
The molecular formula of a saturated compound is $C_{2}H_{4}Cl_{2}$ . This formula permits the existence of two:
A. functional isomers
B. position isomers
C. optical isomers
D. cis-trans isomers
Answer
582.9k+ views
Hint: Draw the different structures possible for the given compound, $C_{2}H_{4}Cl_{2}$ and carefully examine the position of carbon, hydrogen and chlorine in different structures and identify the type of isomerism exhibited by the given compound.
Complete step by step answer:
Complete step by step solution:
Different types of isomers include :
Functional isomers – These are structural isomers which have different functional groups, resulting in significantly different chemical and physical properties.
Position isomers - When the same molecular formula represents two or more compounds which differ in the position of the same functional group, then such compounds are called position isomers and the phenomenon is called position isomerism.
Optical isomers – These type of isomerism are shown in compounds which contain the same number and kinds of atoms, and bonds (i.e., the connectivity between atoms is the same), and different spatial arrangements of the atoms, but which have non-superimposable mirror images. Each non-superimposable mirror image structure is called an enantiomer.
Cis-trans isomers – This type is exhibited in those compounds that have different configurations (groups permanently in different places in space) because of the presence of a rigid structure in their molecule.
As per the definition, we can see that the given compound exhibits two structures with IUPAC name of the compounds as
-$1,1 - $dichloroethane
-dichloroethane
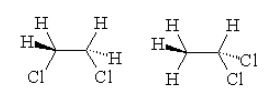
By looking at the structures, we see that in both the structures only difference is in the position of the Chlorine atom. Thus we can say that the position of the same functional group is different and thus they are positional isomers.
Therefore, option B is correct.
Note: The student while doing such problems can get confused between positional and functional isomers. To avoid such errors both the isomers have to be studied in detail so that the errors can be avoided while doing these problems.
Complete step by step answer:
Complete step by step solution:
Different types of isomers include :
Functional isomers – These are structural isomers which have different functional groups, resulting in significantly different chemical and physical properties.
Position isomers - When the same molecular formula represents two or more compounds which differ in the position of the same functional group, then such compounds are called position isomers and the phenomenon is called position isomerism.
Optical isomers – These type of isomerism are shown in compounds which contain the same number and kinds of atoms, and bonds (i.e., the connectivity between atoms is the same), and different spatial arrangements of the atoms, but which have non-superimposable mirror images. Each non-superimposable mirror image structure is called an enantiomer.
Cis-trans isomers – This type is exhibited in those compounds that have different configurations (groups permanently in different places in space) because of the presence of a rigid structure in their molecule.
As per the definition, we can see that the given compound exhibits two structures with IUPAC name of the compounds as
-$1,1 - $dichloroethane
-dichloroethane

By looking at the structures, we see that in both the structures only difference is in the position of the Chlorine atom. Thus we can say that the position of the same functional group is different and thus they are positional isomers.
Therefore, option B is correct.
Note: The student while doing such problems can get confused between positional and functional isomers. To avoid such errors both the isomers have to be studied in detail so that the errors can be avoided while doing these problems.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




