
The mass of a given hydrogen molecule is $3.2\times {{10}^{-27}}Kg$. If 1023 hydrogen molecules strike, per second, a fixed wall of area $2c{{m}^{2}}$ at an angle of $45{}^\circ $ to the normal, and rebound elastically with a speed of $103m{{s}^{-1}}$, then the pressure on the wall is nearly.
$\begin{align}
& A.2.35\times {{10}^{2}}N{{m}^{-2}} \\
& B.4.70\times {{10}^{2}}N{{m}^{-2}} \\
& C.2.35\times {{10}^{3}}N{{m}^{-2}} \\
& D.4.70\times {{10}^{3}}N{{m}^{-2}} \\
\end{align}$
Answer
593.4k+ views
Hint: This question is based on momentum conservation. That is the initial momentum of a body will be as same as the final momentum of the same body. This can be shown in an expression like,
${{m}_{i}}{{u}_{i}}\cos {{\theta }_{i}}={{m}_{f}}{{u}_{f}}\cos {{\theta }_{f}}$
Complete step by step answer:
First of all let us discuss the momentum. Momentum is the impact happening to a body due its mass and its velocity. Momentum is the product of its mass and the velocity. Momentum is a vector quantity in which it is having both direction and magnitude.
Newton's second law of motion states that the time rate of change of momentum is the same as the force acting on the particle. Here in the question it is given that,
$\begin{align}
& u={{10}^{3}}m{{s}^{-1}} \\
& m=3.2\times {{10}^{-27}}kg \\
& n={{10}^{23}} \\
\end{align}$
Therefore the change in momentum in y direction of one \[{{H}_{2}}\] molecule is given by the equation,
\[\Delta P=mu\cos 45{}^\circ -\left( -mu\cos 45{}^\circ \right)=2mu\cos 45{}^\circ \]
Now the change in momentum in y direction of total \[{{H}_{2}}\]will be
\[\Delta P=2mnu\cos 45{}^\circ \]
Area of the wall at which it is incident,
\[A=2c{{m}^{2}}=2\times {{10}^{-4}}{{m}^{2}}\]
Therefore the resultant pressure on the wall will be
\[\begin{align}
&P=\dfrac{\Delta {{P}_{T}}}{A}=\dfrac{2\times {{10}^{23}}\times 3.32\times {{10}^{-27}}\times {{10}^{3}}\times 0.707}{2\times {{10}^{-4}}} \\
& =2.35\times {{10}^{3}}N{{m}^{-2}} \\
\end{align}\]
\[\begin{align}
& P=\dfrac{\Delta {{P}_{T}}}{A}=\dfrac{2\times {{10}^{23}}\times 3.32\times {{10}^{-27}}\times {{10}^{3}}\times 0.707}{2\times {{10}^{-4}}} \\
& =2.35\times {{10}^{3}}N{{m}^{-2}} \\
\end{align}\]
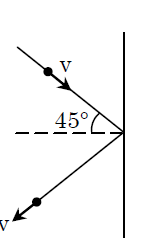
Hence, the correct answer is option C.
Note:
There are two kinds of momentum. Angular momentum and linear momentum. Angular momentum is defined as the inertia of rotation motion. Linear momentum is defined as inertia of translation motion. The significant difference is that the type of motion which is related to each momentum is different. It is important to notice the place where the force related to rotation applies, which appears as 'r' in the equation.
${{m}_{i}}{{u}_{i}}\cos {{\theta }_{i}}={{m}_{f}}{{u}_{f}}\cos {{\theta }_{f}}$
Complete step by step answer:
First of all let us discuss the momentum. Momentum is the impact happening to a body due its mass and its velocity. Momentum is the product of its mass and the velocity. Momentum is a vector quantity in which it is having both direction and magnitude.
Newton's second law of motion states that the time rate of change of momentum is the same as the force acting on the particle. Here in the question it is given that,
$\begin{align}
& u={{10}^{3}}m{{s}^{-1}} \\
& m=3.2\times {{10}^{-27}}kg \\
& n={{10}^{23}} \\
\end{align}$
Therefore the change in momentum in y direction of one \[{{H}_{2}}\] molecule is given by the equation,
\[\Delta P=mu\cos 45{}^\circ -\left( -mu\cos 45{}^\circ \right)=2mu\cos 45{}^\circ \]
Now the change in momentum in y direction of total \[{{H}_{2}}\]will be
\[\Delta P=2mnu\cos 45{}^\circ \]
Area of the wall at which it is incident,
\[A=2c{{m}^{2}}=2\times {{10}^{-4}}{{m}^{2}}\]
Therefore the resultant pressure on the wall will be
\[\begin{align}
&P=\dfrac{\Delta {{P}_{T}}}{A}=\dfrac{2\times {{10}^{23}}\times 3.32\times {{10}^{-27}}\times {{10}^{3}}\times 0.707}{2\times {{10}^{-4}}} \\
& =2.35\times {{10}^{3}}N{{m}^{-2}} \\
\end{align}\]
\[\begin{align}
& P=\dfrac{\Delta {{P}_{T}}}{A}=\dfrac{2\times {{10}^{23}}\times 3.32\times {{10}^{-27}}\times {{10}^{3}}\times 0.707}{2\times {{10}^{-4}}} \\
& =2.35\times {{10}^{3}}N{{m}^{-2}} \\
\end{align}\]

Hence, the correct answer is option C.
Note:
There are two kinds of momentum. Angular momentum and linear momentum. Angular momentum is defined as the inertia of rotation motion. Linear momentum is defined as inertia of translation motion. The significant difference is that the type of motion which is related to each momentum is different. It is important to notice the place where the force related to rotation applies, which appears as 'r' in the equation.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




