
The structure of the carboxylate ion is best represented as:
A.
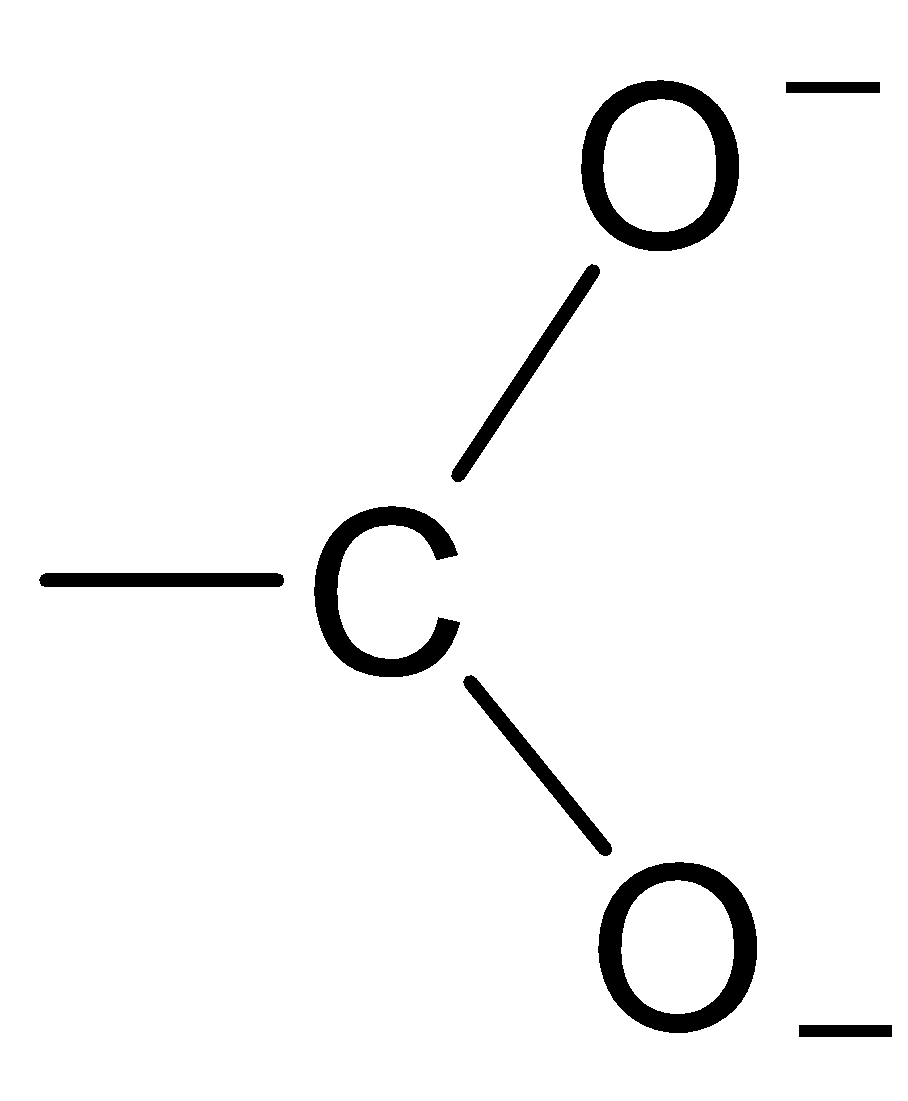
B.
