
The point charges +q and -q are placed at points A and B separated by a small distance. The electric field intensity at the midpoint O of AB
A. is zero
B. Acts along AB
C. Acts along BA
D. Acts perpendicular to AB
Answer
591.6k+ views
Hint: The electric field (lines) of a single negative charge appears to be entering in it and the electric field of positive charge appears to be emerging outwards from it.
Complete step by step answer:
Two equal and opposite charges separated by some distance d constitute a dipole. We know that the magnitude of the electric field of two equal charges separated by a distance d is given as:
$E= \dfrac{1}{4 \pi \epsilon_0} \dfrac{q^2}{d^2}$
So, this clearly is enough to show that option (A) is incorrect i.e., the electric field is not zero.
Now, in a dipole, the resultant field lines tend to emerge out of the positive charge and enter inside the negative charge.
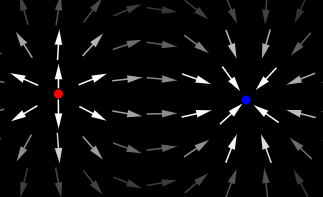
Another way to imagine this is to consider a positive test charge at the point O. What happens to this test charge is our required answer. The positive charge +q at A will repel our test charge and the negative charge -q at B, will attract our test charge. Thus, the direction in which the test charge moves is the answer for us. Because the definition of electric field intensity itself is the force acting on unit test charge. This definition is sufficient to give us even the direction of electric field intensity.
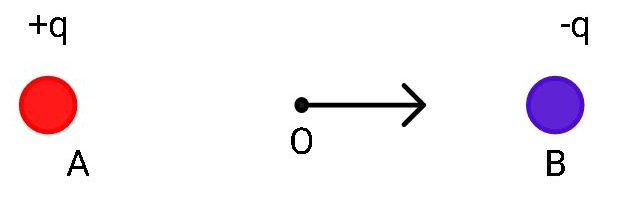
Therefore, as our test charge is bound to move from +q to -q direction.
So, the correct answer is “Option B”.
Note: Naively, looking at the +q and the -q, one might choose (A) as the correct option. To avoid such error, it is recommended to remember the definition of electric field intensity i.e., force acting on unit test charge and then examine the situation.
Complete step by step answer:
Two equal and opposite charges separated by some distance d constitute a dipole. We know that the magnitude of the electric field of two equal charges separated by a distance d is given as:
$E= \dfrac{1}{4 \pi \epsilon_0} \dfrac{q^2}{d^2}$
So, this clearly is enough to show that option (A) is incorrect i.e., the electric field is not zero.
Now, in a dipole, the resultant field lines tend to emerge out of the positive charge and enter inside the negative charge.

Another way to imagine this is to consider a positive test charge at the point O. What happens to this test charge is our required answer. The positive charge +q at A will repel our test charge and the negative charge -q at B, will attract our test charge. Thus, the direction in which the test charge moves is the answer for us. Because the definition of electric field intensity itself is the force acting on unit test charge. This definition is sufficient to give us even the direction of electric field intensity.

Therefore, as our test charge is bound to move from +q to -q direction.
So, the correct answer is “Option B”.
Note: Naively, looking at the +q and the -q, one might choose (A) as the correct option. To avoid such error, it is recommended to remember the definition of electric field intensity i.e., force acting on unit test charge and then examine the situation.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




