
The shape of the interference fringes, on the screen, is
A. Circle
B. Ellipse
C. Parabola
D. Straight line

Answer
583.8k+ views
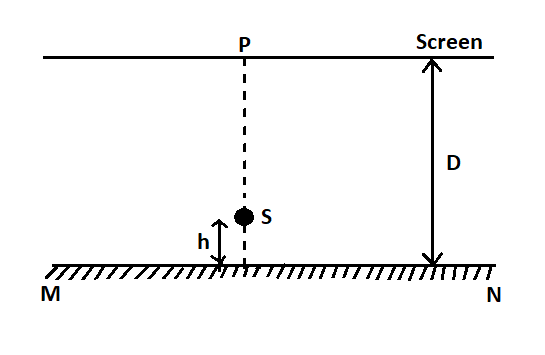
Hint: In the figure, we have a mirror $MN$. A point source $S$ due to the reflection of the mirror at a distance. We have a screen placed at a distance $D$. We have to find the shape of the interference fringes formed on the fringes. Interference happens when two rays from a coherent source interfere with each other. In such a case we will get a pattern of alternate bright and dark fringes.
Complete step by step answer:
We have the setup of the mirror and the object given in the figure.
We know that we need two rays for the formation of an interference pattern.
Therefore, let us consider another point source as shown in the figure below.
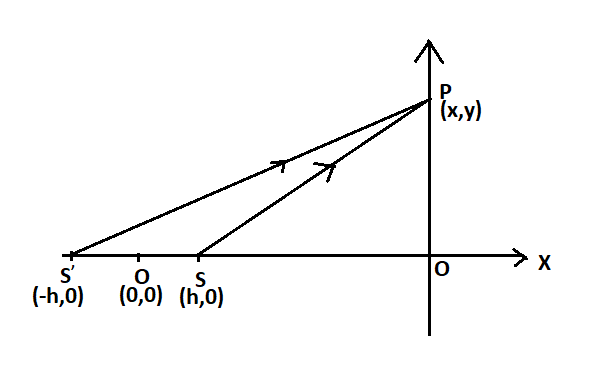
Let ${S'}$ be the other point source due to the reflection of the mirror.
The two rays $S$ and ${S'}$ are coherent and can produce an interference pattern.
Let us consider that the two rays meet at a point $P$ on the screen,
We can write the distance $SP$ as,
$SP = \sqrt {{{(x - h)}^2} + {y^2}} $ (using hypotenuse theorem)
We can write the distance ${S'}P$ as,
${S'}P = \sqrt {{{(x + h)}^2} + {y^2}} $
Let us take $\Delta $to be the path difference at the point $P$
The path difference can be written as,
$\Delta = {S'}P - SP$
From this we can write,
$\Delta + SP = {S'}P$
Squaring on both sides, we get
${\left( {\Delta + SP} \right)^2} = {\left( {{S'}P} \right)^2}$
Substituting the values of $SP$and ${S'}P$ we get
\[{\left( {\Delta + \sqrt {{{(x - h)}^2} + {y^2}} } \right)^2} = {\left( {\sqrt {{{\left( {x + h} \right)}^2} + {y^2}} } \right)^2}\]
On solving we get
${\Delta ^2} + \left( {{x^2} + {h^2} - 2hx} \right) + {y^2} + 2\Delta \sqrt {{{(x - h)}^2} + {y^2}} = \left( {{x^2} + {h^2} + 2xh} \right) + {y^2}$
Cancelling the common terms and rearranging the equation we get,
${\Delta ^2} - 4hx = - 2\Delta \sqrt {{{\left( {x - h} \right)}^2} + {y^2}} $
Again squaring the equation,
${\left( {{\Delta ^2} - 4hx} \right)^2} = {\left( { - 2\Delta \sqrt {{{\left( {x - h} \right)}^2} + {y^2}} } \right)^2}$
Squaring we get
${\Delta ^4} + 16{h^2}{x^2} - 8hx{\Delta ^2} = 4{\Delta ^2}({x^2} + {h^2} - 2hx) + {y^2}$
Expanding the equation we get,
${\Delta ^4} + 16{h^2}{x^2} - 8hx{\Delta ^2} = 4{\Delta ^2}{x^2} + 4{\Delta ^2}{h^2} - 8hx{\Delta ^2} + {y^2}$
Eliminating the common terms and rearranging the equation we get,
$16{h^2}{x^2} - 4{\Delta ^2}{x^2} + {y^2} = 4{\Delta ^2}{h^2} - {\Delta ^4}$
Making the LHS in terms of ${x^2}$and ${y^2}$we get
$\left( {16{h^2} - 4{\Delta ^2}} \right){x^2} + {y^2} = 4{h^2}{\Delta ^2} - {\Delta ^4}$
This equation is of the form, ${x^2} + {y^2} = {r^2}$
This is the equation for circle,
Hence fringes will appear circular.
So, the correct answer is “Option A”.
Note:
Light waves are considered electromagnetic waves. When two light waves of the same frequency overlap with each other interference happens and we get a pattern on the screen. The effect of the resultant pattern will depend on the amplitude of waves as well as the phases of the two waves. The resultant wave of interference is explained by the principle of superposition.
Complete step by step answer:
We have the setup of the mirror and the object given in the figure.
We know that we need two rays for the formation of an interference pattern.
Therefore, let us consider another point source as shown in the figure below.

