
The magnetic moment of ${{\left[ Ni{{X}_{4}} \right]}^{2-}}$ ion is found to be zero. Then the metal of the complex ion is (X=monodentate anionic ligand).
(A) $s{{p}^{3}}$ hybridized
(B) $sp{{d}^{2}}$hybridized
(C) $ds{{p}^{2}}$ hybridized
(D) ${{d}^{2}}sp$ hybridized
Answer
589.8k+ views
Hint: The charge on the nickel atom should be found first. Then from molecular orbital theory we could find how many vacant orbitals are needed for ligands. By arranging the electrons in orbitals according to the details in question, we will get the hybridization of ions.
Complete step by step solution:
-The given complex is ${{\left[ Ni{{X}_{4}} \right]}^{2-}}$.It is given that X is a monodentate ligand. We are asked to find the hybridization of the ion.
Let's start with finding the charge on nickel(x). Since X is a monodentate ligand it will be having charge of −1. There are four ligands, hence total charge on X will be −1 multiplied by four. Thus, we can find the charge on Nickel as follows
$x-4=-2$ $x-4=-2$
$x=+2$
Therefore, nickel will have $N{{i}^{2+}}$ configuration. Hence two electrons would be lost from nickel and its number of electrons reduces to 26 from 28. Its electronic configuration can be given as,
$\left[ Ar \right]3{{d}^{8}}4{{s}^{0}}$. It can be diagrammatically represented by molecular orbital theory as follows,
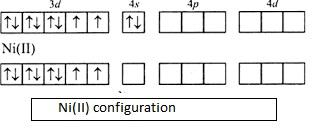
As given in the question the complex is having zero magnetic moment, the electrons should be paired. This is possible only when $N{{i}^{2+}}$ with $3{{d}^{8}}$ outer electronic configuration undergoes $ds{{p}^{2}}$hybridization.
- We need four empty orbitals in order to accommodate the incoming monodentate ligands. Since the net magnetic moment is zero, the outermost electron in $N{{i}^{2+}}$ pairs with the second last electron. Now we have one vacant orbital in $3d$ orbital. Since we need four vacant orbitals, other ligands will occupy in the remaining orbitals. One will occupy in $4s$ orbital and two in $4p$ orbital.
- Thus, we will have the hybridization of $ds{{p}^{2}}$.
Therefore, the answer is option (C).
Note: When we look at the options (B) and (D) may look similar. In $sp{{d}^{2}}$ hybridization, mixing of s, p and d orbitals of same electron shell takes place whereas in ${{d}^{2}}sp$ hybridization , mixing of s and p orbitals of same electron shell with d orbitals of another electron shell takes place. Hence, they are not the same.
Complete step by step solution:
-The given complex is ${{\left[ Ni{{X}_{4}} \right]}^{2-}}$.It is given that X is a monodentate ligand. We are asked to find the hybridization of the ion.
Let's start with finding the charge on nickel(x). Since X is a monodentate ligand it will be having charge of −1. There are four ligands, hence total charge on X will be −1 multiplied by four. Thus, we can find the charge on Nickel as follows
$x-4=-2$ $x-4=-2$
$x=+2$
Therefore, nickel will have $N{{i}^{2+}}$ configuration. Hence two electrons would be lost from nickel and its number of electrons reduces to 26 from 28. Its electronic configuration can be given as,
$\left[ Ar \right]3{{d}^{8}}4{{s}^{0}}$. It can be diagrammatically represented by molecular orbital theory as follows,

As given in the question the complex is having zero magnetic moment, the electrons should be paired. This is possible only when $N{{i}^{2+}}$ with $3{{d}^{8}}$ outer electronic configuration undergoes $ds{{p}^{2}}$hybridization.
- We need four empty orbitals in order to accommodate the incoming monodentate ligands. Since the net magnetic moment is zero, the outermost electron in $N{{i}^{2+}}$ pairs with the second last electron. Now we have one vacant orbital in $3d$ orbital. Since we need four vacant orbitals, other ligands will occupy in the remaining orbitals. One will occupy in $4s$ orbital and two in $4p$ orbital.
- Thus, we will have the hybridization of $ds{{p}^{2}}$.
Therefore, the answer is option (C).
Note: When we look at the options (B) and (D) may look similar. In $sp{{d}^{2}}$ hybridization, mixing of s, p and d orbitals of same electron shell takes place whereas in ${{d}^{2}}sp$ hybridization , mixing of s and p orbitals of same electron shell with d orbitals of another electron shell takes place. Hence, they are not the same.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