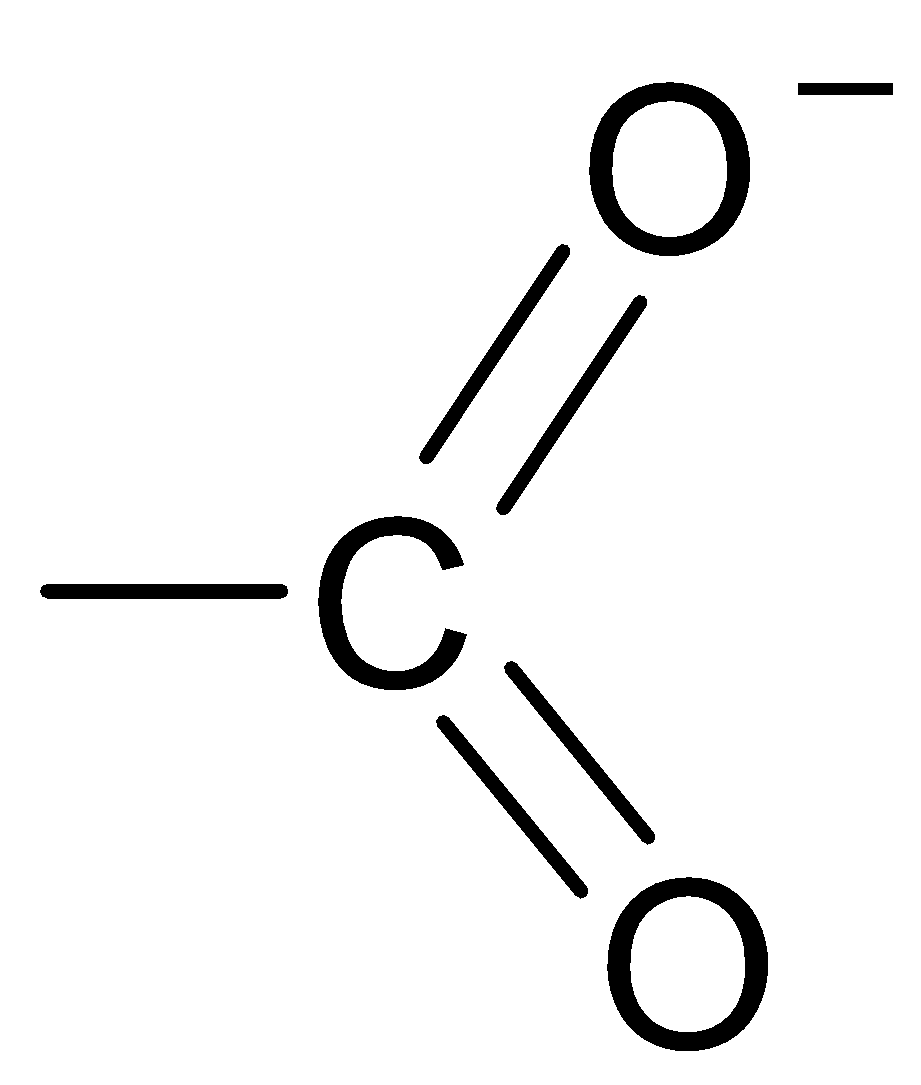
C.
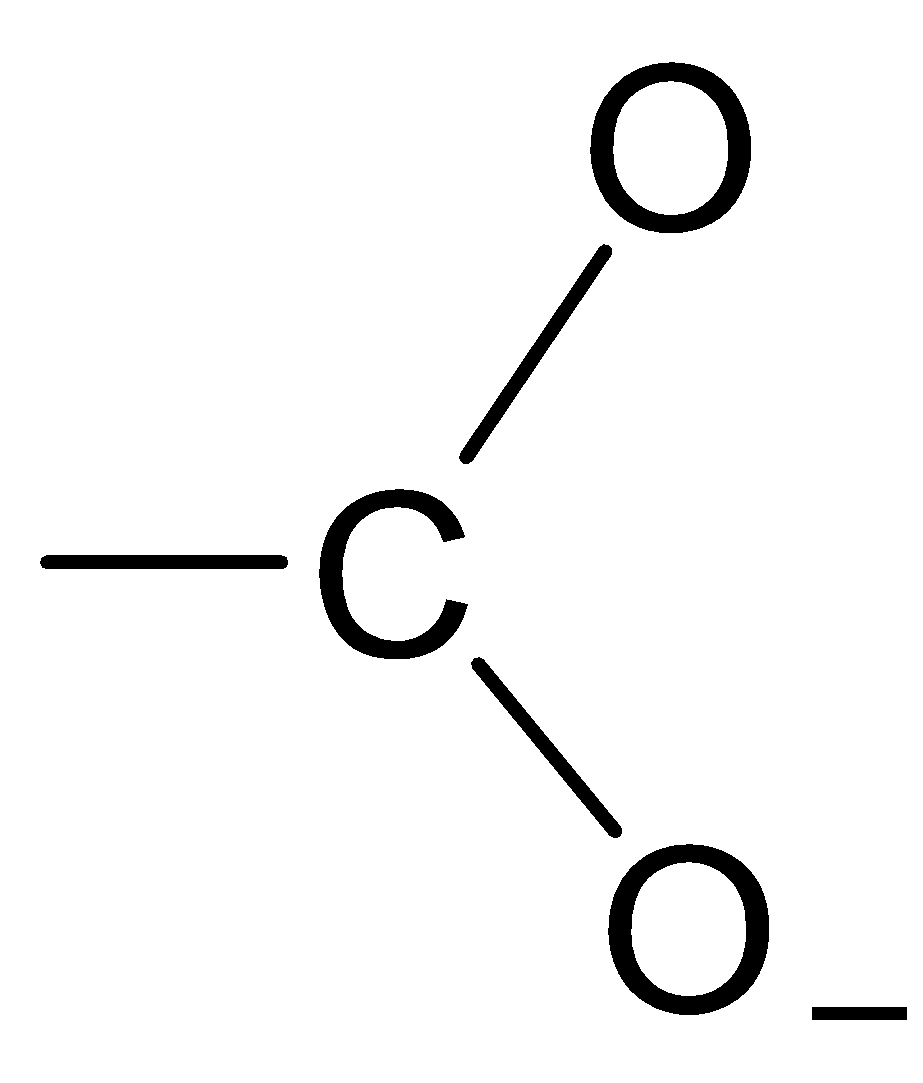
D.
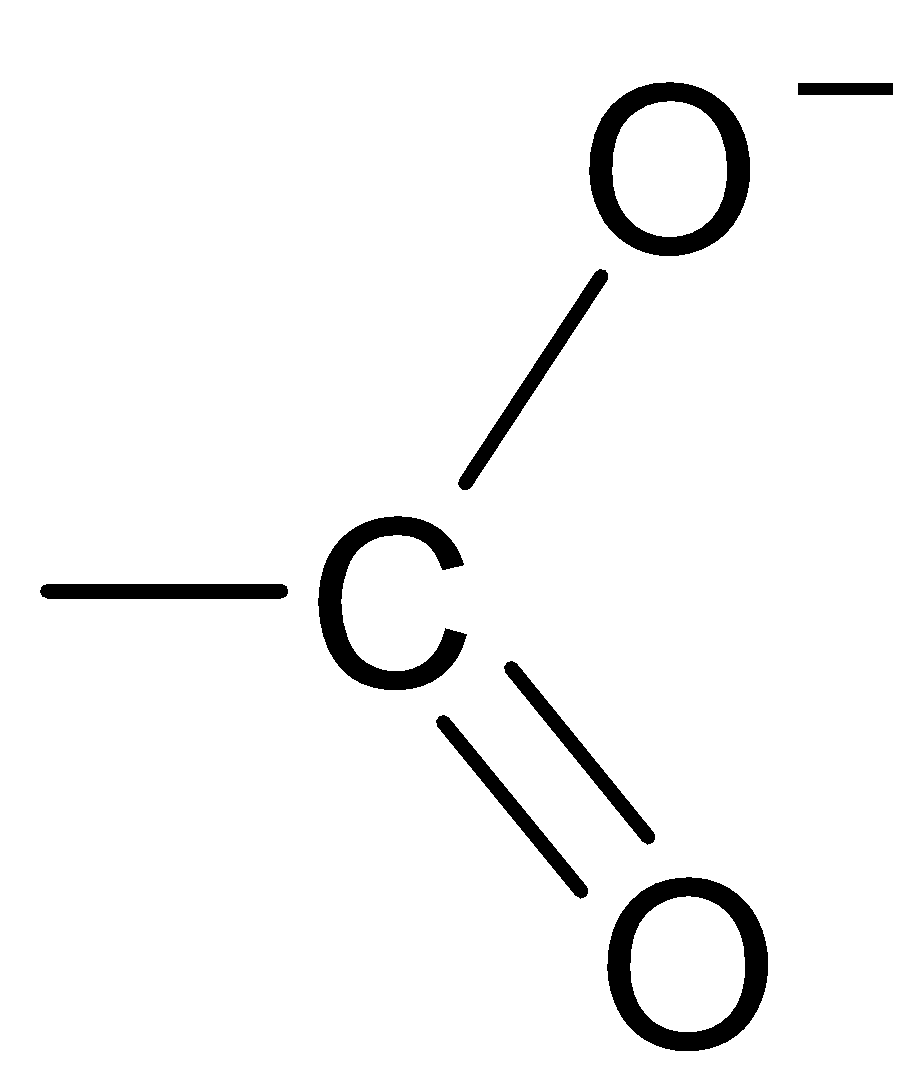




Answer
581.4k+ views
Hint: A carboxylate ion is considered to be the conjugate base of a carboxylic acid.
The organic compounds which contain the carboxyl group, i.e., the ${\text{ - COOH}}$ group as the functional group are called carboxylic acids.
