
The molecular formula of Wilkinson catalyst, used in hydrogenation of alkenes is:
A. ${\text{Co}}{\left( {{\text{CO}}} \right)_{\text{8}}}$
B. ${\left( {{\text{P}}{{\text{h}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{P}}} \right)_{\text{3}}}{\text{RhCl}}$
C. $\left[ {{\text{Pt}}{{\left( {{\text{N}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}} \right)}_{\text{2}}}{\text{C}}{{\text{l}}_{\text{2}}}} \right]$
D. ${\text{K}}\left[ {{\text{Ag}}{{\left( {{\text{CN}}} \right)}_{\text{2}}}} \right]$
Answer
576.9k+ views
Hint: Wilkinson catalyst is a coordination compound. The centre of coordination of Wilkinson catalyst is rhodium. Wilkinson catalyst is named after Sir Geoffrey Wilkinson. The Wilkinson catalyst is reddish-brown coloured solid substance at ambient temperatures.
Complete step by step solution:
We are given that Wilkinson catalyst is used in hydrogenation of alkenes to alkanes. Wilkinson catalyst mainly catalyses hydrogenation of hydrocarbons along with many other reactions like hydroacylation, hydroboration and hydrosilylation of alkenes, it is effective in the selective reduction of olefins.
Wilkinson catalyst is produced by the reaction of rhodium (III) chloride hydrate with excess triphenylphosphine in ethanol. Triphenylphosphine acts as a reducing agent and ethanol acts as a refluxing agent.
The reaction is as follows:
${\text{RhC}}{{\text{l}}_{\text{3}}}{\left( {{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{O}}} \right)_{\text{3}}} + {\text{4PP}}{{\text{h}}_{\text{3}}} \to {\left( {{\text{P}}{{\text{h}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{P}}} \right)_{\text{3}}}{\text{RhCl}} + {\text{OPP}}{{\text{h}}_{\text{3}}} + {\text{2HCl}} + {\text{2}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{O}}$
The IUPAC name of Wilkinson catalyst is chlorotris (triphenylphosphine) rhodium (I). Its molecular formula is ${\left( {{\text{P}}{{\text{h}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{P}}} \right)_{\text{3}}}{\text{RhCl}}$. The structure of Wilkinson catalyst is as follows:
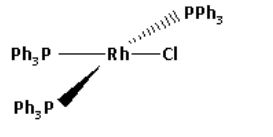
From the structure, we can conclude that the rhodium centre is bound to total four ligands. One chloride ligand and three triphenylphosphine ligands. Thus, the coordination number of the rhodium centre is four.
Thus, the molecular formula of Wilkinson catalyst, used in hydrogenation of alkenes is ${\left( {{\text{P}}{{\text{h}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{P}}} \right)_{\text{3}}}{\text{RhCl}}$.
Thus, the correct option id (B) ${\left( {{\text{P}}{{\text{h}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{P}}} \right)_{\text{3}}}{\text{RhCl}}$.
Note:
Wilkinson catalyst is insoluble in water but it is soluble in many hydrocarbon-based solvents like benzene, tetrahydrofuran, etc. The geometry of Wilkinson catalyst is a slightly distorted square planar having hybridisation $ds{p^2}$. It is diamagnetic in nature. Wilkinson catalyst undergoes dimerization when it is stirred in benzene solution. The formula of the dimer is ${\left[ {{{\left( {{\text{P}}{{\text{h}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{P}}} \right)}_{\text{3}}}{\text{RhCl}}} \right]_2}$.
Complete step by step solution:
We are given that Wilkinson catalyst is used in hydrogenation of alkenes to alkanes. Wilkinson catalyst mainly catalyses hydrogenation of hydrocarbons along with many other reactions like hydroacylation, hydroboration and hydrosilylation of alkenes, it is effective in the selective reduction of olefins.
Wilkinson catalyst is produced by the reaction of rhodium (III) chloride hydrate with excess triphenylphosphine in ethanol. Triphenylphosphine acts as a reducing agent and ethanol acts as a refluxing agent.
The reaction is as follows:
${\text{RhC}}{{\text{l}}_{\text{3}}}{\left( {{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{O}}} \right)_{\text{3}}} + {\text{4PP}}{{\text{h}}_{\text{3}}} \to {\left( {{\text{P}}{{\text{h}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{P}}} \right)_{\text{3}}}{\text{RhCl}} + {\text{OPP}}{{\text{h}}_{\text{3}}} + {\text{2HCl}} + {\text{2}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{O}}$
The IUPAC name of Wilkinson catalyst is chlorotris (triphenylphosphine) rhodium (I). Its molecular formula is ${\left( {{\text{P}}{{\text{h}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{P}}} \right)_{\text{3}}}{\text{RhCl}}$. The structure of Wilkinson catalyst is as follows:

From the structure, we can conclude that the rhodium centre is bound to total four ligands. One chloride ligand and three triphenylphosphine ligands. Thus, the coordination number of the rhodium centre is four.
Thus, the molecular formula of Wilkinson catalyst, used in hydrogenation of alkenes is ${\left( {{\text{P}}{{\text{h}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{P}}} \right)_{\text{3}}}{\text{RhCl}}$.
Thus, the correct option id (B) ${\left( {{\text{P}}{{\text{h}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{P}}} \right)_{\text{3}}}{\text{RhCl}}$.
Note:
Wilkinson catalyst is insoluble in water but it is soluble in many hydrocarbon-based solvents like benzene, tetrahydrofuran, etc. The geometry of Wilkinson catalyst is a slightly distorted square planar having hybridisation $ds{p^2}$. It is diamagnetic in nature. Wilkinson catalyst undergoes dimerization when it is stirred in benzene solution. The formula of the dimer is ${\left[ {{{\left( {{\text{P}}{{\text{h}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{P}}} \right)}_{\text{3}}}{\text{RhCl}}} \right]_2}$.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




