
The reaction
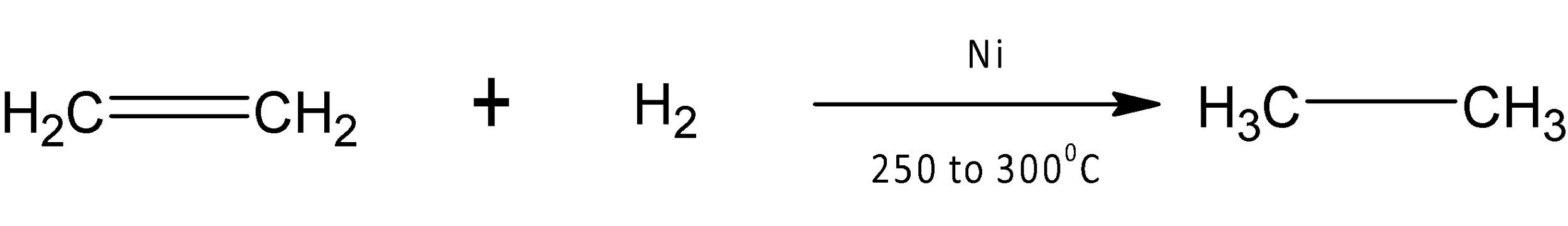
A. Wurtz’s reaction
B. Kolbe’s reaction
C. Sabatier and senderens reaction
D. Carbylamine reaction
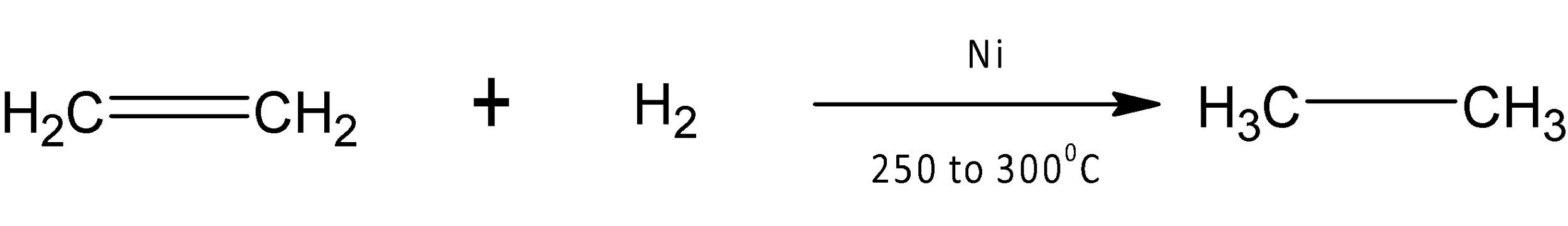
Answer
361.5k+ views
Hint: When alkene reacts with a hydrogen molecule in the presence of a metal catalyst at a very high temperature, a hydrogen atom from the hydrogen molecule is added to each carbon of the double bonds. These reactions are known as catalytic hydrogenation.
Complete Step by Step Answer:
The process of hydrogenation occurs when hydrogen is added to each carbon of a double bond. Generally, the simplest source of two hydrogen atoms is molecular hydrogen ($H_2$). But the addition of molecular hydrogen to a double bond is not easy, a high activation energy is required. Hence under normal conditions, it is not reacted with molecular hydrogenation.
Hydrogenation of alkene is a thermodynamically favourable reaction as it forms a stable product that is an alkane. Catalysts are substances that change the speed of reaction after being consumed in the reaction medium. They can only lower the activation energy but do not change the potential energy of the reaction.
Examples of such catalysts are metals like nickel ($Ni$), palladium ($Pd$), and platinum ($Pt$), which are the most widely used catalysts. The catalytic hydrogenation of ethylene in the presence of nickel catalyst at temperature ${{250}^{{\mathrm O}}}$ ${{300}^{{\mathrm O}}}C$ produces an alkane named ethane. This catalytic hydrogenation reaction is known as Sabatier and Senderens reaction.

Thus, option (C) is correct.
Note: The process of hydrogenation reaction is also carried out in the presence of palladium and platinum catalysts. Palladium is used with charcoal and platinum is used $Pt{{O}_{2}}$, named Adam’s catalyst for the catalytic hydrogenation of alkenes. Generally, the solvent that is used in this process is ethanol or acetic acid.
Complete Step by Step Answer:
The process of hydrogenation occurs when hydrogen is added to each carbon of a double bond. Generally, the simplest source of two hydrogen atoms is molecular hydrogen ($H_2$). But the addition of molecular hydrogen to a double bond is not easy, a high activation energy is required. Hence under normal conditions, it is not reacted with molecular hydrogenation.
Hydrogenation of alkene is a thermodynamically favourable reaction as it forms a stable product that is an alkane. Catalysts are substances that change the speed of reaction after being consumed in the reaction medium. They can only lower the activation energy but do not change the potential energy of the reaction.
Examples of such catalysts are metals like nickel ($Ni$), palladium ($Pd$), and platinum ($Pt$), which are the most widely used catalysts. The catalytic hydrogenation of ethylene in the presence of nickel catalyst at temperature ${{250}^{{\mathrm O}}}$ ${{300}^{{\mathrm O}}}C$ produces an alkane named ethane. This catalytic hydrogenation reaction is known as Sabatier and Senderens reaction.

Thus, option (C) is correct.
Note: The process of hydrogenation reaction is also carried out in the presence of palladium and platinum catalysts. Palladium is used with charcoal and platinum is used $Pt{{O}_{2}}$, named Adam’s catalyst for the catalytic hydrogenation of alkenes. Generally, the solvent that is used in this process is ethanol or acetic acid.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 9 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Class 9 Question and Answer - Your Ultimate Solutions Guide

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What is BLO What is the full form of BLO class 8 social science CBSE

The value of 6 more than 7 is A 1 B 1 C 13 D 13 class 7 maths CBSE

One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

What is the median of the first 10 natural numbers class 10 maths CBSE