The carboxylate ion is an anion with only a single negative charge.
Complete step by step answer:
The name ‘carboxyl’ is derived from ‘carb’ from carbonyl group and ‘oxyl’ from hydroxyl group.
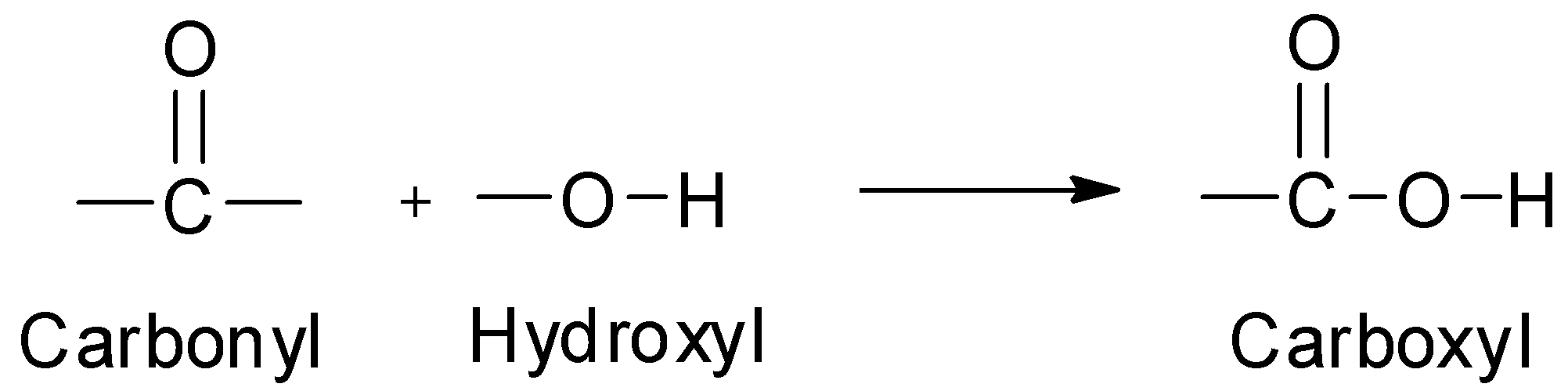
In other words, a carboxyl group is made up of a carbonyl group joined to a hydroxyl group.
In a carboxyl group, the carbon atom is attached to two oxygen atoms: one by a double bond and the other by a single bond which, in turn, is linked to a hydrogen atom by a single bond. The remaining free valency of the carbon atom of the carboxyl group is satisfied by an alkyl or an aryl group.
