
The stability of carbocation $${1^o},{2^o},{3^o}$$ and benzyl carbocation is of order:
A) $${1^o} > {2^o} > {3^o} > benzyl$$
B) $$benzyl > {3^o} > {2^o} > {1^o}$$
C) $${3^o} > {2^o} > {1^o} > benzyl$$
D) $${3^o} > benzyl > {2^o} > {1^o}$$
Answer
561k+ views
Hint: The benzyl carbocation is a resonance stabilized carbocation. It has four resonance structures which makes its stability good. It shares the charges of four different atoms making itself the most stable. The tertiary carbocation is also stable due to the presence of inductive effect whereas in primary carbocation we have only resonance effect.
Complete answer:
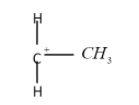
An electron donating group is defined as the group or atom which releases its electron density to its adjacent or neighbouring atoms from itself by the resonance effect or inductive effects. The carbocations are said to be stabilized because of the presence of electron donating groups in them. The stability of the carbocations increases from primary carbocation to tertiary carbocation as the methyl group increases. This is due to the hyconjugation which therefore stabilizes by donating the electrons to carbon hydrogen sigma bonds to the empty p orbital of the carbocation. But out of all these carbocation the benzyl carbocation is considered to be most stable because of the delocalization of charge over the ring due to resonance of $$\pi electrons$$.
For more clarification look at the structure of the following benzyl carbocation:
The benzyl carbocation:
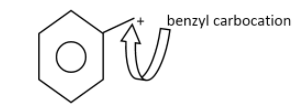
The primary carbocation :
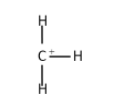
The secondary carbocation:
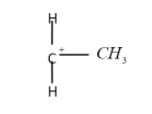
The tertiary carbocation:
So the correct option for this question will be option ‘B’.
Note: Inductive effect is defined as the phenomenon where a permanent dipole arises in the molecule because of unequal sharing of electrons. The resonance or the mesomeric effect determines the polarity which is induced in the molecule by reacting the lone pair of electron and a pi bond. Hyperconjugation is referred to as the stabilising interaction that results in the interaction of electrons in a sigma bond with empty or partially filled orbital so that an extended molecular orbital is formed which increases the stability of the system.
Complete answer:
An electron donating group is defined as the group or atom which releases its electron density to its adjacent or neighbouring atoms from itself by the resonance effect or inductive effects. The carbocations are said to be stabilized because of the presence of electron donating groups in them. The stability of the carbocations increases from primary carbocation to tertiary carbocation as the methyl group increases. This is due to the hyconjugation which therefore stabilizes by donating the electrons to carbon hydrogen sigma bonds to the empty p orbital of the carbocation. But out of all these carbocation the benzyl carbocation is considered to be most stable because of the delocalization of charge over the ring due to resonance of $$\pi electrons$$.
For more clarification look at the structure of the following benzyl carbocation:
The benzyl carbocation:

The primary carbocation :

The secondary carbocation:

The tertiary carbocation:

So the correct option for this question will be option ‘B’.
Note: Inductive effect is defined as the phenomenon where a permanent dipole arises in the molecule because of unequal sharing of electrons. The resonance or the mesomeric effect determines the polarity which is induced in the molecule by reacting the lone pair of electron and a pi bond. Hyperconjugation is referred to as the stabilising interaction that results in the interaction of electrons in a sigma bond with empty or partially filled orbital so that an extended molecular orbital is formed which increases the stability of the system.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Chemistry: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Draw a diagram of nephron and explain its structur class 11 biology CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

Chemical formula of Bleaching powder is A Ca2OCl2 B class 11 chemistry CBSE

Name the part of the brain responsible for the precision class 11 biology CBSE

The growth of tendril in pea plants is due to AEffect class 11 biology CBSE

One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE




