[\left( {{x}_{2}},\text{ }{{y}_{2}} \right)\]will lie on the same side of the line \[ax+by+c=0\] if \[a{{x}_{1}}+b{{y}_{1}}+c\] and \[a{{x}_{2}}+b{{y}_{2}}+c\] will have same signs.
From the above figure it is clear that the points B and D lie on the same side of the line AC. So, it should satisfy the above condition, i.e.,
\[2-2(0)+4=6>0\]
So, when we substitute the value of point D in line AC, it should be greater than zero, i.e.,
\[\alpha -2(2\alpha )+4>0\]
\[\alpha -4\alpha +4>0\]
\[-3\alpha +4>0\]
\[4>3\alpha \]
\[\Rightarrow \alpha <\dfrac{4}{3}.........(iv)\]
Now from the above figure it is clear that the points C and D lie on the same side of the line AB. Substitute value of point C in equation of line AB, we get
\[4+4-2=6>0\]
So, when we substitute the value of point D in line AB, it should be greater than zero, i.e.,
\[\alpha +2\alpha -2>0\]
\[3\alpha -2>0\]
\[3\alpha >2\]
\[\Rightarrow \alpha >\dfrac{2}{3}.........(v)\]
So, from equation (iv) and (v), we get
\[\alpha \in \left( \dfrac{2}{3},\dfrac{4}{3} \right)\]
Hence the correct answer is option (c).
Note: We can solve this by finding boundaries of x and y. But the options are given in fraction form, using this method it gives the exact answer.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