Thus, the carboxylate ions are formed by the deprotonation of the carboxylic acids as they can be easily deprotonated by many bases like sodium hydroxide or sodium bicarbonate.
Thus, the dissociation of carboxylic acids into carboxylate ions and protons is much more easier than that of alcohols dissociating into an alkoxide ion and a proton as the carboxylate ion is stabilized by resonance. The negative charge which is left after the deprotonation of the carboxyl group is delocalized between the two electronegative oxygen atoms.
Thus, the carboxylate ion can be best represented as the resonance hybrid of the following structures.
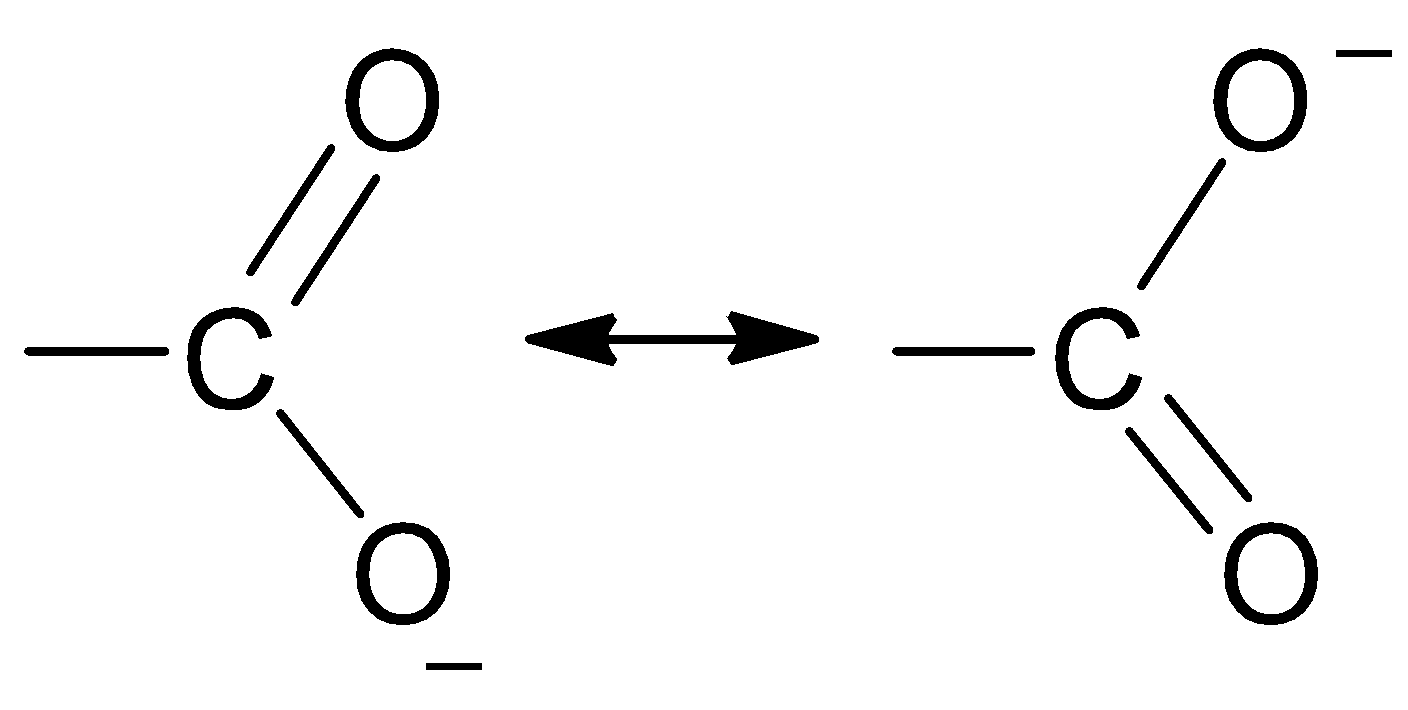
So, the correct option is D.
Note:
The carboxylate ions act as good nucleophiles and react with alkyl halides to form esters.
The nucleophilic character of the carboxylate ion is stronger than the halide ions but weaker than the alkoxide and hydroxide ions.
Examples of carboxylate ion are the formate ion ${\text{HCO}}{{\text{O}}^{\text{ - }}}$ and the acetate ion ${\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_3}{\text{CO}}{{\text{O}}^{\text{ - }}}$ .
The organic compounds which contain the carboxyl group, i.e., the ${\text{ - COOH}}$ group as the functional group are called carboxylic acids.
The carboxylate ion is an anion with only a single negative charge.
Complete step by step answer:
The name ‘carboxyl’ is derived from ‘carb’ from carbonyl group and ‘oxyl’ from hydroxyl group.
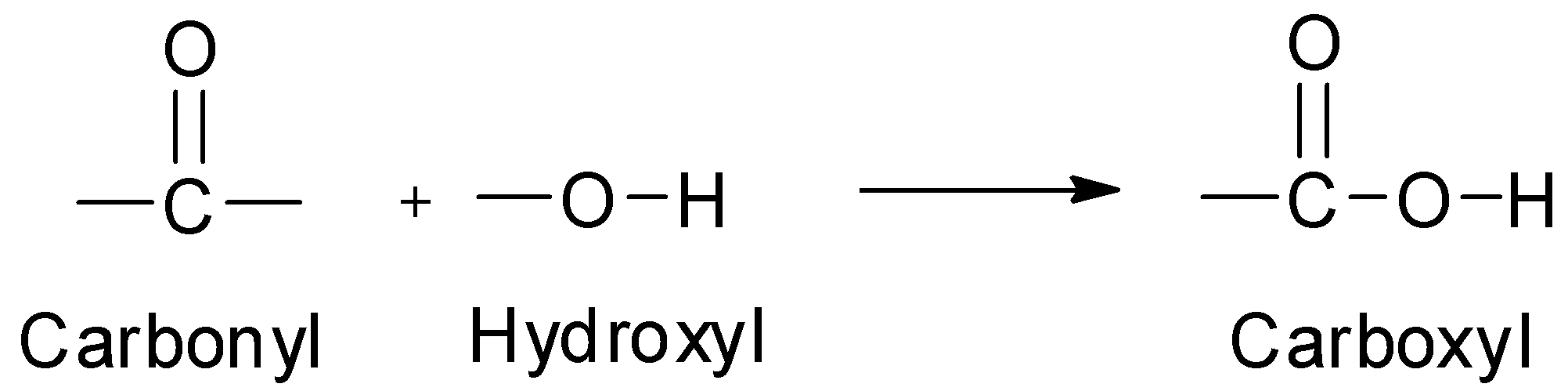
In other words, a carboxyl group is made up of a carbonyl group joined to a hydroxyl group.
In a carboxyl group, the carbon atom is attached to two oxygen atoms: one by a double bond and the other by a single bond which, in turn, is linked to a hydrogen atom by a single bond. The remaining free valency of the carbon atom of the carboxyl group is satisfied by an alkyl or an aryl group.
Thus, the carboxylate ions are formed by the deprotonation of the carboxylic acids as they can be easily deprotonated by many bases like sodium hydroxide or sodium bicarbonate.
Thus, the dissociation of carboxylic acids into carboxylate ions and protons is much more easier than that of alcohols dissociating into an alkoxide ion and a proton as the carboxylate ion is stabilized by resonance. The negative charge which is left after the deprotonation of the carboxyl group is delocalized between the two electronegative oxygen atoms.
Thus, the carboxylate ion can be best represented as the resonance hybrid of the following structures.

So, the correct option is D.
Note:
The carboxylate ions act as good nucleophiles and react with alkyl halides to form esters.
The nucleophilic character of the carboxylate ion is stronger than the halide ions but weaker than the alkoxide and hydroxide ions.
Examples of carboxylate ion are the formate ion ${\text{HCO}}{{\text{O}}^{\text{ - }}}$ and the acetate ion ${\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_3}{\text{CO}}{{\text{O}}^{\text{ - }}}$ .
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




