
The length of the common chord of two circles ${\left( {x - a} \right)^2} + {\left( {y - b} \right)^2} = {c^2}{\text{ and }}{\left( {x - b} \right)^2} + {\left( {y - a} \right)^2} = {c^2}$ is
A. $\sqrt {4{c^2} + 2{{\left( {a - b} \right)}^2}} $
B. $\sqrt {4{c^2} + 2{{\left( {a + b} \right)}^2}} $
C. $\sqrt {4{c^2} - 2{{\left( {a - b} \right)}^2}} $
D. $\sqrt {{c^2} - 2{{\left( {a - b} \right)}^2}} $
Answer
615k+ views
Hint: If ${S_1}$ is the equation of first circle and ${S_2}$ is the equation of the second circle then the equation of common chord of both the circle is given as ${S_1} - {S_2} = 0$ and the distance from the point $\left( {{x_1},{y_1}} \right)$ on the line $ax - by = 0$ is given as $\left| {\dfrac{{a{x_1} - b{x_2}}}{{\sqrt {{a^2} + {b^2}} }}} \right|$.
Complete step by step answer:
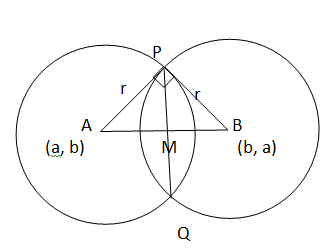
The equation of first circle is
\[{S_1} = {\left( {x - a} \right)^2} + {\left( {y - b} \right)^2} = {c^2}.............\left( 1 \right)\]
And equation of the second circle is
${S_2} = {\left( {x - b} \right)^2} + {\left( {y - a} \right)^2} = {c^2}...............\left( 2 \right)$
Then the center of circle ${S_1}$ is A (a, b) and radius is c.
The center of the circle of the circle ${S_2}$ is B (b, a) and radius is c.
Now, PQ is a common chord AB intersect PQ at M and
AP=BP=c
Equation of PQ is given by,
${S_1} - {S_2} = 0$
$
\Rightarrow \left[ {{{\left( {x - a} \right)}^2} + {{\left( {y - b} \right)}^2} = {c^2}{\text{ }}} \right]{\text{ - }}\left[ {{{\left( {x - b} \right)}^2} + {{\left( {y - a} \right)}^2} = {c^2}} \right] \\
\Rightarrow 2bx - 2by + 2ay - 2ax = 0 \\
\Rightarrow 2b\left( {x - y} \right) + 2a\left( {y - x} \right) = 0 \\
\Rightarrow 2b\left( {x - y} \right) - 2a\left( {x - y} \right) = 0 \\
\Rightarrow \left( {x - y} \right)\left( {2b - 2a} \right) = 0 \\
\Rightarrow x - y = 0 \\
$
Then equation of PQ is $x - y = 0$
AM = length of perpendicular from A (a, b) on PQ whose equation is $x - y = 0$
Therefore, AM $ = \dfrac{{\left| {1 \times a - 1 \times b} \right|}}{{\sqrt {{{\left( 1 \right)}^2} + {{\left( { - 1} \right)}^2}} }} = \dfrac{{\left| {a - b} \right|}}{{\sqrt 2 }}$
In right $\Delta {\text{PMA,}}$
$
PM = \sqrt {{{\left( {AP} \right)}^2} - {{\left( {AM} \right)}^2}} \\
PM = \sqrt {{c^2} - \dfrac{{{{\left( {a - b} \right)}^2}}}{2}} \\
\left[ {{\text{as AP = c }}\left( {{\text{radius of the circle}}} \right)} \right] \\
$
But M is the midpoint of PQ
Then, PQ =2PM = 2
$
\sqrt {{c^2} - \dfrac{{{{\left( {a - b} \right)}^2}}}{2}} \\
= \sqrt {4{c^2} - \dfrac{{4{{\left( {a - b} \right)}^2}}}{2}} \\
= \sqrt {4{c^2} - 2{{\left( {a - b} \right)}^2}} \\
$
Hence, the correct option is “C”.
Note: In order to solve these types of problems remember all the formulas and equations of lines and circles. Draw the diagram of the given problem; this helps in solving the problem and visualization of the problem. Be familiar with the terms like length of the perpendicular, foot of the perpendicular, chord, tangent and many more.
Complete step by step answer:

The equation of first circle is
\[{S_1} = {\left( {x - a} \right)^2} + {\left( {y - b} \right)^2} = {c^2}.............\left( 1 \right)\]
And equation of the second circle is
${S_2} = {\left( {x - b} \right)^2} + {\left( {y - a} \right)^2} = {c^2}...............\left( 2 \right)$
Then the center of circle ${S_1}$ is A (a, b) and radius is c.
The center of the circle of the circle ${S_2}$ is B (b, a) and radius is c.
Now, PQ is a common chord AB intersect PQ at M and
AP=BP=c
Equation of PQ is given by,
${S_1} - {S_2} = 0$
$
\Rightarrow \left[ {{{\left( {x - a} \right)}^2} + {{\left( {y - b} \right)}^2} = {c^2}{\text{ }}} \right]{\text{ - }}\left[ {{{\left( {x - b} \right)}^2} + {{\left( {y - a} \right)}^2} = {c^2}} \right] \\
\Rightarrow 2bx - 2by + 2ay - 2ax = 0 \\
\Rightarrow 2b\left( {x - y} \right) + 2a\left( {y - x} \right) = 0 \\
\Rightarrow 2b\left( {x - y} \right) - 2a\left( {x - y} \right) = 0 \\
\Rightarrow \left( {x - y} \right)\left( {2b - 2a} \right) = 0 \\
\Rightarrow x - y = 0 \\
$
Then equation of PQ is $x - y = 0$
AM = length of perpendicular from A (a, b) on PQ whose equation is $x - y = 0$
Therefore, AM $ = \dfrac{{\left| {1 \times a - 1 \times b} \right|}}{{\sqrt {{{\left( 1 \right)}^2} + {{\left( { - 1} \right)}^2}} }} = \dfrac{{\left| {a - b} \right|}}{{\sqrt 2 }}$
In right $\Delta {\text{PMA,}}$
$
PM = \sqrt {{{\left( {AP} \right)}^2} - {{\left( {AM} \right)}^2}} \\
PM = \sqrt {{c^2} - \dfrac{{{{\left( {a - b} \right)}^2}}}{2}} \\
\left[ {{\text{as AP = c }}\left( {{\text{radius of the circle}}} \right)} \right] \\
$
But M is the midpoint of PQ
Then, PQ =2PM = 2
$
\sqrt {{c^2} - \dfrac{{{{\left( {a - b} \right)}^2}}}{2}} \\
= \sqrt {4{c^2} - \dfrac{{4{{\left( {a - b} \right)}^2}}}{2}} \\
= \sqrt {4{c^2} - 2{{\left( {a - b} \right)}^2}} \\
$
Hence, the correct option is “C”.
Note: In order to solve these types of problems remember all the formulas and equations of lines and circles. Draw the diagram of the given problem; this helps in solving the problem and visualization of the problem. Be familiar with the terms like length of the perpendicular, foot of the perpendicular, chord, tangent and many more.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




