
The reaction, \[Phenol\xrightarrow[{NaOH}]{{{K_2}{S_2}{O_8}}}Quinol\], is called
A) Lederer-Manasse reaction
B) Reimer-Tiemann reaction
C) Elbs persulfate oxidation
D) Kolbe’s reaction
Answer
569.4k+ views
Hint: As we can see that the above mechanism is applied to get quinol from phenol in the presence of a base \[NaOH\] and \[{K_2}{S_2}{O_8}\]. We also know that quinol is commonly known as the dihydric phenol having two alcoholic groups on opposite places of the benzene ring.
Complete step-by-step answer:
The following reactions involve phenol as their reactant-
A) First is the Lederer-Manasse reaction: This reaction deals with phenol and formaldehyde under basic conditions and is referred to as the Lederer-Manasse reaction. The resulting products from this reaction are known as “shellac substitutes”, which are soluble in alcohol, acetone, and alkaline hydroxide and melt on heating and re-solidify after cooling.
In this reaction phenol is treated at low temperature in the presence of diluted acid or alkali to yield ortho-hydroxy-benzyl alcohol or para hydroxy benzyl alcohol.
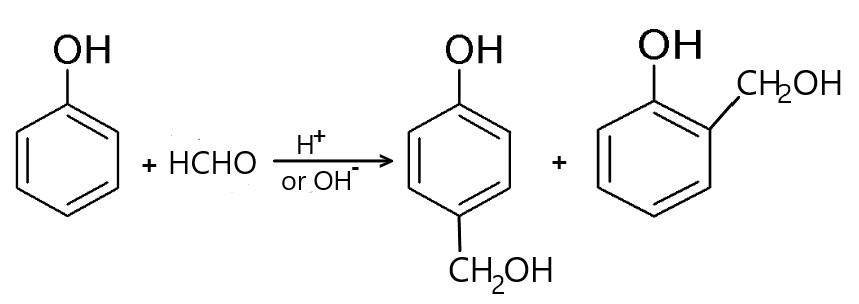
Hence it is not the required equation.
B) Then we have Reimer-Tiemann reaction: We know that Reimer-Tiemann reaction takes place when phenol is treated with \[CHC{l_3}\]in the presence of \[NaOH\] then an aldehyde group is introduced at the ortho-position of the benzene ring leading to the formation of ortho-hydroxy benzaldehyde.
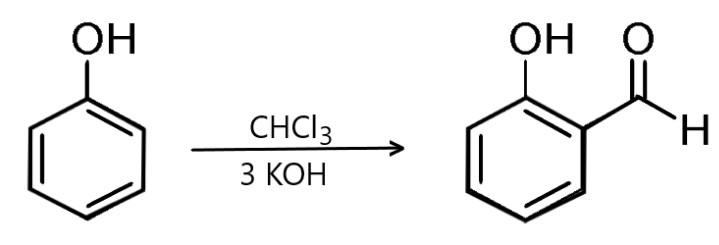
Hence the used reagent is not the same therefore this is not the required reaction.
C) Then comes the Elbs persulfate oxidation- reaction: In this reaction monohydric phenols are oxidized to dihydric phenols by alkaline persulfate. Hydroxylation occurs at the para position. But if it is not free then the \[ - OH\] group is attached to the ortho position.
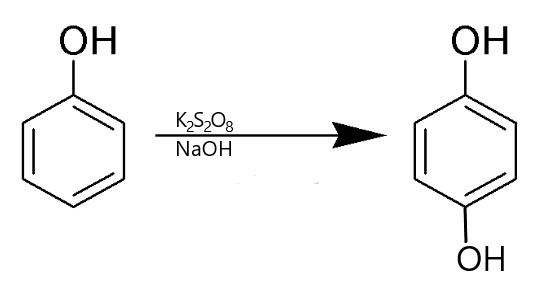
Hence this process has the required reagent and phenol is getting converted to dihydric phenols (Quinol). Therefore, it is the required reaction.
D) Lastly we have Kolbe’s Reaction: We know that Kolbe’s Reaction occurs when sodium phenoxide is treated with carbon dioxide under a pressure of $4 - 7atm$ and at $400K$, and the sodium salicylate is formed as an intermediate, which on further reaction gives salicylic acid.
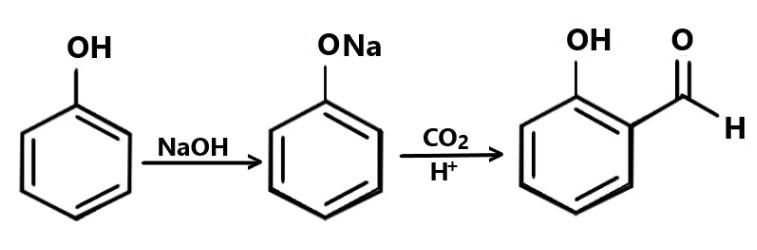
In this reaction the required product is not found hence it is the wrong option.
Hence the correct answer is option ‘C’.
Note: Always remember that the IUPAC name of Quinol is dihydric phenol. It is formed most commonly and easily by treating phenol with alkaline persulfate. Also Reimer-Tiemann and Kolbe’s reaction both result in the formation of salicylic acid.
Complete step-by-step answer:
The following reactions involve phenol as their reactant-
A) First is the Lederer-Manasse reaction: This reaction deals with phenol and formaldehyde under basic conditions and is referred to as the Lederer-Manasse reaction. The resulting products from this reaction are known as “shellac substitutes”, which are soluble in alcohol, acetone, and alkaline hydroxide and melt on heating and re-solidify after cooling.
In this reaction phenol is treated at low temperature in the presence of diluted acid or alkali to yield ortho-hydroxy-benzyl alcohol or para hydroxy benzyl alcohol.

Hence it is not the required equation.
B) Then we have Reimer-Tiemann reaction: We know that Reimer-Tiemann reaction takes place when phenol is treated with \[CHC{l_3}\]in the presence of \[NaOH\] then an aldehyde group is introduced at the ortho-position of the benzene ring leading to the formation of ortho-hydroxy benzaldehyde.

Hence the used reagent is not the same therefore this is not the required reaction.
C) Then comes the Elbs persulfate oxidation- reaction: In this reaction monohydric phenols are oxidized to dihydric phenols by alkaline persulfate. Hydroxylation occurs at the para position. But if it is not free then the \[ - OH\] group is attached to the ortho position.

Hence this process has the required reagent and phenol is getting converted to dihydric phenols (Quinol). Therefore, it is the required reaction.
D) Lastly we have Kolbe’s Reaction: We know that Kolbe’s Reaction occurs when sodium phenoxide is treated with carbon dioxide under a pressure of $4 - 7atm$ and at $400K$, and the sodium salicylate is formed as an intermediate, which on further reaction gives salicylic acid.

In this reaction the required product is not found hence it is the wrong option.
Hence the correct answer is option ‘C’.
Note: Always remember that the IUPAC name of Quinol is dihydric phenol. It is formed most commonly and easily by treating phenol with alkaline persulfate. Also Reimer-Tiemann and Kolbe’s reaction both result in the formation of salicylic acid.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Draw ray diagrams each showing i myopic eye and ii class 12 physics CBSE

Give 10 examples of unisexual and bisexual flowers

Coming together federation is practiced in A India class 12 social science CBSE

Write the formula to find the shortest distance between class 12 maths CBSE