Let ${S'}$ be the other point source due to the reflection of the mirror.
The two rays $S$ and ${S'}$ are coherent and can produce an interference pattern.
Let us consider that the two rays meet at a point $P$ on the screen,
We can write the distance $SP$ as,
$SP = \sqrt {{{(x - h)}^2} + {y^2}} $ (using hypotenuse theorem)
We can write the distance ${S'}P$ as,
${S'}P = \sqrt {{{(x + h)}^2} + {y^2}} $
Let us take $\Delta $to be the path difference at the point $P$
The path difference can be written as,
$\Delta = {S'}P - SP$
From this we can write,
$\Delta + SP = {S'}P$
Squaring on both sides, we get
${\left( {\Delta + SP} \right)^2} = {\left( {{S'}P} \right)^2}$
Substituting the values of $SP$and ${S'}P$ we get
\[{\left( {\Delta + \sqrt {{{(x - h)}^2} + {y^2}} } \right)^2} = {\left( {\sqrt {{{\left( {x + h} \right)}^2} + {y^2}} } \right)^2}\]
On solving we get
${\Delta ^2} + \left( {{x^2} + {h^2} - 2hx} \right) + {y^2} + 2\Delta \sqrt {{{(x - h)}^2} + {y^2}} = \left( {{x^2} + {h^2} + 2xh} \right) + {y^2}$
Cancelling the common terms and rearranging the equation we get,
${\Delta ^2} - 4hx = - 2\Delta \sqrt {{{\left( {x - h} \right)}^2} + {y^2}} $
Again squaring the equation,
${\left( {{\Delta ^2} - 4hx} \right)^2} = {\left( { - 2\Delta \sqrt {{{\left( {x - h} \right)}^2} + {y^2}} } \right)^2}$
Squaring we get
${\Delta ^4} + 16{h^2}{x^2} - 8hx{\Delta ^2} = 4{\Delta ^2}({x^2} + {h^2} - 2hx) + {y^2}$
Expanding the equation we get,
${\Delta ^4} + 16{h^2}{x^2} - 8hx{\Delta ^2} = 4{\Delta ^2}{x^2} + 4{\Delta ^2}{h^2} - 8hx{\Delta ^2} + {y^2}$
Eliminating the common terms and rearranging the equation we get,
$16{h^2}{x^2} - 4{\Delta ^2}{x^2} + {y^2} = 4{\Delta ^2}{h^2} - {\Delta ^4}$
Making the LHS in terms of ${x^2}$and ${y^2}$we get
$\left( {16{h^2} - 4{\Delta ^2}} \right){x^2} + {y^2} = 4{h^2}{\Delta ^2} - {\Delta ^4}$
This equation is of the form, ${x^2} + {y^2} = {r^2}$
This is the equation for circle,
Hence fringes will appear circular.
So, the correct answer is “Option A”.
Note:
Light waves are considered electromagnetic waves. When two light waves of the same frequency overlap with each other interference happens and we get a pattern on the screen. The effect of the resultant pattern will depend on the amplitude of waves as well as the phases of the two waves. The resultant wave of interference is explained by the principle of superposition.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

The largest wind power cluster is located in the state class 11 social science CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

State and prove Bernoullis theorem class 11 physics CBSE

What steps did the French revolutionaries take to create class 11 social science CBSE

Which among the following are examples of coming together class 11 social science CBSE




