
The total number of isomers for a square planar complex
$\left[ {M{\text{ }}\left( F \right)\left( {Cl} \right)\left( {SCN} \right)\left( {NO2} \right)} \right]:$
$A){\text{ }}12$
B) $8$
C) $16$
D) $\;14$
Answer
517.5k+ views
Hint :Isomerism is the phenomenon in which more than one compound has the same chemical formula but different chemical structures. Chemical compounds that have identical chemical formulas but differ in properties and the arrangement of atoms in the molecule are called isomers.
Complete Step By Step Answer:
The total number of isomer for a square planar complex $\left[ {M\left( F \right)\left( {Cl} \right)\left( {SCN} \right)\left( {NO{\text{ }}2{\text{ }}{\text{ }}} \right)} \right]{\text{ }}is{\text{ }}12.$
In principle, square planar geometry is achieved by flattening a tetrahedron. As such, the interconversion of tetrahedral and square planar geometries provides a pathway for the isomerization of tetrahedral compounds.
Square planar could be a molecular shape that results when there are four bonds and two lone pairs on the central atom within the molecule.
Two orbitals contain lone pairs of electrons on opposite sides of the central atom. The remaining four atoms connected to the central atom give the molecule a square planar shape.
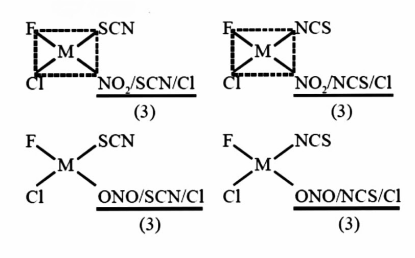
These complexes differ from the octahedral complexes in that the orbital levels are raised in energy because of the interference with electrons from ligands. This implies that almost all square planar complexes are low spin, strong field ligands
Hence option (A) is correct.
Note :
The square planar molecular geometry in chemistry describes the stereochemistry that is adopted by certain chemical compounds. In square planar molecular geometry, a central atom is surrounded by constituent atoms, which form the corners of a square on the same plane.
Complete Step By Step Answer:
The total number of isomer for a square planar complex $\left[ {M\left( F \right)\left( {Cl} \right)\left( {SCN} \right)\left( {NO{\text{ }}2{\text{ }}{\text{ }}} \right)} \right]{\text{ }}is{\text{ }}12.$
In principle, square planar geometry is achieved by flattening a tetrahedron. As such, the interconversion of tetrahedral and square planar geometries provides a pathway for the isomerization of tetrahedral compounds.
Square planar could be a molecular shape that results when there are four bonds and two lone pairs on the central atom within the molecule.
Two orbitals contain lone pairs of electrons on opposite sides of the central atom. The remaining four atoms connected to the central atom give the molecule a square planar shape.

These complexes differ from the octahedral complexes in that the orbital levels are raised in energy because of the interference with electrons from ligands. This implies that almost all square planar complexes are low spin, strong field ligands
Hence option (A) is correct.
Note :
The square planar molecular geometry in chemistry describes the stereochemistry that is adopted by certain chemical compounds. In square planar molecular geometry, a central atom is surrounded by constituent atoms, which form the corners of a square on the same plane.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




