
The process AB is shown in the diagram. As the gas is taken from A to B.
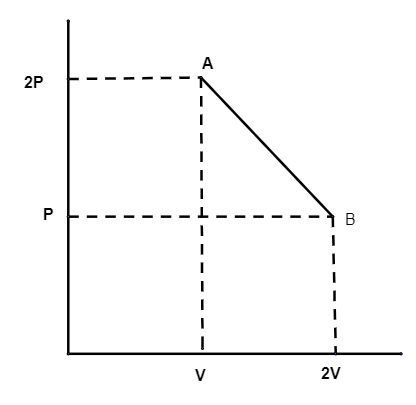
Its temperature will be
(i) Initially increases and then decreases
(ii) Initially decreases and then increases
(iii) Remains constant
(iv) Variation depends on type of gas

Answer
519k+ views
Hint: Gas laws are the generalisations which are made from the study of behaviours of gases. The study of gases is much easier than the study of liquids and solids because the physical properties of all gases are identical. Like the volume of all the gases depends upon the amount of the gas taken, temperature and pressure applied on it.
Complete answer:
In this question, Boyle's law is applied.
It was given by Anglo-Irish scientist named Robert Boyle in 1662 who gave the pressure volume relationships.
This law is applicable only if the temperature and number of moles are constant, then the pressure is inversely proportional to volume. Which means if pressure is doubled, then the volume is halved.
Mathematically, the Boyle's law can be expressed as
\[P{\text{ }} \propto {\text{ }}\dfrac{1}{V}\] (At constant temperature and moles)
\[or{\text{ V}} \propto {\text{ }}\dfrac{1}{P}\](At constant temperature and moles)
Here, P is pressure and V is volume of gas.
\[ \Rightarrow V = {K_1}\dfrac{1}{P}\]
$K_1$ is the proportionality constant, whose value depends on amount of gas and temperature.
So, in the question, the pressure is decreasing and volume doubles. So temperature is constant.
Option (iii) is correct.
Note:
The relationships among the pressure, temperature and volume of a given mass of a gas are best described in the form of gas laws. PV is constant at constant temperature and for a fixed amount of the gas.
Complete answer:
In this question, Boyle's law is applied.
It was given by Anglo-Irish scientist named Robert Boyle in 1662 who gave the pressure volume relationships.
This law is applicable only if the temperature and number of moles are constant, then the pressure is inversely proportional to volume. Which means if pressure is doubled, then the volume is halved.
Mathematically, the Boyle's law can be expressed as
\[P{\text{ }} \propto {\text{ }}\dfrac{1}{V}\] (At constant temperature and moles)
\[or{\text{ V}} \propto {\text{ }}\dfrac{1}{P}\](At constant temperature and moles)
Here, P is pressure and V is volume of gas.
\[ \Rightarrow V = {K_1}\dfrac{1}{P}\]
$K_1$ is the proportionality constant, whose value depends on amount of gas and temperature.
So, in the question, the pressure is decreasing and volume doubles. So temperature is constant.
Option (iii) is correct.

Note:
The relationships among the pressure, temperature and volume of a given mass of a gas are best described in the form of gas laws. PV is constant at constant temperature and for a fixed amount of the gas.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




