
The most polar compound among the following is:




Answer
590.4k+ views
Hint: Think about the concept of polarity. Fluorine is the most electronegative atom in the periodic table. Assign the partial positive and negative charges on each compound. If there are of the same signs opposite to each other, then the dipole moments will get cancelled and the compound will be non-polar. Only if there are opposite signs on opposite sides will the molecule be polar. Use this data and draw a conclusion.
Complete step by step answer:
- Polarity is the difference in the electronegativity between two atoms forming a bond such that the bond is shared more towards the electronegative atom and less towards electropositive atom which leads to development of partial negative and positive charges on the respective atoms and the bond becomes polar.
- Let’s have a look at each compound given in the question.
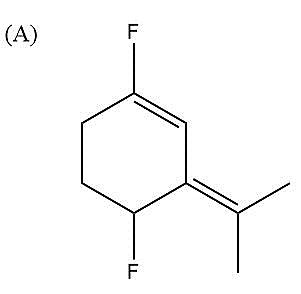
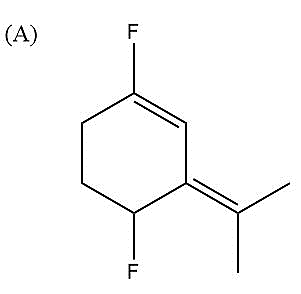
Here, fluorine groups are present para to each other. That is, both the F atoms are present exactly in opposite positions on the ring. F will always develop negative charge due to its high electronegativity and therefore, carbon atoms attached to F will develop partial positive charge on them. There are two conjugated double bonds present in the molecule. But as such their charges arising due to conjugation will not contribute much in this case. Since both F atoms are opposite to each other, so most of their charges and dipole moments get nullified.
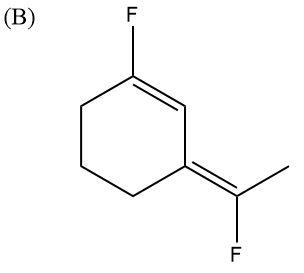
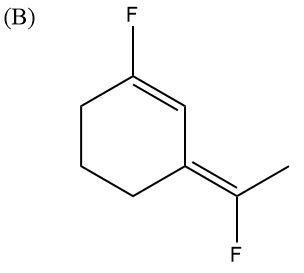
Here, F atoms are in opposite directions to each other as well, but they are diagonally opposite. Here also, some charges and dipole moments will get balanced and nullified. So, overall, the molecule will have very low polarity.
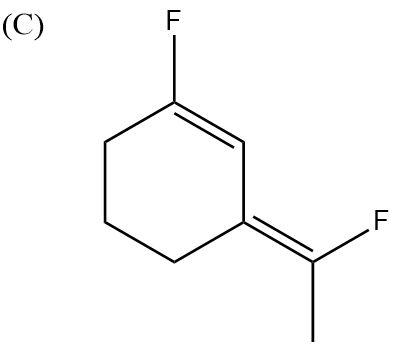
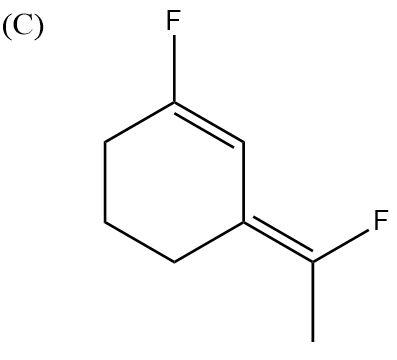
In this case, both the F atoms are pointing upwards. Their dipole moments are in two different directions. One is upwards and one is at another angle but upwards only. So, the partial positive charges are pointing downwards and partial negative charges are pointing upwards. Hence, no dipole moments will get cancelled and the molecule will be highly polar.
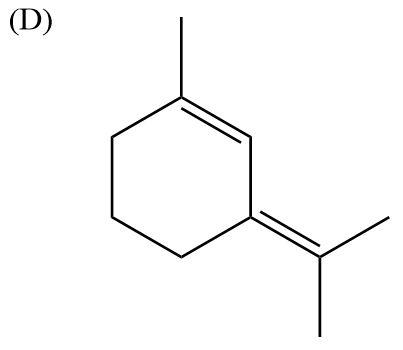
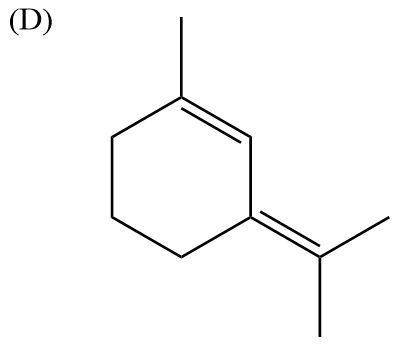
Here, there is absence of electronegative atoms. There is conjugate effect in the molecule due to the presence of double bonds, but it becomes equal to zero. Therefore, this molecule is nonpolar.
So, the correct answer is “Option C”.
Note: Although in the first compound one of the fluorine atoms is attached to $s{{p}^{3}}$ carbon, it will still be in the opposite direction and the dipole moments will get cancelled. Remember, if the dipole moments having the same charge are opposite to each other then they get cancelled and the molecule is nonpolar, for example, carbon dioxide or oxygen, nitrogen in their diatomic states. Only if the dipole moments have different charges in opposite directions then the molecule will be polar, for example, HCl.
Complete step by step answer:
- Polarity is the difference in the electronegativity between two atoms forming a bond such that the bond is shared more towards the electronegative atom and less towards electropositive atom which leads to development of partial negative and positive charges on the respective atoms and the bond becomes polar.
- Let’s have a look at each compound given in the question.

Here, fluorine groups are present para to each other. That is, both the F atoms are present exactly in opposite positions on the ring. F will always develop negative charge due to its high electronegativity and therefore, carbon atoms attached to F will develop partial positive charge on them. There are two conjugated double bonds present in the molecule. But as such their charges arising due to conjugation will not contribute much in this case. Since both F atoms are opposite to each other, so most of their charges and dipole moments get nullified.

Here, F atoms are in opposite directions to each other as well, but they are diagonally opposite. Here also, some charges and dipole moments will get balanced and nullified. So, overall, the molecule will have very low polarity.

In this case, both the F atoms are pointing upwards. Their dipole moments are in two different directions. One is upwards and one is at another angle but upwards only. So, the partial positive charges are pointing downwards and partial negative charges are pointing upwards. Hence, no dipole moments will get cancelled and the molecule will be highly polar.

Here, there is absence of electronegative atoms. There is conjugate effect in the molecule due to the presence of double bonds, but it becomes equal to zero. Therefore, this molecule is nonpolar.
So, the correct answer is “Option C”.
Note: Although in the first compound one of the fluorine atoms is attached to $s{{p}^{3}}$ carbon, it will still be in the opposite direction and the dipole moments will get cancelled. Remember, if the dipole moments having the same charge are opposite to each other then they get cancelled and the molecule is nonpolar, for example, carbon dioxide or oxygen, nitrogen in their diatomic states. Only if the dipole moments have different charges in opposite directions then the molecule will be polar, for example, HCl.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

What is a transformer Explain the principle construction class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE




