
The significance of meiosis is that it
(a) Produce four cells having chromosomal numbers equal to the mother cell.
(b) Occurs in all types of cells.
(c) Maintains the constant chromosomes number of a particular species
(d) Growth of animal body organ
Answer
528.5k+ views
Hint: Meiosis is a specialized type of cell division found in special types of cells at a specific period. It is reported in diploid germ cells of the sex organs. In this type of cell division, the cell divides two times.
Complete answer:
In meiosis, After the DNA replication, two rounds of cell division occur to produce four daughter cells with half the number of chromosomes as the original parent cell. These two meiotic divisions are known as meiosis I and meiosis II. Because the number of chromosomes is halved during the meiosis, this allows gametes to fuse forming a zygote containing a mixture of paternal and maternal chromosomes. so, in this way meiosis and fertilization facilitate sexual reproduction with successive generations maintaining the same number of chromosomes.
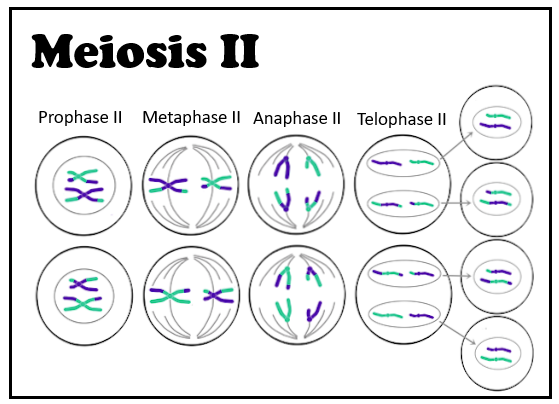
So, the correct answer is, ‘Maintains the number of the constant chromosome of a particular species.’
Additional Information:
- Meiosis was first demonstrated by Van Benden in 1883 A.D. but was described by Winiwarter in 1900 A.D.
- The term meiosis was given by Farmer and Moore in 1905 A.D.
- Meiosis-I and meiosis-II occur one after another with short or no interphase.
- In meiosis-I, the prophase-I is of the longest duration.
- The four haploid cells produced during meiosis may or may not be of equal size.
- Meiosis-II is also known as equational or homotypical division because the number of chromosomes remains the same as in meiosis-I.
Note: Reproduction without meiosis will result in tetraploidy (4n), while sexual reproduction without fertilization will lead to haploidy in an organism. Meiosis is also known as reductional division because one parent cell produces four daughter cells each having half the number of chromosomes and DNA amount than the normal parental cell.
Complete answer:
In meiosis, After the DNA replication, two rounds of cell division occur to produce four daughter cells with half the number of chromosomes as the original parent cell. These two meiotic divisions are known as meiosis I and meiosis II. Because the number of chromosomes is halved during the meiosis, this allows gametes to fuse forming a zygote containing a mixture of paternal and maternal chromosomes. so, in this way meiosis and fertilization facilitate sexual reproduction with successive generations maintaining the same number of chromosomes.

So, the correct answer is, ‘Maintains the number of the constant chromosome of a particular species.’
Additional Information:
- Meiosis was first demonstrated by Van Benden in 1883 A.D. but was described by Winiwarter in 1900 A.D.
- The term meiosis was given by Farmer and Moore in 1905 A.D.
- Meiosis-I and meiosis-II occur one after another with short or no interphase.
- In meiosis-I, the prophase-I is of the longest duration.
- The four haploid cells produced during meiosis may or may not be of equal size.
- Meiosis-II is also known as equational or homotypical division because the number of chromosomes remains the same as in meiosis-I.
Note: Reproduction without meiosis will result in tetraploidy (4n), while sexual reproduction without fertilization will lead to haploidy in an organism. Meiosis is also known as reductional division because one parent cell produces four daughter cells each having half the number of chromosomes and DNA amount than the normal parental cell.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




